Abstract
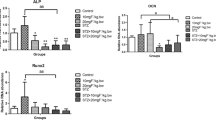
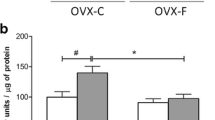
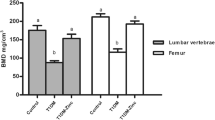
The role of insulin in the mechanism underlying the excessive fluoride that causes skeletal lesion was studied. The in vitro bone marrow stem cells (BMSC) collected from Kunming mice were exposed to varying concentrations of fluoride with or without insulin. The cell viability and early differentiation of BMSC co-treated with fluoride and insulin were measured by using cell counting kit-8 and Gomori modified calcium–cobalt method, respectively. We further investigated the in vivo effects of varying dose of fluoride on rats co-treated with streptozotocin (STZ). Wistar rats were divided into six groups which included normal control, 10 mg fluoride/kg day group, 20 mg fluoride/kg day group, STZ control, STZ + 10 mg fluoride/kg day group, and STZ + 20 mg fluoride/kg day group. The rats were administered with sodium fluoride (NaF) by gavage with water at doses 10 and 20 mg fluoride/kg day for 2 months. In a period of one month, half of rats in every group were treated with streptozotocin (STZ) once through intraperitoneal injection at 52 mg/kg body weight. The serum glucose, HbA1c, and insulin were determined. Bone mineral content and insulin release were assessed. The results showed insulin combined with fluoride stimulated BMSC cell viability in vitro. The bone mineral content reduced in rats treated with higher dose of fluoride and decreased immensely in rat co-treated with fluoride and STZ. Similarly, a combination treatment of a high dose of fluoride and STZ decreased insulin sensitivity and activity. To sum up, these data indicated fluoride influenced insulin release, activity, and sensitivity. Furthermore, the insulin state in vivo interfered in the osteogenesis in turn and implied there was a close relation between insulin and bone pathogenesis in the mechanism of fluoride toxicity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mousny M, Omelone S, Wise L et al (2008) Fluoride effects on bone formation and mineralization are influenced by genetics. Bone 43(6):1067–1074
Khokher MA, Dandona P (1990) Fluoride stimulates [3H]thymidine incorporation and alkaline phosphatase production by human osteoblasts. Metabolism 39:1118–1121
Rodriguez JP, Rosselot G (2001) Sodium fluoride induces changes on proteoglycans synthesized by avian osteoblasts in culture. J Cell Biochem 83:607–616
Mohapatra M, Anand S, Mishra BK, Mohapatra M, Anand S, Mishra BK (2009) Review of fluoride removal from drinking water. J Environ Manag 91(1):67–77
Sang ZC, Zhou W, Zhang ZJ et al (2010) X-ray analysis on 114 patients with moderate endemic skeletal fluorosis by treatment of Guo’s Chinese herbal. Zhongguo Gu Shang 23(5):379–382
Jha SK, Mishra VK, Sharma DK et al (2011) Fluoride in the environment and its metabolism in humans. Rev Environ ContamToxicol 211:121–142
Perumal E, Paul V, Govindarajan V (2013) A brief review on experimental fluorosis. ToxicolLett 25 223(2):236–251
Ruzicska E, Poór G (2011) Diabetes and bone metabolism. Orv Hetil 152:1156–1160
Fulzele K, Riddle RC, Digirolamo DJ et al (2010) Insulin receptor signaling in osteoblasts regulates postnatal bone acquisition and body composition. Cell 142:309–319
Ng KW (2011) Regulation of glucose metabolism and the skeleton. ClinEndocrinol (Oxf) 75:147–155
Zofkova I (2014) Bone tissue as a systemic endocrine regulator. Physiol Res. 2014 Dec 3. [Epub ahead of print]
Hu CY, Ren LQ, Li XN et al (2012) Effect of fluoride on insulin level of rats and insulin receptor expression in the MC3T3-E1 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 150(1–3):297–305
Pramojanee SN, Phimphilai M, Chttipakorn N et al (2014) Possible roles of insulin signaling in osteoblasts. Endocr Res 39:144–151
Lupo M, Buzalaf MA, Rigalli A (2011) Effect of fluoridated water on plasma insulin levels and glucose homeostasis in rats with renal deficiency. Biol Trace Elem Res 140:198–207
Lombarte M, Fina BL, Lupo M (2013) Physical exercise ameliorates the toxic effect of fluoride on the insulin-glucose system. J Endocrinol 218(1):99–103
Chiba FY, Colombo NH, Shirakashi DJ et al (2012) NaF treatment increases TNF-a and resistin concentrations and reduces insulin signal in rats. J Fluor Chem 136:3–7
Sun F, Li X, Yang C et al (2014) A role for PERK in the mechanism underlying fluoride-induced bone turnover. Toxicology 325:52–66
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants for skeletal fluorosis research from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81072249), the Norman Bethune Program of Jilin University (2012222), and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20130061110084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Zhang, M., Li, Y. et al. Streptozotocin Aggravated Osteopathology and Insulin Induced Osteogenesis Through Co-treatment with Fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res 168, 453–461 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0374-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0374-8