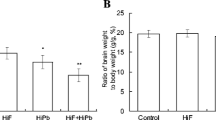
Abstract
Fluoride and lead are two common pollutants in the environment. Previous investigations have found that high fluoride exposure can increase the lead burden. In this experiment, in order to study on the molecular mechanisms of central neural system injury induced by the above two elements, differently expressed protein spots in hippocampus of male mice treated with 150 mg sodium fluoride/L and/or 300 mg lead acetate/L in their drinking water were detected by two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) and mass spectrometry (MS). The behavior tests showed that 56 days of fluoride and lead administration significantly reduced the vertical activity and lowered the memory ability of mice. In addition, results of 2-DE and MS revealed that nine spots demonstrated above a twofold change in the same trend in all treatment groups, which were mainly related with (1) energy metabolism, (2) cell stress response/chaperones, (3) cytoskeleton development, (4) protein metabolism, and (5) cell surface signal transduction. The findings could provide potential biomarkers for lesion in nervous system induced by fluoride and lead exposure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo OL, Shallie PD, Salau BA et al (2013) Comparative study on the influence of fluoride on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants levels in the different brain regions of well-fed and protein undernourished rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 27(4):370–374
Zhang J, Zhu WJ, Xu XH et al (2011) Effect of fluoride on calcium ion concentration and expression of nuclear transcription factor kappa-B r65 in rat hippocampus. Exp Toxicol Pathol 67(5):407–411
Liu YJ, Guan ZZ, Gao Q et al (2011) Increased level of apoptosis in rat brains and SH-SY5Y cells exposed to excessive fluoride—a mechanism connected with activating JNK phosphorylation. Toxicol Lett 204(2–3):183–189
Zhou BH, Wang HW, Wang JM et al (2007) Effects of malnutrition and supplemented nutrition on non-specific immune function changes induced by fluoride in rabbits. Fluoride 40(3):169–177
Xu H, Hu LS, Chang M et al (2005) Proteomic analysis of kidney in fluoride-treated rat. Toxicol Lett 160(1):69–75
Liu HT, Niu RY, Wang JM et al (2008) Changes caused by fluoride and lead in energy metabolic enzyme activities in the reproductive system of male offspring rats. Fluoride 41(3):184–191
Bouaziz H, Ben Amara I, Essefi M et al (2010) Fluoride-induced brain damages in suckling mice. Pestic Biochem Physiol 96(1):24–29
Ding Y, Gao Y, Sun H et al (2011) The relationships between low levels of urine fluoride on children's intelligence, dental fluorosis in endemic fluorosis areas in Hulunbuir, Inner Mongolia, China. J Hazard Mater 186(2–3):1942–1946
Wang SX, Wang ZH, Cheng XT et al (2007) Arsenic and fluoride exposure in drinking water: children's IQ and growth in Shanyin county, Shanxi province, China. Environ Health Perspect 115(4):643–647
Eswar P, Nagesh L, Devarajc C (2011) Intelligence quotients of 12–14 years old school children in a high and a low fluoride village in India. Fluoride 44(3):168–172
Saxena S, Sahay A, Goel P (2012) Effect of fluoride exposure on the intelligence of school children in Madhya Pradesh, India. J Neurosci Rural Pract 3(2):144–149
Trivedi M, Sangai N, Patel R et al (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality with special reference to fluoride and its impact on IQ of schoolchildren in six villages of the Mundra region, Kachchh, Gujarat, India. Fluoride 45(4):377–383
Shivaprakash PK, Ohri K, Noorani H (2011) Relation between dental fluorosis and intelligence quotient in school children of Bagalkot district. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent 29(2):117–120
Poureslami HR, Horri A, Garrusib B (2011) IQ of children age 7–9 in a high and a low F water city in Iran. Fluoride 44(3):163–167
Seraj B, Shahrabi M, Shadfar M et al (2012) Effect of high water fluoride concentration on the intellectual development of children in makoo/iran. J Dent (Tehran) 9(3):221–229
Rocha-Amador D, Navarro ME, Carrizales L et al (2007) Decreased intelligence in children and exposure to fluoride and arsenic in drinking water. Cad Saude Publ 23(Suppl 4):579–587
Whishaw IQ, Haun F, Kolb BL (1999) Analysis of behavior in laboratory rodents. IN: Windhorst U, Johansson H, editors. Modern techniques in neuroscience research. Secaucus: Springer; 1243–1244
Niu RY, Sun ZL, Wang JM et al (2008) Effects of fluoride and lead on locomotor behavior and expression of Nissl body in brain of adult rats. Fluoride 41(4):276–282
Ekambaram P, Paul V (2001) Calcium preventing locomotor behavioral and dental toxicities of fluoride by decreasing serum fluoride level in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 9(4):141–146
Balaji B, Kumar EP, Kumar A (2012) Evaluation of standardized Bacopa monniera extract in sodium fluoride-induced behavioural, biochemical, and histopathological alterations in mice. Toxicol Ind Health. doi:10.1177/0748233712468018
Jiang S, Su J, Yao S et al (2014) Fluoride and arsenic exposure impairs learning and memory and decreases mGluR5 expression in the hippocampus and cortex in rats. PLoS One 9(4):e96041
Niu RY, Sun ZL, Cheng ZT et al (2008) Effects of fluoride and lead on n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor 1 expression in the hippocampus of offspring rat pups. Fluoride 41(2):101–110
Gao Q, Liu YJ, Guan ZZ (2008) Oxidative stress might be a mechanism connected with the decreased alpha 7 nicotinic receptor influenced by high-concentration of fluoride in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro 22(4):837–843
