Abstract
Background
In multiply injured patients, bilateral femur fractures invoke a substantial systemic inflammatory impact and remote organ dysfunction. However, it is unclear whether isolated bone or soft tissue injury contributes to the systemic inflammatory response and organ injury after fracture.
Questions/purposes
We therefore asked whether the systemic inflammatory response and remote organ dysfunction are attributable to the bone fragment injection, adjacent soft tissue injury, or both.
Methods
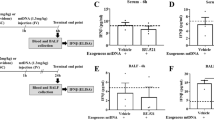
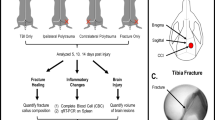
Male C57/BL6 mice (8–10 weeks old, 20–30 g) were assigned to four groups: bone fragment injection (BF, n = 9) group; soft tissue injury (STI, n = 9) group; BF + STI (n = 9) group, in which both insults were applied; and control group, in which neither insult was applied. Animals were sacrificed at 6 hours. As surrogates for systemic inflammation, we measured serum IL-6, IL-10, osteopontin, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and nuclear factor (NF)-κB and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in the lung.
Results
The systemic inflammatory response (mean IL-6 level) was similar in the BF (61.8 pg/mL) and STI (67.9 pg/mL) groups. The combination (BF + STI) of both traumatic insults induced an increase in mean levels of inflammatory parameters (IL-6: 189.1 pg/mL) but not in MPO levels (1.21 ng/mL) as compared with the BF (0.82 ng/mL) and STI (1.26 ng/mL) groups. The model produced little evidence of remote organ inflammation.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest both bone and soft tissue injury are required to induce systemic changes. The absence of remote organ inflammation suggests further fracture-associated factors, such as hemorrhage and fat liberation, may be more critical for induction of remote organ damage.
Clinical Relevance
Both bone and soft tissue injuries contribute to the systemic inflammatory response.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkose S, Ozgurer A, Bulut M, Koksal O, Ozdemir F, Ozguc H. Relationships between markers of inflammation, severity of injury, and clinical outcomes in hemorrhagic shock. Adv Ther. 2007;24:955–962.
Ayala A, Wang P, Ba ZF, Perrin MM, Ertel W, Chaudry IH. Differential alterations in plasma IL-6 and TNF levels after trauma and hemorrhage. Am J Physiol. 1991;260(1 pt 2):R167–R171.
Bardenheuer M, Obertacke U, Waydhas C, Nast-Kolb D; AG Polytrauma der DGU. [Epidemiology of severe multiple trauma: a prospective registration of preclinical and clinical supply] [in German]. Unfallchirurg. 2000;103:355–363.
Chen J, Raj N, Kim P, Andrejko KM, Deutschman CS. Intrahepatic nuclear factor-kB activity and a1-acid glycoprotein transcription do not predict outcome after cecal ligation and puncture in the rat. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:589–596.
Chow CC, Clermont G, Kumar R, Lagoa C, Tawadrous Z, Gallo D, Betten B, Bartels J, Constantine G, Fink MP, Billiar TR, Vodovotz Y. The acute inflammatory response in diverse shock states. Shock. 2005;24:74–84.
Copeland CE, Mitchell KA, Brumback RJ, Gens DR, Burgess AR. Mortality in patients with bilateral femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1998;12:315–319.
Darwiche SS, Pfeifer R, Menzel CL, Ruan X, Hoffman M, Cai C, Chanthaphavong RS, Loughran P, Pitt BR, Hoffman R, Pape HC, Billiar TR. Inducible nitric oxide synthase contributes to immune dysfunction following trauma. Shock. 2012;38:499–507.
Denhardt DT, Guo X. Osteopontin: a protein with diverse functions. FASEB J. 1993;7:1475–1482.
Flohe SB, Bangen JM, Flohe S, Agrawal H, Bergmann K, Schade FU. Origin of immunomodulation after soft tissue trauma: potential involvement of extracellular heat-shock proteins. Shock. 2007;27:494–502.
Gebhard F, Pfetsch H, Steinbach G, Stecker W, Kinzl L, Brückner UB. Is interleukin 6 an early marker of injury severity following major trauma in humans. Arch Surg. 2000;135:291–295.
Giannoudis PV, Harwood PJ, Loughenbury P, van Griensven M, Krettek C, Pape HC. Correlation between IL-6 levels and the systemic inflammatory response score: can an IL-6 cutoff predict a SIRS state? J Trauma. 2008;65:646–652.
Gross S, Gammon ST, Moss B, Rauch D, Harding J, Heinecke JW, Ratner L, Piwnica-Worms D. Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo. Nat Med. 2009;15:455–461.
Harwood PJ, Giannoudis PV, van Griensven M, Krettek C, Pape HC. Alterations in the systemic inflammatory response after early total care and damage control procedures for femoral shaft fractures in severely injured patients. J Trauma. 2005;58:446–454.
Hauser C, Zhou X, Joshi P, Cuchens MA, Kregor P, Devidas M, Kennedy RJ, Poole GV, Hughes JL. The immune microenvironment of human fracture/soft-tissue hematomas and its relationship to systemic immunity. J Trauma. 1997;42:895–904.
