Abstract
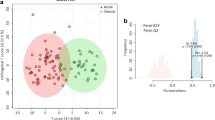
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is characterized by a sudden blockage of one of the main arteries supplying blood to the brain, leading to insufficient oxygen and nutrients for brain cells to function properly. Unfortunately, metabolic alterations in the biofluids with AIS are still not well understood. In this study, we performed high-throughput target metabolic analysis on 44 serum samples, including 22 from AIS patients and 22 from healthy controls. Multiple-reaction monitoring analysis of 180 common metabolites revealed a total of 29 metabolites that changed significantly (VIP > 1, p < 0.05). Multivariate statistical analysis unraveled a striking separation between AIS patients and healthy controls. Comparing the AIS group with the control group, the contents of argininosuccinic acid, beta-D-glucosamine, glycerophosphocholine, L-abrine, and L-pipecolic acid were remarkably downregulated in AIS patients. Twenty-nine out of 112 detected metabolites enriched in disturbed metabolic pathways, including aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, glycerophospholipid metabolism, lysine degradation, phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan biosynthesis metabolic pathways. Collectively, these results will provide a sensitive, feasible diagnostic prospect for AIS patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AIS:
-
Acute ischemic stroke
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTA:
-
Computed tomography angiography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- MRM:
-
Multiple reaction monitoring
- UPLC:
-
Ultra performance liquid chromatography
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- NIHSS:
-
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
- QC:
-
Quality control
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- OPLS-DA:
-
Orthogonal projections to latent structures-discriminant analysis
- VIP:
-
Variable importance in projection
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area under curve
- PtdCho:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- GroPCho:
-
Glycerophosphocholine
- L-PA:
-
L-pipecolic acid
References
Tsao, C. W., Aday, A. W., Almarzooq, Z. I., Alonso, A., Beaton, A. Z., Bittencourt, M. S., Boehme, A. K., Buxton, A. E., Carson, A. P., Commodore-Mensah, Y., Elkind, M. S. V., Evenson, K. R., Eze-Nliam, C., Ferguson, J. F., Generoso, G., Ho, J. E., Kalani, R., Khan, S. S., Kissela, B. M., … Martin, S. S. (2022). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 145, e153–e639.
Collaborators, G. B. D. S. (2021). Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurology, 20, 795–820.
Jiang, B., Wang, W. Z., Chen, H., Hong, Z., Yang, Q. D., Wu, S. P., Du, X. L., & Bao, Q. J. (2006). Incidence and trends of stroke and its subtypes in China: Results from three large cities. Stroke, 37, 63–68.
Krishnamurthi, R. V., Feigin, V. L., Forouzanfar, M. H., Mensah, G. A., Connor, M., Bennett, D. A., Moran, A. E., Sacco, R. L., Anderson, L. M., Truelsen, T., O’Donnell, M., Venketasubramanian, N., Barker-Collo, S., Lawes, C. M., Wang, W., Shinohara, Y., Witt, E., Ezzati, M., Naghavi, M., … Global Burden of Diseases, I. R. F. S. and Group, G. B. D. S. E. (2013). Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob Health, 1, e259-281.
Andersen, K. K., Olsen, T. S., Dehlendorff, C., & Kammersgaard, L. P. (2009). Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes compared: Stroke severity, mortality, and risk factors. Stroke, 40, 2068–2072.
Salvadori, E., Papi, G., Insalata, G., Rinnoci, V., Donnini, I., Martini, M., Falsini, C., Hakiki, B., Romoli, A., Barbato, C., Polcaro, P., Casamorata, F., Macchi, C., Cecchi, F. and Poggesi, A. (2020) Comparison between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes in functional outcome at discharge from an intensive rehabilitation hospital. Diagnostics (Basel), 11.
