Abstract
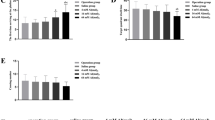
Recent industrialization has increased human exposure to bio-available aluminum (Al). If more Al enters the brain than leaves, Al concentration will rise in the brain leading to neurodegenerative disorders. The aim of the present study was to determine Al concentration, neurodegeneration, and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) gene expression in the cortex and amygdala after oral ingestion of Al salt. The effect of Al on cortex- and amygdala-dependent learning and memory functions was also assessed. Mice were given AlCl3 (250 mg/kg) in drinking water for 42 days. nAChR gene expression was determined in the cortex and amygdala. The mice were subjected to behavior tests (fear conditioning, fear extinction, and open field), to assess memory deficits. The acquisition of fear memory in the fear conditioning test remained unaffected due to the Al administration. However, fear extinction (which is a new learning) was severely impaired. The behavioral analysis in the open field test showed greater anxiety and less adaptability to the new environment in Al-treated animals. High Al concentration and severe neurodegeneration in the cortex were observed following Al treatment while a slight, non-significant elevation in Al concentration was observed in the amygdala of Al-treated animals. The analysis of nAChR gene expression via RT-PCR showed a significant reduction in expression of α7, α4, and β2 nAChR genes in the cortex of Al-treated animals, while in the amygdala, the level of the α4 nAChR gene remained unaltered. Oral Al ingestion causes neuropathological changes and suppresses expression of nAChR genes that lead to deficits in learning and higher anxiety in Al-treated animals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Elhady RM, Elsheikh AM, Khalifa AE (2013) Anti-amnestic properties of Ginkgo biloba extract on impaired memory function induced by aluminum in rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 31(7):598–607
Hashmi AN, Yaqinuddin A, Ahmed T (2015) Pharmacological effects of Ibuprofen on learning and memory, muscarinic receptors gene expression and APP isoforms level in pre-frontal cortex of AlCl3-induced toxicity mouse model. Int J Neurosci 125(4):277–287
Jalbani N, Kazi TG, Jamali MK, Arain BM, Afridi HI, Baloch A (2007) Evaluation of aluminum contents in different bakery foods by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometer. J Food Compos Anal 20(3):226–231
McLachlan D, Kruck TP, Lukiw WJ, Krishnan SS (1991) Would decreased aluminum ingestion reduce the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease? CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association Journal 145(7):793
Ferreira PC, Piai KA, Takayanagui AMM, Segura-Muñoz SI (2008) Aluminum as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem 16(1):151–157
Walton J (2007) A longitudinal study of rats chronically exposed to aluminum at human dietary levels. Neurosci Lett 412(1):29–33
Yokel RA, Hicks CL, Florence RL (2008) Aluminum bioavailability from basic sodium aluminum phosphate, an approved food additive emulsifying agent, incorporated in cheese. Food Chem Toxicol 46(6):2261–2266
Organization WH (2004) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: recommendations, vol 1. World Health Organization
Flaten TP (2001) Aluminium as a risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Res Bull 55(2):187–196
Stevanović ID, Jovanović MD, Čolić M, Jelenković A, Bokonjić D, Ninković M (2010) Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors protect cholinergic neurons against AlCl 3 excitotoxicity in the rat brain. Brain Res Bull 81(6):641–646
Hu W-P, Li X-M, Chen J-G, Li Z-W (2007) Potentiation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by aluminum in mammalian neurons. Neuroscience 149(1):1–6
Gulya K, Rakonczay Z, Kasa P (1990) Cholinotoxic effects of aluminum in rat brain. J Neurochem 54(3):1020–1026
Maheswari S, Venkatakrishna Murali R, Balaji R (2014) Aluminium induced cholinotoxicity in zebra fish brain—a sequel of oxidative stress. Int J Adv Res 2:322–335
Johnson GV, Jope RS (1986) Aluminum impairs glucose utilization and cholinergic activity in rat brain in vitro. Toxicology 40(1):93–102
