Abstract
Background
Despite the successes of hip arthroscopy, clinical failures do occur, and identifying risk factors for failure may facilitate refinement of surgical indications and treatment. Knowledge regarding the reasons for treatment failures may also improve surgical decision making.
Questions/purposes
We (1) characterized patients whose symptoms recurred after hip arthroscopy necessitating a revision hip preservation procedure or hip arthroplasty, (2) determined the etiologies of failure, (3) and reported the profile of revision surgical procedures.
Methods
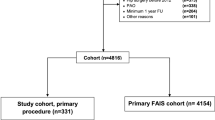
In a prospective database of 1724 consecutive hip surgeries, we identified 58 patients (60 hips) with a history of failed hip arthroscopy. Thirty-seven patients (38 hips) underwent revision hip preservation and 21 (22) hip arthroplasty. Thirty-nine (67%) were female. Demographics, etiology of failure, and type of revision surgery were analyzed.
Results
Patients treated with revision hip preservation were younger, had a lower BMI, and lower Tönnis osteoarthritis grade at the time of revision surgery compared to patients treated with hip arthroplasty. Common etiologies of failure were residual femoroacetabular impingement (68%) and acetabular dysplasia (24%) in patients treated with revision hip preservation and advanced osteoarthritis in patients treated with hip arthroplasty. The revision preservation procedures included arthroscopy in 16 (42%), arthroscopy with limited open capsulorraphy in two (5.3%), periacetabular osteotomy in nine (24%), and surgical dislocation in 12 (32%).
Conclusions
Residual or unaddressed structural deformity of the hip and underlying osteoarthritis are commonly associated with failure after hip arthroscopy. Thorough patient evaluation with detailed characterization of structural hip anatomy and articular cartilage integrity are critical to the selection of proper surgical intervention and successful patient outcome.
Level of Evidence
Level IV, prognostic study. See Instructions for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnard GA. A new test for 2 × 2 tables. Nature. 1945;156:177.
Bedi A, Zaltz I, De La Torre K, Kelly BT. Radiographic comparison of surgical hip dislocation and hip arthroscopy for treatment of cam deformity in femoroacetabular impingement. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(suppl):20S–28S.
Byrd JW, Jones KS. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: minimum 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:1379–1388.
Clohisy JC, Beaule PE, O’Malley A, Safran MR, Schoenecker P. AOA symposium. Hip disease in the young adult: current concepts of etiology and surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:2267–2281.
Clohisy JC, Carlisle JC, Beaule PE, Kim YJ, Trousdale RT, Sierra RJ, Leunig M, Schoenecker PL, Millis MB. A systematic approach to the plain radiographic evaluation of the young adult hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(suppl 4):47–66.
Clohisy JC, Keeney JA, Schoenecker PL. Preliminary assessment and treatment guidelines for hip disorders in young adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;441:168–179.
Clohisy JC, Zebala LP, Nepple JJ, Pashos G. Combined hip arthroscopy and limited open osteochondroplasty for anterior femoroacetabular impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:1697–1706.
Colvin AC, Harrast J, Harner C. Trends in hip arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:e23.
Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Notzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;417:112–120.
Grahame R, Bird HA, Child A. The revised (Brighton 1998) criteria for the diagnosis of benign joint hypermobility syndrome (BJHS). J Rheumatol. 2000;27:1777–1779.
Heyworth BE, Shindle MK, Voos JE, Rudzki JR, Kelly BT. Radiologic and intraoperative findings in revision hip arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2007;23:1295–1302.
Kain MS, Novais EN, Vallim C, Millis MB, Kim YJ. Periacetabular osteotomy after failed hip arthroscopy for labral tears in patients with acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(suppl 2):57–61.
Larson CM, Giveans MR, Taylor M. Does arthroscopic FAI correction improve function with radiographic arthritis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:1667–1676.
Lequesne M, de Séze S. [False profile of the pelvis: a new radiographic incidence for the study of the hip. Its use in dysplasias and different coxopathies] [in French]. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1961;28:643–652.
Leunig M, Beaule PE, Ganz R. The concept of femoroacetabular impingement: current status and future perspectives. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:616–622.
Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:556–560.
Philippon MJ, Schenker ML, Briggs KK, Kuppersmith DA, Maxwell RB, Stubbs AJ. Revision hip arthroscopy. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:1918–1921.
Ross JR, Zaltz I, Nepple JJ, Schoenecker PL, Clohisy JC. Arthroscopic disease classification and interventions as an adjunct in the treatment of acetabular dysplasia. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(suppl):72S–78S.
Siebenrock KA, Scholl E, Lottenbach M, Ganz R. Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;363:9–20.
Tönnis D. Congenital Dysplasia and Dislocation of the Hip in Children and Adults. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 1987.
Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint: with special reference to the complication of osteo-arthritis. Acta Chir Scand. 1939;83(suppl 58):5–135.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Deborah Long and Karla Crook for their assistance with this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One of the authors certifies that he (JCC), or a member of his immediate family, has or may receive payments or benefits during the study period, an amount of less than USD 10,000 from Pivot Medical (Sunnyvale, CA, USA), an amount of less than USD 10,000 from Biomet, Inc (Warsaw, IN, USA), and an amount of USD 10,000 to USD 100,000 from Zimmer, Inc (Warsaw, IN, USA).
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Bogunovic, L., Gottlieb, M., Pashos, G. et al. Why Do Hip Arthroscopy Procedures Fail?. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471, 2523–2529 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3015-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3015-6