Abstract
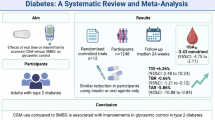
There is conflicting evidence regarding the relationship between magnesium deficiency and metabolic syndrome, and a systematic assessment of the literature has not been performed. Our objective was to clarify the association between magnesium levels and metabolic syndrome by performing a meta-analysis. Based on 13 eligible studies involving 14 analyses and 5496 enrolled participants, magnesium levels were significantly lower in adults with metabolic syndrome than in controls (standardized mean difference [SMD] = −0.98, 95 % confidence interval [CI] = −1.44 to −0.52). There was marked heterogeneity when all comparisons were considered (I 2 = 98 %, p < 0.001). In the subgroup meta-analysis and meta-regression model, a significant difference in magnesium levels was noted by geographic location and study quality. Magnesium levels were lower in the experimental cases than in the controls in West Asia (SMD = −3.80, 95 % CI = −5.36, −2.23) and Latin America (SMD = −1.38, 95 % CI = −1.88, −0.87), but not in East Asia (SMD = −0.01, 95 % CI = −0.30, 0.29) or Europe/Oceania (SMD = −0.25, 95 % CI = −0.53, 0.03). Moreover, the inverse association was greater in high-quality studies (SMD = −2.52, 95 % CI = −3.72, −1.32) than in low-quality studies (SMD = −0.33, 95 % CI = −0.57, −0.08). In conclusion, although there was a high level of heterogeneity, this meta-analysis provided convincing evidence of reduced magnesium levels in adults with metabolic syndrome based on the findings of observational studies. However, the present findings should be validated by additional prospective studies or trans-regional multicenter randomized controlled trials, which generally yield higher-level evidence than case–control studies and cross-sectional studies.
Clinical Trial Registration Number: NCT02151227 (ClinicalTrials.gov Protocol Registration System); CRD42015017946 (www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart JC, James WP, Loria CM, Smith Jr SC (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120:1640–1645. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.109.192644
Kaur J (2014) A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract 2014:943162. doi:10.1155/2014/943162
Barbagallo M, Dominguez LJ, Galioto A, Ferlisi A, Cani C, Malfa L, Pineo A, Busardo’ A, Paolisso G (2003) Role of magnesium in insulin action, diabetes and cardio-metabolic syndrome X. Mol Asp Med 24:39–52. doi:10.1016/S0098-2997(02)00090-0
Marier JR (1986) Magnesium content of the food supply in the modern-day world. Magnesium 5:1–8
Guerrera MP, Volpe SL, Mao JJ (2009) Therapeutic uses of magnesium. Am Fam Physician 80:157–162
Ju SY, Choi WS, Ock SM, Kim CM, Kim DH (2014) Dietary magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome in the adult population: dose-response meta-analysis and meta-regression. Nutrients 6:6005–6019. doi:10.3390/nu6126005
Barbagallo M, Dominguez LJ (2007) Magnesium metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Arch Biochem Biophys 458:40–47. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2006.05.007
Corica F, Corsonello A, Ientile R, Cucinotta D, Di Benedetto A, Perticone F, Dominguez LJ, Barbagallo M (2006) Serum ionized magnesium levels in relation to metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients. J Am Coll Nutr 25:210–215. doi:10.1080/07315724.2006.10719534
Guerrero-Romero F, Rodriguez-Moran M (2006) Hypomagnesemia, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 22:471–476. doi:10.1002/dmrr.644
Lima Mde L, Cruz T, Rodrigues LE, Bomfim O, Melo J, Correia R, Porto M, Cedro A, Vicente E (2009) Serum and intracellular magnesium deficiency in patients with metabolic syndrome–evidences for its relation to insulin resistance. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 83:257–262. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2008.11.019
Yu Y, Cai Z, Zheng J, Chen J, Zhang X, Huang XF, Li D (2012) Serum levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids are low in Chinese men with metabolic syndrome, whereas serum levels of saturated fatty acids, zinc, and magnesium are high. Nutr Res 32:71–77. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2011.12.004
Chung JH, Yum KS (2012) Correlation of hair mineral concentrations with insulin resistance in Korean males. Biol Trace Elem Res 150:26–30. doi:10.1007/s12011-012-9474-x
