Abstract
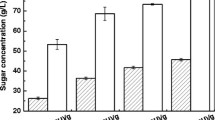
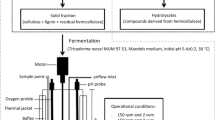
Corn fiber and sweet sorghum bagasse (SSB) are both pre-processed lignocellulosic materials that can be used to produce liquid biofuels. Pretreatment using dilute sulfuric acid at a severity factor of 1.06 and 1.02 released 83.2 and 86.5 % of theoretically available sugars out of corn fiber and SSB, respectively. The resulting hydrolysates derived from pretreatment of SSB at SF of 1.02 supported growth of Cryptococcus curvatus well. In 6 days, the dry cell density reached 10.8 g/l with a lipid content of 40 % (w/w). Hydrolysates from corn fiber, however, did not lead to any significant cell growth even with addition of nutrients. In addition to consuming glucose, xylose, and arabinose, C. curvatus also utilized formic acid, acetic acid, 4-hydroxymethylfurfural, and levulinic acid for growth. Thus, C. curvatus appeared to be an excellent yeast strain for producing lipids from hydrolysates developed from lignocellulosic feedstocks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira, P., Tomás-PejÃ, E., Ballesteros, M., & Negro, M. J. (2010). Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresource Technology, 101, 4851–4861.
Banerji, A., Balakrishnan, M., & Kishore, V. V. N. (2013). Low severity dilute-acid hydrolysis of sweet sorghum bagasse. Applied Energy, 104, 197–206.
Choudhary, R., Umagiliyage, A. L., Liang, Y., Siddaramu, T., Haddock, J., & Markevicius, G. (2012). Microwave pretreatment for enzymatic saccharification of sweet sorghum bagasse. Biomass and Bioenergy, 39, 218–226.
Cui, Y., Blackburn, J. W., & Liang, Y. (2012). Fermentation optimization for the production of lipid by Cryptococcus curvatus: use of response surface methodology. Biomass and Bioenergy, 47, 410–417.
Cui, Y., & Liang, Y. (2014). Direct transesterification of wet Cryptococcus curvatus cells to biodiesel through use of microwave irradiation. Applied Energy, 119, 438–444.
Du, B., Sharma, L. N., Becker, C., Chen, S. F., Mowery, R. A., van Walsum, G. P., et al. (2010). Effect of varying feedstock–pretreatment chemistry combinations on the formation and accumulation of potentially inhibitory degradation products in biomass hydrolysates. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 107, 430–440.
Hector, R. E., Qureshi, N., Hughes, S. R., & Cotta, M. A. (2008). Expression of a heterologous xylose transporter in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain engineered to utilize xylose improves aerobic xylose consumption. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80, 675–684.
Klinke, H. B., Thomsen, A. B., & Ahring, B. K. (2004). Inhibition of ethanol-producing yeast and bacteria by degradation products produced during pre-treatment of biomass. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 66, 10–26.
Larsson, S., Palmqvist, E., Hahn-Hägerdal, B. R., Tengborg, C., Stenberg, K., Zacchi, G., et al. (1999). The generation of fermentation inhibitors during dilute acid hydrolysis of softwood. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 24, 151–159.
Liang, Y., Sarkany, N., & Cui, Y. (2009). Biomass and lipid productivities of Chlorella vulgaris under autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic growth conditions. Biotechnology Letters, 31, 1043–1049.
Liang, Y., Tang, T., Siddaramu, T., Choudhary, R., & Umagiliyage, A. L. (2012). Lipid production from sweet sorghum bagasse through yeast fermentation. Renewable Energy, 40, 130–136.
Liang, Y., Tang, T., Umagiliyage, A. L., Siddaramu, T., McCarroll, M., & Choudhary, R. (2012). Utilization of sorghum bagasse hydrolysates for producing microbial lipids. Applied Energy, 91, 451–458.
Liang, Y., Yesuf, J., Schmitt, S., Bender, K., & Bozzola, J. (2009). Study of cellulases from a newly-isolated thermophilic and cellulolytic Brevibacillus sp. strain JXL. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 36, 961–970.
Mussatto, S. I., & Roberto, I. C. (2004). Alternatives for detoxification of diluted-acid lignocellulosic hydrolyzates for use in fermentative processes: a review. Bioresource Technology, 93, 1–10.
Palmqvist, E., & Hahn-Hägerdal, B. R. (2000). Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. I: inhibition and detoxification. Bioresource Technology, 74, 17–24.
Palmqvist, E., & Hahn-Hägerdal, B. (2000). Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. II: inhibitors and mechanisms of inhibition. Bioresource Technology, 74, 25–33.
Saha, B. C., & Bothast, R. J. (1999). Pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification of corn fiber. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 76, 65–77.
Saha, B. C., Dien, B. S., & Bothast, R. J. (1998). Fuel ethanol production from corn fiber current status and technical prospects. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 70, 115–125.
Serrano-Ruiz, J. C., Ramos-Fernández, E. V., & Sepúlveda-Escribano, A. (2012). From biodiesel and bioethanol to liquid hydrocarbon fuels: new hydrotreating and advanced microbial technologies. Energy & Environmental Science, 5, 5638–5652.
Sipos, B., Reczey, J., Somorai, Z., Kadar, Z., Dienes, D., & Reczey, K. (2009). Sweet sorghum as feedstock for ethanol production: enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-pretreated bagasse. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 153, 151–162.
Yu, X., Zheng, Y., Dorgan, K. M., & Chen, S. (2011). Oil production by oleaginous yeasts using the hydrolysate from pretreatment of wheat straw with dilute sulfuric acid. Bioresource Technology, 102, 6134–6140.
Acknowledgments
Kimberly Jarosz thankfully acknowledges the opportunity and financial support from the McNair Scholars Program at SIUC. Ashley T. Wardlow from Florida International University appreciates support from a NSF REU program (DMR 1157058) at SIUC. We also thank Dr. Sabrina Trupia at National Corn-to-ethanol Research Center for providing the corn fiber samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Jarosz, K., Wardlow, A.T. et al. Lipid Production by Cryptococcus curvatus on Hydrolysates Derived from Corn Fiber and Sweet Sorghum Bagasse Following Dilute Acid Pretreatment. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173, 2086–2098 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1007-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1007-y