Inkielewicz-Stepniak I, Czarnowski W (2010) Oxidative stress parameters in rats exposed to fluoride and caffeine. Food Chem Toxicol 48(6):1607–1611
Coplan MJ, Patch SC, Masters RD et al (2007) Confirmation of and explanations for elevated blood lead and other disorders in children exposed to water disinfection and fluoridation chemicals. Neurotoxicology 28(5):1032–1042
Masters RD, Coplan MJ, Hone BT et al (2000) Association of silicofluoride treated water with elevated blood lead. Neurotoxicology 21(6):1091–1100
Zhai Y, Dong J, Cao XZ et al (2006) Epidemiological investigation about the relation between blood lead level and high fluorine drinking water in children. Child Health Care China 21(8):1088–1090 [in Chinese]
Sawan RM, Leite GA, Saraiva MC et al (2010) Fluoride increases lead concentrations in whole blood and in calcified tissues from lead-exposed rats. Toxicology 271(1–2):21–26
Bevins RA, Besheer J (2006) Object recognition in rats and mice: a one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study ‘recognition memory’. Nat Protoc 1(3):1306–1311
Ge Y, Niu R, Zhang J et al (2011) Proteomic analysis of brain proteins of rats exposed to high fluoride and low iodine. Arch Toxicol 85(1):27–33
Okajima K, Korotchkina LG, Prasad C et al (2008) Mutations of the E1beta subunit gene (PDHB) in four families with pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 93(4):371–380
Patel MS, Korotchkina LG (2006) Regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem Soc Trans 34:217–222
Kerr DS, Schmotzer C (2004) Variability of human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency. In: Patel MS, Jordan F (eds) Thiamine: catalytic mechanisms and role in normal and disease states. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 471–483
Lissens W, De Meirleir L, Seneca S et al (2000) Mutations in the X-linked pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) alpha subunit gene (PDHA1) in patients with a pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency. Hum Mutat 15(3):209–219
Korotchkina LG, Ciszak EM, Patel MS (2004) Function of several critical amino acids in human pyruvate dehydrogenase revealed by its structure. Arch Biochem Biophys 429(2):171–179
Soole KL, Menz RI (1995) Functional molecular aspects of the NADH dehydrogenases of plant mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomembr 27(4):397–406
Rupik W, Jasik K, Bembenek J et al (2011) The expression patterns of heat shock genes and proteins and their role during vertebrate's development. Comp Biochem Physiol A 159(4):349–366
Heikkila JJ (2010) Heat shock protein gene expression and function in amphibian model systems. Comp Biochem Physiol A 156(1):19–33
Mayer MP, Bukau B (2005) Hsp70 chaperones: cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 62(6):670–684
Elicker KS, Hutson LD (2007) Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the small heat shock proteins in zebrafish. Gene 403(1–2):60–69
Christensen JH, Nielsen MN, Hansen J et al (2010) Inactivation of the hereditary spastic paraplegia-associated Hspd1 gene encoding the Hsp60 chaperone results in early embryonic lethality in mice. Cell Stress Chaperones 15(6):851–863
Samali A, Cai J, Zhivotovsky B et al (1999) Presence of a pre-apoptotic complex of pro-caspase-3, Hsp60 and Hsp10 in the mitochondrial fraction of Jurkat cells. EMBO J 18(8):2040–2048
Quinn CC, Gray GE, Hockfield S (1999) A family of proteins implicated in axon guidance and outgrowth. J Neurobiol 41(1):158–164
Wang LH, Strittmatter SM (1996) A family of rat CRMP genes is differentially expressed in the nervous system. J Neurosci 16(19):6197–6207
Voas MG, Lyons DA, Naylor SG et al (2007) AlphaII-spectrin is essential for assembly of the nodes of Ranvier in myelinated axons. Curr Biol 17(6):562–568
Zhang M, Huang K, Zhang Z et al (2011) Proteome alterations of cortex and hippocampus tissues in mice subjected to vitamin A depletion. J Nutr Biochem 22(11):1003–1008
Chen A, Liao WP, Lu Q et al (2007) Upregulation of dihydropyrimidinase-related protein 2, spectrin α II chain, heat shock cognate protein 70 pseudogene 1 and tropomodulin 2 after focal cerebral ischemia in rats—a proteomics approach. Neurochem Int 50(7–8):1078–1086
Matsuda-Matsumoto H, Iwazaki T, Kashem MA et al (2007) Differential protein expression profiles in the hippocampus of human alcoholics. Neurochem Int 51(6–7):370–376
Indraswari F, Wong PT, Yap E et al (2009) Upregulation of Dpysl2 and Spna2 gene expression in the rat brain after ischemic stroke. Neurochem Int 55(4):235–242
Valdez-Jiménez L, Soria Fregozo C, Miranda Beltrán ML et al (2011) Effects of the fluoride on the central nervous system. Neurologia 26(5):297–300
Thornhill PB, Cohn JB, Stanford WL et al (2008) The adaptor protein Grb2 regulates cell surface Fas ligand in Schwann cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376(2):341–346
Anteby EY, Ayesh S, Shochina M et al (2005) Growth factor receptor-protein bound 2 (GRB2) up-regulation in the placenta in preeclampsia implies a possible role for ras-signalling. J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 118(2):174–181
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 31101869, 31201965, and 31172376), Shanxi Province Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2012021027–5), and Program for the Top Young Academic Leaders of Higher Learning Institutions of Shanxi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ruiyan Niu and Shuangling Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, R., Liu, S., Wang, J. et al. Proteomic Analysis of Hippocampus in Offspring Male Mice Exposed to Fluoride and Lead. Biol Trace Elem Res 162, 227–233 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0117-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0117-2