Abstract
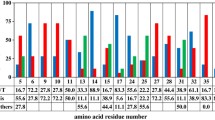
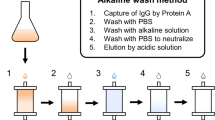
Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus has been widely used as an affinity ligand for the purification of immunoglobulin. However, the low elution pH and the sensitivity to alkaline condition restricted the large-scale application of antibody purification. To overcome these disadvantages, the B domain was selected and mutated to Z domain and the recombinant Protein A was reconstructed by linking five Z domains. First, a section of six glycines was inserted into the second loop of Z domain, Z (6G). This increased the elution pH to 4.0–5.0. Then, the site-specific mutagenesis was conducted by replacing the 23rd asparagines to threonine and 30th phenylalanine to alanine, Z (N23T, F30A). These mutations made the recombinant Protein A shown a higher alkaline resistance than the nature Protein A. The work confirmed the modification of Protein A and exhibited the characteristics of recombinant Staphylococcal Protein A for antibody purification.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sjöquist, J., Movitz, J., Johansson, I. B., & Hjelm, H. (1972). Localization of protein A in the bacteria. European Journal of Biochemistry, 30, 190–194.
Björk, I., Petersson, B. Å., & Sjöquist, J. (1972). Some physicochemical properties of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. European Journal of Biochemistry, 29, 579–584.
Sjöholm, I. (1975). Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Spectropolarmetric and spectrophotometric studies. European Journal of Biochemistry, 51, 55–61.
Moks, T., Abrahmsén, L., Nilsson, B., Hellman, U., Sjöquist, J., & Uhlén, M. (1986). Staphylococcal protein A cosists of five IgG-binding domains. European Journal of Biochemistry, 156, 637–643.
Lindmark, R., Thorén-Tolling, K., & Sjöquist, J. (1983). Binding of immunoglobulins to protein A and immunoglobulin levels in mammalian sera. Journal of Immunological Methods, 62, 1–13.
Goding, J. W. (1978). Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. Journal of Immunological Methods, 20, 241–253.
Hale, G., Drumm, A., Harrison, P., & Phillips, J. (1994). Repeated cleaning of protein A affinity column with sodium hydroxide. Journal of Immunological Methods, 171, 15–21.
Deinenhofer, J. (1981). Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of a human Fc fragment and its complex with fragment B of Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus at 2.9- and 2.8-Å resolution. Biochemistry, 20, 2361–2370.
Tashiro, M., Tejero, R., Zimmerman, D. E., Celda, B., Nilsson, B., & Montelione, G. T. (1997). High-resolution solution NMR structure of the Z domain of Staphylococcal Protein A. Journal of Molecular Biology, 272, 573–590.
Brunet, A. P., Huang, E. S., Huffine, M. E., Loeb, J. E., Weltman, R. J., & Hecht, M. H. (1993). The role of turns in the structure of an α-helical protein. Nature, 364, 355–358.
Castagnoli, L., Vetriani, C., & Cesareni, G. (1994). Linking an easily detectable phenotype to the folding of a common structural motif. Selection of rare turn mutations that prevent the folding of Rop. Journal of Molecular Biology, 237, 378–387.
Predki, P. L., & Regan, L. (1995). Redesigning the topology of a four-helix-bundle protein: monomeric Rop. Biochemistry, 34, 9834–9839.
Nagi, A. D., & Regan, L. (1997). An inverse correlation between loop length and stability in a four-helix-bundle protein. Folding and Design, 2, 67–75.
Nagi, A. D., Anderson, K. S., & Regan, L. (1999). Using loop length variants to dissect the folding pathway of a four-helix-bundle protein. Journal of Molecular Biology, 286, 257–265.
Gülich, S., Uhlén, M., & Hober, S. (2000). Protein engineering of an IgG-binding domain allows milder elution conditions during affinity chromatography. Journal of Biotechnology, 76, 233–244.
Cedergren, L., Andersson, R., Jansson, B., Uhlén, M., & Nilsson, B. (1993). Mutational analysis of the interaction between staphylococcal protein A and human IgG1. Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, 6, 441–448.
Kotsuka, T., Akanuma, S., Tomuro, M., Yamagishi, A., & Oshima, T. (1996). Further stabilization of 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase of an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus, by a suppressor mutation method. Journal of Bacteriology, 178, 723–727.
Sieber, V., Plückthun, A., & Schmid, F. X. (1998). Selecting proteins with improved stability by a phage-based method. Nature Biotechnology, 16, 955–960.
Gülich, S., Linhult, M., Uhlén, M., Nygren, P. Å., & Hober, S. (2000). Stability towards alkaline conditions can be engineered into a protein ligand. Journal of Biotechnology, 80, 169–178.
Kossiakoff, A. A. (1988). Tertiary structure is a principal determinant to protein deamidation. Science, 240, 191–194.
Lura, R., & Schirch, V. (1988). Role of peptide conformation in the rate and mechanism of deamidation of asparaginyl residues. Biochemistry, 27, 7671–7677.
Kosky, A. A., Razzaq, U. O., Treuheit, M. J., & Brems, D. N. (1999). The effects of alpha-helix on the stebility of Asn residues: deamidation rates in peptides of varying helicity. Protein Science, 8, 2519–2523.
Geiger, T., & Clarke, S. (1987). Deamidation, isomerization, and racemization at asparaginyl and aspartyl residues in peptides. Succinimide-linker reactions that contribute to protein degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 262, 785–794.
Linhult, M., Gülich, S., Gräslund, T., Simon, A., Karlsson, M., Sjöberg, A., Nord, K., & Hobe, S. (2004). Improving the tolerance of a Protein A analogue to repeated alkaline exposures using a bypass mutagenesis approach. Proteins, 55, 407–416.
Higuchi, R., Krummel, B., & Saiki, R. K. (1988). A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Research, 16, 351–7367.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Johansson, B. L., Belew, M., Eriksson, S., Glad, G., Lind, O., Maloisel, J. L., & Norrman, N. (2003). Preparation and characterization of prototypes for multi-modal separation media aimed for capture of negatively charged biomolecules at high salt conditions. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1016, 21–33.
Cuatrecasas, P., & Parikh, I. (1972). Adsorbents for affinity chromatography. Use of N-hydrox ysuccinimide esters of agarose. Biochemistry, 11, 2291–2299.
Van Sommeren, A. P. G., Machielsen, P. A. G. M., & Gribnau, T. C. J. (1993). Comparison of three activated agaroses for use in affinity chromatography: effects on coupling performance and ligand leakage. Journal of Chromatography. A, 639, 23–31.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2012AA021201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21206054), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20110093120001), the 111 Project (No. 111-2-06), and the Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, HF., Liang, ZD., Wang, SL. et al. Molecular Modification of Protein A to Improve the Elution pH and Alkali Resistance in Affinity Chromatography. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 4002–4012 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0818-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0818-1