Abstract
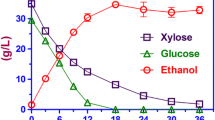
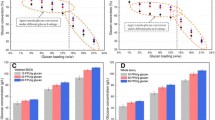
Steam-exploded corn stalk biomass was used as the substrate for succinic acid production via lignocellulose enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation. Succinic acid fermentation was investigated in Escherichia coli strains overexpressing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. 7120 ecaA gene encoding carbonic anhydrase (CA). For the washed steam-exploded corn stalk at 30 % substrate concentration, i.e., 30 % water-insoluble solids (WIS), enzymatic hydrolysis yielded 97.5 g/l glucose solution and a cellulose conversion of 73.6 %, thus a high succinic acid level up to 38.6 g/l. With the unwashed steam-exploded corn stalk, though a cellulose conversion of 71.2 % was obtained in hydrolysis at 30 % solid concentration (27.9 % WIS), its hydrolysate did not ferment at all, and the hydrolysate of 25 % solid loading containing 3.8 g/l acetic acid and 168.2 mg/l furfural exerted a strong inhibition on succinic acid production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, R., Liang, L., Chen, K., Ma, J., Jiang, M., Wei, P., et al. (2012). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 94, 959–968.
Steen, E. J., Kang, Y., Bokinsky, G., Hu, Z., Schirmer, A., McClure, A., et al. (2010). Nature, 463, 559–563.
Galaction, A. I., Rotaru, R., Kloetzer, L., Vlysidis, A., Webb, C., Turnea, M., et al. (2011). Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 21, 1257–1263.
Wang, C., Li, Q., Tang, H., Yan, D., Zhou, W., Xing, J., et al. (2012). Bioresource Technology, 116, 366–371.
Litsanov, B., Brocker, M., & Bott, M. (2012). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 3325–3337.
Li, Q., Li, W., Wang, D., Liu, B., Tang, H., Yang, M., et al. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 438–445.
Chen, K., Zhang, H., Miao, Y., Wei, P., & Chen, J. (2011). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 48, 339–344.
Zheng, P., Fang, L., Xu, Y., Dong, J. J., Ni, Y., & Sun, Z. H. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 7889–7894.
Lin, C. S. K., Luque, R., Clark, J. H., Webb, C., & Du, C. (2012). Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 6, 88–104.
Li, Q., Yang, M., Wang, D., Li, W., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 3292–3294.
Du, C., Lin, S. K. C., Koutinas, A., Wang, R., Dorado, P., & Webb, C. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 8310–8315.
Rudolf, A., Alkasrawi, M., Zacchi, G., & Liden, G. (2005). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 37, 195–204.
Jorgensen, H., Vibe-Pedersen, J., Larsen, J., & Felby, C. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 96, 862–870.
Dien, B. S., Li, X. L., Iten, L. B., Jordan, D. B., Nichols, N. N., O'Bryan, P. J., et al. (2006). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 39, 1137–1144.
Klinke, H. B., Thomsen, A. B., & Ahring, B. K. (2006). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 66, 10–26.
Wang, D., Li, Q., Li, W., Xing, J., & Su, Z. (2009). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 45, 491–497.
Wang, D., Li, Q., Li, W., Liu, Q. F., Xing, J., & Su, Z. (2008). Journal of Biotechnology, 136, 26–27.
Gokarn, R. R., Eiteman, M. A., & Altman, E. (1998). Biotechnology Letters, 20, 795–798.
Tengborg, C., Galbe, M., & Zacchi, G. (2001). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 28, 835–844.
Yoo, C., Kuo, M., & Kim, T. (2012). Process Biochemistry, 47, 319–326.
Zhang, K., Agrawal, M., Harper, J., Chen, R., & Koros, W. (2011). Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 50, 14055–14060.
Yang, X., Zhang, S., Zuo, Z., Men, X., & Tian, S. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 7840–7844.
Horn, S. J., & Eijsink, V. G. H. (2010). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 74, 1157–1163.
Zhu, M., Li, P., Gong, X., & Wang, J. (2012). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 76, 671–678.
Acknowledgments
Financial support by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 21206175, and 21106191) were gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dexi Wu and Qiang Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, D., Li, Q., Wang, D. et al. Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Succinic Acid Fermentation from Steam-Exploded Corn Stalk at High Solid Concentration by Recombinant Escherichia coli . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170, 1942–1949 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0319-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0319-7