Huang JH, Lu YF, Cheng FC, Lee JN, Tsai LC (2012) Correlation of magnesium intake with metabolic parameters, depression and physical activity in elderly type 2 diabetes patients: a cross-sectional study. Nutr J 11:41. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-11-41
Simmons D, Joshi S, Shaw J (2010) Hypomagnesaemia is associated with diabetes: not pre-diabetes, obesity or the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87:261–266. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2009.11.003
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol 62:e1–34. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006
Higgins JPT, Green S, Cochrane Collaboration (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester, England ; Hoboken, NJ
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188. doi:10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Hjelmesaeth J, Hofso D, Aasheim ET, Jenssen T, Moan J, Hager H, Roislien J, Bollerslev J (2009) Parathyroid hormone, but not vitamin D, is associated with the metabolic syndrome in morbidly obese women and men: a cross-sectional study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 8:7. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-8-7
Choi WS, Kim SH, Chung JH (2014) Relationships of hair mineral concentrations with insulin resistance in metabolic syndrome. Biol Trace Elem Res 158:323–329. doi:10.1007/s12011-014-9946-2
Evangelopoulos AA, Vallianou NG, Panagiotakos DB, Georgiou A, Zacharias GA, Alevra AN, Zalokosta GJ, Vogiatzakis ED, Avgerinos PC (2008) An inverse relationship between cumulating components of the metabolic syndrome and serum magnesium levels. Nutr Res 28:659–663. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2008.07.001
Ghasemi A, Zahediasl S, Syedmoradi L, Azizi F (2010) Low serum magnesium levels in elderly subjects with metabolic syndrome. Biol Trace Elem Res 136:18–25. doi:10.1007/s12011-009-8522-7
Guerrero-Romero F, Rodriguez-Moran M (2002) Low serum magnesium levels and metabolic syndrome. Acta Diabetol 39:209–213. doi:10.1007/s005920200036
Park SB, Choi SW, Nam AY (2009) Hair tissue mineral analysis and metabolic syndrome. Biol Trace Elem Res 130:218–228. doi:10.1007/s12011-009-8336-7
Karar AH, Al-Huwaidi E, Lamlums SM (2007) Serum phosphorus and magnesium levels in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Bahrain Med Soc 19:56–62
Xu J, Xu W, Yao H, Sun W, Zhou Q, Cai L (2013) Associations of serum and urinary magnesium with the pre-diabetes, diabetes and diabetic complications in the Chinese Northeast population. PLoS One 8:e56750. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056750
Djurhuus MS, Skøtt P, Hother-Nielson O, Klitgaard NA, Beck-Nielsen H (1995) Insulin increases renal magnesium excretion: a possible cause of magnesium depletion in hyperinsulinaemic states. Diabet Med 12:664–669. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.1995.tb00566.x
Sales CH, Santos AR, Cintra DE, Colli C (2014) Magnesium-deficient high-fat diet: effects on adiposity, lipid profile and insulin sensitivity in growing rats. Clin Nutr 33:879–888. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2013.10.004
Rayssiguier Y, Gueux E, Weiser D (1981) Effect of magnesium deficiency on lipid metabolism in rats fed a high carbohydrate diet. J Nutr 111:1876–1883
Cao Y, Wang C, Guan K, Xu Y, Su YX, Chen YM (2015) Association of magnesium in serum and urine with carotid intima-media thickness and serum lipids in middle-aged and elderly Chinese: a community-based cross-sectional study. Eur J Nutr. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-0839-8
Dey R, Rajappa M, Parameswaran S, Revathy G (2015) Hypomagnesemia and atherogenic dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease: surrogate markers for increased cardiovascular risk. Clin Exp Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s10157-015-1097-z
Guerrero-Romero F, Rodriguez-Moran M (2000) Hypomagnesemia is linked to low serum HDL-cholesterol irrespective of serum glucose values. J Diabetes Complicat 14:272–276. doi:10.1016/S1056-8727(00)00127-6
Houston M (2011) The role of magnesium in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 13:843–847. doi:10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00538.x
Johansson HE, Zethelius B, Ohrvall M, Sundbom M, Haenni A (2009) Serum magnesium status after gastric bypass surgery in obesity. Obes Surg 19:1250–1255. doi:10.1007/s11695-008-9536-5