Hashmi AN, Yaqinuddin A, Ahmed T (2014) Pharmacological effects of Ibuprofen on learning and memory, muscarinic receptors genes expression and APP isoforms levels in Pre-frontal cortex of AlCl3-induced toxicity mouse model. International Journal of Neuroscience (0):1–37
Grammas P, Caspers M (1991) The effect of aluminum on muscarinic receptors in isolated cerebral microvessels. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 72(1):69–79
Harkany T, Lengyel Z, Kasa P, Gulya K (1995) Chronic aluminum treatment results in aluminum deposits and affects Ml muscarinic receptors in rat brain. Neurobiology (Budapest, Hungary) 4(1–2):35–43
Pohanka M (2012) Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is a target in pharmacology and toxicology. Int J Mol Sci 13(2):2219–2238
Orr-Urtreger A, Göldner FM, Saeki M, Lorenzo I, Goldberg L, De Biasi M, Dani JA, Patrick JW, Beaudet AL (1997) Mice deficient in the α7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor lack α-bungarotoxin binding sites and hippocampal fast nicotinic currents. J Neurosci 17(23):9165–9171
Lee S, Ahmed T, Kim H, Choi S, Kim DS, Kim SJ, Cho J, Shin HS (2012) Bidirectional modulation of fear extinction by mediodorsal thalamic firing in mice. Nat Neurosci 15(2):308–314
Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC (1969) Crouching as an index of fear. J Comp Physiol Psychol 67(3):370
Arendash GW, Lewis J, Leighty RE, McGowan E, Cracchiolo JR, Hutton M, Garcia MF (2004) Multi-metric behavioral comparison of APPsw and P301L models for Alzheimer’s disease: linkage of poorer cognitive performance to tau pathology in forebrain. Brain Res 1012(1):29–41
Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Jamali MK, Arain MB, Jalbani N, Syed N (2007) Evaluation of zinc status in whole blood and scalp hair of female cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta 379(1):66–70
Gage GJ, Kipke DR, Shain W (2012) Whole animal perfusion fixation for rodents. Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE (65)
Ahmed T, Enam S, Gilani A (2010) Curcuminoids enhance memory in an amyloid-infused rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 169(3):1296–1306
Kaizer R, Correa M, Gris L, Da Rosa C, Bohrer D, Morsch V, Schetinger MRC (2008) Effect of long-term exposure to aluminum on the acetylcholinesterase activity in the central nervous system and erythrocytes. Neurochem Res 33(11):2294–2301
Commissaris R, Cordon J, Sprague S, Keiser J, Mayor G, Rech R (1982) Behavioral changes in rats after chronic aluminum and parathyroid hormone administration. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 4(3):403
Farhat SM, Mahboob A, Iqbal G, Ahmed T (2016) Aluminum-induced cholinergic deficits in different brain parts and its implications on sociability and cognitive functions in mouse. Biol Trace Elem Res:1–7
Golub MS, Donald JM, Gershwin ME, Keen CL (1989) Effects of aluminum ingestion on spontaneous motor activity of mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 11(3):231–235
Julka D, Sandhir R, Gill KD (1995) Altered cholinergic metabolism in rat CNS following aluminum exposure: implications on learning performance. J Neurochem 65(5):2157–2164
Ehrlich I, Humeau Y, Grenier F, Ciocchi S, Herry C, Lüthi A (2009) Amygdala inhibitory circuits and the control of fear memory. Neuron 62(6):757–771
Raybuck JD, Lattal KM (2011) Double dissociation of amygdala and hippocampal contributions to trace and delay fear conditioning. PLoS One 6(1):e15982
Pang M-H, Kim N-S, Kim I-H, Kim H, Kim H-T, Choi J-S (2010) Cholinergic transmission in the dorsal hippocampus modulates trace but not delay fear conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 94(2):206–213
Gould TJ, Feiro O, Moore D (2004) Nicotine enhances trace cued fear conditioning but not delay cued fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. Behav Brain Res 155(1):167–173
Wilson MA, Fadel JR (2016) Cholinergic regulation of fear learning and extinction. J Neurosci Res
Terry RL (1970) Primate grooming as a tension reduction mechanism. The Journal of psychology 76(1):129–136
Smolinsky AN, Bergner CL, LaPorte JL, Kalueff AV (2009) Analysis of grooming behavior and its utility in studying animal stress, anxiety, and depression. In: Mood and anxiety related phenotypes in mice. Springer, pp 21–36