Powers, W. J., Rabinstein, A. A., Ackerson, T., Adeoye, O. M., Bambakidis, N. C., Becker, K., Biller, J., Brown, M., Demaerschalk, B. M., Hoh, B., Jauch, E. C., Kidwell, C. S., Leslie-Mazwi, T. M., Ovbiagele, B., Scott, P. A., Sheth, K. N., Southerland, A. M., Summers, D. V., & Tirschwell, D. L. (2019). Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke, 50, e344–e418.
Hurford, R., Sekhar, A., Hughes, T. A. T., & Muir, K. W. (2020). Diagnosis and management of acute ischaemic stroke. Practical Neurology, 20, 304–316.
Hacke, W., Kaste, M., Bluhmki, E., Brozman, M., Davalos, A., Guidetti, D., Larrue, V., Lees, K. R., Medeghri, Z., Machnig, T., Schneider, D., von Kummer, R., Wahlgren, N., Toni, D., & Investigators, E. (2008). Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine, 359, 1317–1329.
Jovin, T. G., Chamorro, A., Cobo, E., de Miquel, M. A., Molina, C. A., Rovira, A., San Roman, L., Serena, J., Abilleira, S., Ribo, M., Millan, M., Urra, X., Cardona, P., Lopez-Cancio, E., Tomasello, A., Castano, C., Blasco, J., Aja, L., Dorado, L., … Investigators, R. T. (2015). Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine, 372, 2296–2306.
Latchaw, R. E., Alberts, M. J., Lev, M. H., Connors, J. J., Harbaugh, R. E., Higashida, R. T., Hobson, R., Kidwell, C. S., Koroshetz, W. J., Mathews, V., Villablanca, P., Warach, S., Walters, B., American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular, R., Intervention, S. C. and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular, D. (2009). Recommendations for imaging of acute ischemic stroke: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Stroke, 40, 3646–3678.
Boers, A. M. M., Sales Barros, R., Jansen, I. G. H., Berkhemer, O. A., Beenen, L. F. M., Menon, B. K., Dippel, D. W. J., van der Lugt, A., van Zwam, W. H., Roos, Y., van Oostenbrugge, R. J., Slump, C. H., Majoie, C., Marquering, H. A., investigators, M. C. (2018). Value of quantitative collateral scoring on CT angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 39, 1074–1082.
Kim, Y., Lee, S., Abdelkhaleq, R., Lopez-Rivera, V., Navi, B., Kamel, H., Savitz, S. I., Czap, A. L., Grotta, J. C., McCullough, L. D., Krause, T. M., Giancardo, L., Vahidy, F. S., & Sheth, S. A. (2021). Utilization and availability of advanced imaging in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Circulation. Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, 14, e006989.
Dettmer, K., Aronov, P. A., & Hammock, B. D. (2007). Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 26, 51–78.
Smith, C. A., Want, E. J., O’Maille, G., Abagyan, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 779–787.
Tautenhahn, R., Cho, K., Uritboonthai, W., Zhu, Z., Patti, G. J., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). An accelerated workflow for untargeted metabolomics using the METLIN database. Nature Biotechnology, 30, 826–828.
Wang, D., Kong, J., Wu, J., Wang, X., & Lai, M. (2017). GC-MS-based metabolomics identifies an amino acid signature of acute ischemic stroke. Neuroscience Letters, 642, 7–13.
Yu, F., Li, X., Feng, X., Wei, M., Luo, Y., Zhao, T., Xiao, B., & Xia, J. (2021). Phenylacetylglutamine, a novel biomarker in acute ischemic stroke. Front Cardiovasc Med, 8, 798765.
Sidorov, E. V., Xu, C., Garcia-Ramiu, J., Blair, A., Ortiz-Garcia, J., Gordon, D., Chainakul, J., & Sanghera, D. K. (2022). Global metabolomic profiling reveals disrupted lipid and amino acid metabolism between the acute and chronic stages of ischemic stroke. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 31, 106320.
Kimberly, W. T., Wang, Y., Pham, L., Furie, K. L., & Gerszten, R. E. (2013). Metabolite profiling identifies a branched chain amino acid signature in acute cardioembolic stroke. Stroke, 44, 1389–1395.
