Abstract
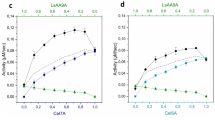
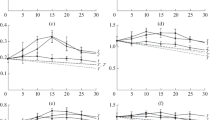
In order to establish which are the contribution of linear (total), hyperbolic (partial) or parabolic inhibitions by cellobiose, and also a special case of substrate inhibition, the kinetics of cellobiohydrolase Cel7A obtained from Trichoderma reesei was investigated. Values of kinetic parameters were estimated employing integrated forms of Michaelis–Menten equations through the use of non-linear regression, and criteria for selecting inhibition models are discussed. With cellobiose added at the beginning of the reaction, it was found that cellulose hydrolysis follows a kinetic model, which takes into account a mixed hyperbolic inhibition, by cellobiose with the following parameter values: K m 5.0 mM, K ic 0.029 mM, K iu 1.1 mM, k cat 3.6 h−1 and k cat′ 0.2 h−1. Cellulose hydrolysis without initial cellobiose added also follows the same inhibition model with similar values (4.7, 0.029 and 1.5 mM and 3.2 and 0.2 h−1, respectively). According to Akaike information criterion, more complex models that take into account substrate and parabolic inhibitions do not increase the modulation performance of cellulose hydrolysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E:
-
Free enzyme
- EI:
-
Enzyme inhibitor complex
- EIS:
-
Enzyme substrate inhibitor complex
- ES:
-
Enzyme substrate complex
- k cat :
-
Catalytic constant (per hour) to the breakdown of the ES complex
- k cat′ :
-
Catalytic constant (per hour) to the breakdown of the ESI complex
- K ic :
-
Competitive inhibition constant (millimolar) to cellobiose
- K iu :
-
Uncompetitive inhibition constant (millimolar) to cellobiose
- K ip :
-
Parabolic inhibition constant (millimolar) to cellobiose
- K m :
-
Michaelis constant (millimolar)
- n :
-
Experimental points
- P:
-
Reaction product (cellobiose)
- pA, pB:
-
Parameters
- Po :
-
Initial Product
- Pt :
-
Product at time t (minutes)
- S:
-
Substrate
- SSE:
-
Sum of squares error
- t :
-
Time (minutes)
- V max :
-
Maximum velocity
References
He, X.-Y., Yang, S.-Y., & Schulz, H. (1989). Analytical Biochemistry, 180, 105–109.
Bezerra, R. M. F., & Dias, A. A. (2007). Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education, 35, 145–150.
Yun, S.-L., & Suelter, C. H. (1977). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 480, 1–13.
Duggleby, R. G. (1995). Methods in Enzymology, 249, 61–90.
Liao, F., Tian, K.-C., Yang, X., Zhou, Q.-X., Zeng, Z.-C., & Zuo, Y.-P. (2003). Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 375, 756–762.
Zhang, Y.-H. P., & Lynd, L. R. (2004). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 88, 797–824.
Gusakov, A. V., & Sinitsyn, A. P. (1992). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 40, 663–671.
Bezerra, R. M. F., & Dias, A. A. (2004). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 112, 173–184.
Huang, A. A. (1975). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 7, 1421–1433.
Suga, K., van Dedem, G., & Moo-Young, M. (1975). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 17, 185–201.
Howell, J. A., & Mangat, M. (1978). Biotechnology and bioengineering, 20, 847–863.
Ryu, D. D. Y., Lee, S. B., Tassinari, T., & Macy, C. (1982). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 24, 1047–1067.
Lee, Y.-H., & Fan, L. T. (1982). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 24, 2383–2406.
Ohmine, K., Ooshima, H., & Harano, Y. (1983). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 25, 2041–2053.
Holtzapple, M. T., Caram, H. S., & Humphrey, A. E. (1984). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 26, 775–780.
Fujii, M., Homma, T., Ooshima, K., & Taniguchi, M. (1991). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 28/29, 145–156.
Bader, J., Bellgardt, K.-H., Singh, A., Kumar, P. K. R., & Schügerl, K. (1992). Bioprocess Engineering, 7, 235–240.
Converse, A. O., & Optekar, J. D. (1993). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 42, 145–148.
Sattler, W., Esterbauer, H., Glatter, Q., & Steiner, W. (1989). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 33, 1221–1234.
Nidetzky, B., Hayn, M., Macarron, R., & Steiner, W. (1993). Biotechnological Letters, 15, 71–76.
Väljamäe, P., Kipper, K., Petterson, G., & Johansson, G. (2003). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 84, 254–257.
Zhang, P. Y.-H., & Lynd, R. L. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 94, 888–898.
Andrić, P., Meyer, A. S., Jensen, P. A., & Dam-Johansen, K. (2010). Biotechnology Advances, 28, 308–324.
Pereira, A. N. (1987). PhD thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN.
Kim, D. W., Kim, T. S., Jeong, Y. K., & Lee, J. K. (1992). Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 73, 461–466.
Bezerra, R. M. F., Dias, A. A., Fraga, I., & Pereira, A. N. (2006). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 134, 27–38.
Medve, J., Ståhlberg, J., & Tjerneld, F. (1997). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 66, 39–56.
Palmer, T. (1985). Understanding the enzymes (4th ed.). Chichester: Ellis Horwood.
Fontes, R., Ribeiro, J. M., & Sillero, A. (2000). Acta Biochimica Polonica, 47, 233–257.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Nelson, N. (1944). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 153, 375–380.
Bezerra, R. M. F., & Dias, A. A. (2005). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 126, 49–59.
Klyosov, A. A., & Rabinovitch, M. L. (1980). In L. B. Wingard Jr., I. V. Berezin, & A. A. Klyosov (Eds.), Enzyme engineering future directions (pp. 83–165). New York: Plenum.
Väljamäe, P., Petterson, G., & Johansson, G. (2001). European Journal of Biochemistry, 268, 4520–4526.
Harjunpää, V., Teleman, A., Koivula, A., Ruohonen, L., Teeri, T. T., Teleman, O., et al. (1998). European Journal of Biochemistry, 240, 584–591.
Mannervik, B. (1982). Methods in Enzymology, 87C, 370–391.
Akaike, H. (1974). IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 19, 716–723.
Motulsky, H. J., & Christopoulos, A. (2003). Fitting models to biological data using linear and non-linear regression. A practical guide to curve fitting. San Diego: Oxford University Press.
Pitt, M. A., & Myung, I. J. (2002). Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 6, 421–425.
Myung, I. J., & Pitt, M. A. (2004). Methods in Enzymology, 383, 351–366.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bezerra, R.M.F., Dias, A.A., Fraga, I. et al. Cellulose Hydrolysis by Cellobiohydrolase Cel7A Shows Mixed Hyperbolic Product Inhibition. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 178–189 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9242-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9242-y