Sethi P, Jyoti A, Singh R, Hussain E, Sharma D (2008) Aluminium-induced electrophysiological, biochemical and cognitive modifications in the hippocampus of aging rats. Neurotoxicology 29(6):1069–1079
MISAWA T, SHIGETA S (1992) Behavioral effects of repeated aluminum administration in the rat. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 17(5):155–159
Rosana A, Marco Antonio Campana V (2012) High-and low-rearing rats differ in the brain excitability controlled by the allosteric benzodiazepine site in the GABA A receptor. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science 2012
Platt B, Fiddler G, Riedel G, Henderson Z (2001) Aluminium toxicity in the rat brain: histochemical and immunocytochemical evidence. Brain Res Bull 55(2):257–267
Petersen CC (2007) The functional organization of the barrel cortex. Neuron 56(2):339–355
Grant R, Itskov PM, Towal B, Prescott TJ (2014) Active touch sensing: finger tips, whiskers, and antennae. Front Behav Neurosci 8:50
Ross SA, Wong JY, Clifford JJ, Kinsella A, Massalas JS, Horne MK, Scheffer IE, Kola I, Waddington JL, Berkovic SF (2000) Phenotypic characterization of an α4 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit knock-out mouse. J Neurosci 20(17):6431–6441
Yokel RA, Allen DD, Ackley DC (1999) The distribution of aluminum into and out of the brain. J Inorg Biochem 76(2):127–132
Linardaki ZI, Orkoula MG, Kokkosis AG, Lamari FN, Margarity M (2012) Investigation of the neuroprotective action of saffron (< i> Crocus sativus</i> L.) in aluminium-exposed adult mice through behavioral and neurobiochemical assessment. Food Chem Toxicol
Sánchez-Iglesias S, Soto-Otero R, Iglesias-Gonzalez J, Barciela-Alonso MC, Bermejo-Barrera P, Méndez-Álvarez E (2007) Analysis of brain regional distribution of aluminium in rats via oral and intraperitoneal administration. J Trace Elem Med Biol 21:31–34
Doming J, Llorens J, Sanchez D, Gomez M, Llobet J, Corbella J (1996) Age-related effects of aluminum ingestion on brain aluminum accumulation and behavior in rats. Life Sci 58(17):1387–1395
Golub MS, Germann SL, Han B, Keen CL (2000) Lifelong feeding of a high aluminum diet to mice. Toxicology 150(1):107–117
Gómez M, Sánchez DJ, Llobet JM, Corbella J, Domingo J (1997) The effect of age on aluminum retention in rats. Toxicology 116(1):1–8
Nayak P, Chatterjee A (2001) Effects of aluminium exposure on brain glutamate and GABA systems: an experimental study in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 39(12):1285–1289
Chen S-M, Fan C-C, Chiue M-S, Chou C, Chen J-H, Hseu R-S (2013) Hemodynamic and neuropathological analysis in rats with aluminum trichloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 8(12):e82561
Rubinow MJ, Mahajan G, May W, Overholser JC, Jurjus GJ, Dieter L, Herbst N, Steffens DC, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Rajkowska G (2016) Basolateral amygdala volume and cell numbers in major depressive disorder: a postmortem stereological study. Brain Struct Funct 221(1):171–184
Shaw CA, Petrik MS (2009) Aluminum hydroxide injections lead to motor deficits and motor neuron degeneration. J Inorg Biochem 103(11):1555–1562
Kaizer RR, Correa MC, Spanevello RM, Morsch VM, Mazzanti CM, Goncalves JF, Schetinger MRC (2005) Acetylcholinesterase activation and enhanced lipid peroxidation after long-term exposure to low levels of aluminum on different mouse brain regions. J Inorg Biochem 99(9):1865–1870. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2005.06.015
Dani JA (2001) Overview of nicotinic receptors and their roles in the central nervous system. Biol Psychiat 49(3):166–174. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(00)01011-8
Wang HY, Lee DH, Davis CB, Shank RP (2000) Amyloid peptide Aβ1-42 binds selectively and with picomolar affinity to α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurochem 75(3):1155–1161
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, for providing funding, support, and research facilities to carry out this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farhat, S.M., Mahboob, A. & Ahmed, T. Cortex- and Amygdala-Dependent Learning and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Gene Expression is Severely Impaired in Mice Orally Treated with AlCl3 . Biol Trace Elem Res 179, 91–101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0942-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0942-1