Choi, S. H., Arai, A. L., Mou, Y., Kang, B., Yen, C. C., Hallenbeck, J., & Silva, A. C. (2018). Neuroprotective effects of MAGL (monoacylglycerol lipase) inhibitors in experimental ischemic stroke. Stroke, 49, 718–726.
Geng, J., Zhang, Y., Li, S., Li, S., Wang, J., Wang, H., Aa, J., & Wang, G. (2019). Metabolomic profiling reveals that reprogramming of cerebral glucose metabolism is involved in ischemic preconditioning-induced neuroprotection in a rodent model of ischemic stroke. Journal of Proteome Research, 18, 57–68.
Johnson, C. H., Ivanisevic, J., & Siuzdak, G. (2016). Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 17, 451–459.
Hu, L., Liu, J., Zhang, W., Wang, T., Zhang, N., Lee, Y. H., & Lu, H. (2020). Functional metabolomics decipher biochemical functions and associated mechanisms underlie small-molecule metabolism. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 39, 417–433.
Rinschen, M. M., Ivanisevic, J., Giera, M., & Siuzdak, G. (2019). Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 20, 353–367.
Wishart, D. S., Guo, A., Oler, E., Wang, F., Anjum, A., Peters, H., Dizon, R., Sayeeda, Z., Tian, S., Lee, B. L., Berjanskii, M., Mah, R., Yamamoto, M., Jovel, J., Torres-Calzada, C., Hiebert-Giesbrecht, M., Lui, V. W., Varshavi, D., Varshavi, D., … Gautam, V. (2022). HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Research, 50, D622–D631.
Wei, R., Li, G., & Seymour, A. B. (2010). High-throughput and multiplexed LC/MS/MRM method for targeted metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 82, 5527–5533.
Zheng, F., Zhao, X., Zeng, Z., Wang, L., Lv, W., Wang, Q., & Xu, G. (2020). Development of a plasma pseudotargeted metabolomics method based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 15, 2519–2537.
Gaugler, S., Rykl, J., Wegner, I., von Daniken, T., Fingerhut, R., & Schlotterbeck, G. (2018). Extended and fully automated newborn screening method for mass spectrometry detection. Int J Neonatal Screen, 4, 2.
Cai, Z., Zhang, Q., Xia, Z., Zheng, S., Zeng, L., Han, L., Yan, J., Ke, P., Zhuang, J., Wu, X., & Huang, X. (2020). Determination of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status among population in southern China by a high accuracy LC-MS/MS method traced to reference measurement procedure. Nutrition & Metabolism (London), 17, 8.
Lin, L., Ding, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Yin, X., Yan, G., Zhang, L., Yang, P., & Shen, H. (2017). Functional lipidomics: Palmitic acid impairs hepatocellular carcinoma development by modulating membrane fluidity and glucose metabolism. Hepatology, 66, 432–448.
Nemet, I., Saha, P. P., Gupta, N., Zhu, W., Romano, K. A., Skye, S. M., Cajka, T., Mohan, M. L., Li, L., Wu, Y., Funabashi, M., Ramer-Tait, A. E., Naga Prasad, S. V., Fiehn, O., Rey, F. E., Tang, W. H. W., Fischbach, M. A., DiDonato, J. A., & Hazen, S. L. (2020). A cardiovascular disease-linked gut microbial metabolite acts via adrenergic receptors. Cell, 180(862–877), e822.
Liu, L., Feng, R., Guo, F., Li, Y., Jiao, J., & Sun, C. (2015). Targeted metabolomic analysis reveals the association between the postprandial change in palmitic acid, branched-chain amino acids and insulin resistance in young obese subjects. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 108, 84–93.
Kim, S., Jang, W. J., Yu, H., Kim, J., Lee, S. K., Jeong, C. H. and Lee, S. (2020) Revealing metabolic perturbation following heavy methamphetamine abuse by human hair metabolomics and network analysis. Int J Mol Sci, 21.