Lecube A, Baena-Fustegueras JA, Fort JM, Pelegrí D, Hernández C, Simó R (2012) Diabetes is the main factor accounting for hypomagnesemia in obese subjects. PLoS One 7:e30599. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030599
Hernán MA, Hernández-Díaz S, Robins JM (2004) A structural approach to selection bias. Epidemiology 15:615–625. doi:10.1097/01.ede.0000135174.63482.43
Muneyyirci-Delale O, Nacharaju VL, Dalloul M, Altura BM, Altura BT (1999) Serum ionized magnesium and calcium in women after menopause: inverse relation of estrogen with ionized magnesium. Fertil Steril 71:869–872. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00065-5
Olatunji LA, Oyeyipo IP, Micheal OS, Soladoye AO (2008) Effect of dietary magnesium on glucose tolerance and plasma lipid during oral contraceptive administration in female rats. Afr J Med Med Sci 37:135–139
Maggio M, Ceda GP, Lauretani F, Cattabiani C, Avantaggiato E, Morganti S, Ablondi F, Bandinelli S, Dominguez LJ, Barbagallo M, Paolisso G, Semba RD, Ferrucci L (2011) Magnesium and anabolic hormones in older men. Int J Androl 34:e594–e600. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2605.2011.01193.x
Chandra AK, Sengupta P, Goswami H, Sarkar M (2013) Effects of dietary magnesium on testicular histology, steroidogenesis, spermatogenesis and oxidative stress markers in adult rats. Indian J Exp Biol 51:37–47
Antonio L, Wu FC, O'Neill TW, Pye SR, Carter EL, Finn JD, Rutter MK, Laurent MR, Huhtaniemi IT, Han TS, Lean ME, Keevil BG, Pendleton N, Rastrelli G, Forti G, Bartfai G, Casanueva FF, Kula K, Punab M, Giwercman A, Claessens F, Decallonne B, Vanderschueren D (2015) Associations between sex steroids and the development of metabolic syndrome: a longitudinal study in European men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:1396–1404. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-4184
Arnaud MJ (2008) Update on the assessment of magnesium status. Br J Nutr 99(Suppl 3):S24–S36. doi:10.1017/s000711450800682x
Sjögren A, Florén CH, Nilsson A (1986) Magnesium deficiency in IDDM related to level of glycosylated hemoglobin. Diabetes 35:459–463. doi:10.2337/diab.35.4.459
Seidel S, Kreutzer R, Smith D, McNeel S, Gilliss D (2001) Assessment of commercial laboratories performing hair mineral analysis. JAMA 285:67–72. doi:10.1001/jama.285.1.67
Mikulewicz M, Chojnacka K, Gedrange T, Górecki H (2013) Reference values of elements in human hair: a systematic review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:1077–1086. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.09.012
Assarian GS, Oberleas D (1977) Effect of washing procedures on trace-element content of hair. Clin Chem 23:1771–1772
Beydoun MA, Gary TL, Caballero BH, Lawrence RS, Cheskin LJ, Wang Y (2008) Ethnic differences in dairy and related nutrient consumption among US adults and their association with obesity, central obesity, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 87:1914–1925
Acknowledgments
We thank Kim, Na-Jin from the Medical Library, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, for performing database searches. This project was supported by a research grant from the Catholic Medical Center Research Foundation during the 2015 program year. Our study was partly supported by Food and Drug Networking Co., Ltd. The funding sources had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author Contributions
The author’s responsibilities were as follows: S.Y.J. had full access to the entire study; took responsibility for the study integrity and the accuracy of the data analysis; designed the study; reviewed and revised the final manuscript; and contributed to the conception, design, statistical analysis, data interpretation, and manuscript drafting of this study. E.L.S. and D.H.K. contributed to the data interpretation. S.Y.J and S.A.L. contributed to the data extraction regarding evaluations of study methodological quality using criteria that had been previously established. J.Y.L contributed to the statistical analysis and provided technical support. J.H.P. contributed technical support. All of the authors approved the final manuscript for submission.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
La, S.A., Lee, J.Y., Kim, D.H. et al. Low Magnesium Levels in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: a Meta-Analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 170, 33–42 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0446-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0446-9