Pang, Z., Chong, J., Zhou, G., de Lima Morais, D. A., Chang, L., Barrette, M., Gauthier, C., Jacques, P. E., Li, S., & Xia, J. (2021). MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, W388–W396.
Holthuis, J. C., & Menon, A. K. (2014). Lipid landscapes and pipelines in membrane homeostasis. Nature, 510, 48–57.
Fernandez-Murray, J. P., & McMaster, C. R. (2005). Glycerophosphocholine catabolism as a new route for choline formation for phosphatidylcholine synthesis by the Kennedy pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 38290–38296.
Winrow, C. J., Hemming, M. L., Allen, D. M., Quistad, G. B., Casida, J. E., & Barlow, C. (2003). Loss of neuropathy target esterase in mice links organophosphate exposure to hyperactivity. Nature Genetics, 33, 477–485.
Muhlig-Versen, M., da Cruz, A. B., Tschape, J. A., Moser, M., Buttner, R., Athenstaedt, K., Glynn, P., & Kretzschmar, D. (2005). Loss of Swiss cheese/neuropathy target esterase activity causes disruption of phosphatidylcholine homeostasis and neuronal and glial death in adult Drosophila. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 2865–2873.
Pena, I. A., Marques, L. A., Laranjeira, A. B., Yunes, J. A., Eberlin, M. N., & Arruda, P. (2016). Simultaneous detection of lysine metabolites by a single LC-MS/MS method: Monitoring lysine degradation in mouse plasma. Springerplus, 5, 172.
Perez-Garcia, F., Brito, L. F., & Wendisch, V. F. (2019). Function of L-pipecolic acid as compatible solute in corynebacterium glutamicum as basis for its production under hyperosmolar conditions. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 340.
Hallen, A., Jamie, J. F., & Cooper, A. J. (2013). Lysine metabolism in mammalian brain: An update on the importance of recent discoveries. Amino Acids, 45, 1249–1272.
Posset, R., Opp, S., Struys, E. A., Volkl, A., Mohr, H., Hoffmann, G. F., Kolker, S., Sauer, S. W., & Okun, J. G. (2015). Understanding cerebral L-lysine metabolism: The role of L-pipecolate metabolism in Gcdh-deficient mice as a model for glutaric aciduria type I. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 38, 265–272.
Gerhards, N., Neubauer, L., Tudzynski, P., & Li, S. M. (2014). Biosynthetic pathways of ergot alkaloids. Toxins (Basel), 6, 3281–3295.
Yu, X., Liu, Y., Xie, X., Zheng, X. D., & Li, S. M. (2012). Biochemical characterization of indole prenyltransferases: Filling the last gap of prenylation positions by a 5-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase from Aspergillus clavatus. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 1371–1380.
Herraiz, T., & Galisteo, J. (2004). Endogenous and dietary indoles: A class of antioxidants and radical scavengers in the ABTS assay. Free Radical Research, 38, 323–331.
Funding
This work was supported by Fujian Health Talent Training Project (2019–2-62), Xiamen Science and Technology Huimin Project (3502Z20184006), and Xiamen Medical and Health Technology Project (3502Z20194033, 3502Z20194028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. The methodology was performed by Biao Qi and Yanyu Zhang. Data analysis and investigation were performed by Bing Xu and Guoqiang Fei. The original manuscript was written by Biao Qi, Yanyu Zhang, and Bing Xu, while the manuscript review and editing was done by Ling Lin and Qiuping Li. Funding acquisition was gained by Biao Qi, Guoqiang Fei, and Qiuping Li. Resources were prepared by Yuhao Zhang. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article contains a metabolomic study with human subjects. Ethical approval from the Research Ethics Committee from Xiamen Branch, Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University was obtained.
Consent to Participate
Patient written informed consent was obtained.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, B., Zhang, Y., Xu, B. et al. Metabolomic Characterization of Acute Ischemic Stroke Facilitates Metabolomic Biomarker Discovery. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 5443–5455 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04024-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04024-1