Hildebrand F, Pape HC, Krettek C. The importance of cytokines in the posttraumatic inflammatory reaction. Unfallchirurg. 2005;108:793–803.
Johnson KD, Cadambi A, Seibert GB. Incidence of adult respiratory distress syndrome in patients with multiple musculoskeletal injuries: effect of early operative stabilisation of fractures. J Trauma. 1985;25:375–384.
Kobbe P, Kaczorowski DJ, Vodovotz Y, Tzioupis CH, Mollen KP, Billiar TR, Pape HC. Local exposure of bone components to injured soft tissue induces Toll-like-receptor-4 dependent systemic inflammation with acute lung injury. Shock. 2008;30:686–691.
Kobbe P, Vodovotz Y, Kaczorowski D, Mollen KP, Billiar TR, Pape HC. Patterns of cytokine release and evolution of remote organ dysfunction after bilateral femur fracture. Shock. 2008;30:43–47.
Kobbe P, Vodovotz Y, Kaczorowski DJ, Billiar TR, Pape HC. The role of fracture-associated soft tissue injury in the induction of systemic inflammation and remote organ dysfunction after bilateral femur fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22:385–390.
Koh A, Batista da Silva AP, Bansal AK, Bansal M, Sun C, Lee H, Glogauer M, Sodek J, Zohar R. Role of osteopontin in neutrophil function. Immunology. 2007;122:466–475.
Levy RM, Prince JM, Yang R, Mollen KP, Liao H, Watson GA, Fink MP, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR. Systemic inflammation and remote organ damage following bilateral femur fracture requires Toll-like receptor 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006;291:R970–R976.
Menzel CL, Pfeifer R, Darwiche SS, Kobbe P, Gill R, Shapiro RA, Loughran P, Vodovotz Y, Scott MJ, Zenati MS, Billiar TR, Pape HC. Models of lower extremity damage in mice: time course of organ damage and immune response. J Surg Res. 2011;166:e149–e156.
Mori R, Shaw TJ, Martin P. Molecular mechanisms linking wound inflammation and fibrosis: knockdown of osteopontin leads to rapid repair and reduced scarring. J Exp Med. 2008;205:43–51.
Neidhardt R, Keel M, Steckholzer, U Safret A, Ungethuem U, Trentz O, Ertel W. Relationship of interleukin-10 plasma levels to severity of injury and clinical outcome in injured patients. J Trauma. 1997;42:863–871.
Pape HC, Schmidt R, Rice J van Griensven M, das Gupta R, Krettek C, Tscherne H. Biochemical changes after trauma and skeletal surgery of the lower extremity: quantification of the operative burden. Crit Care Med. 2000;28:3441–3448.
Perl M, Gebhard F, Knöferl MW, Bachem M, Gross HJ, Kinzl L, Strecker W. The pattern of preformed cytokines in tissues frequently affected by trauma. Shock. 2003;19:299–304.
Pfeifer R, Kobbe P, Darwiche S, Billiar TR, Pape HC. Role of hemorrhage in the induction of systemic inflammation and remote organ damage: analysis of combined pseudo-fracture and hemorrhagic shock. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:270–274.
Robinson CM. Current concepts of respiratory insufficiency syndromes after fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:781–791.
Rose S, Marzi I. Mediators in polytrauma—pathophysiological significance and clinical relevance. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg. 1998;383:199–208.
Roumen RM, Hendriks T, van der Ven-Jongekrijg J, Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Sauerwein RW, van der Meer JW, Goris RJ. Cytokine patterns in patients after major vascular surgery, hemorrhagic shock, and severe blunt trauma. Ann Surg. 1993;218:769–776.
Schemitsch EH, Turchin DC, Anderson GI, Byrick RJ, Mullen JB, Richards RR. Pulmonary and systemic fat embolization after medullary canal pressurization: a hemodynamic and histologic investigation in the dog. J Trauma. 1998;45:738–742.
Schmidt-Bleek K, Schell H, Kolar P, Pfaff M, Perka C, Buttgereit F, Duda G, Lienau J. Cellular composition of the initial fracture hematoma compared to a muscle hematoma: a study in sheep. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:1147–1151.
Schmitz D, Bangen J, Herborn C, Husain B, Lendemans S, Flohé SB, Metz KA, Schade FU, Taeger G, Oberbeck JR, Kobbe P, Waydhas C, Flohé S. Isolated closed minor-muscle injury of lower leg did not cause an obvious systemic immune response. Inflamm Res. 2010;59:141–149.
Sodek J, Ganss B, McKee MD. Osteopontin. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2000;11:279–303.
Willett K, Al-Khateeb H, Kotnis R, Bouamra O, Lecky F. Risk of mortality: the relationship with associated injuries and fracture treatment methods in patients with unilateral or bilateral femoral shaft fractures. J Trauma. 2010;69:405–410.
Acknowledgments
We thank John Brumfield, Roop Gill MD, Derek Barclay MD, and the laboratory of the Department of Surgery, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she, or a member of his or her immediate family, has no funding or commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the animal protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
This work was performed at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
About this article
Cite this article
Pfeifer, R., Darwiche, S., Kohut, L. et al. Cumulative Effects of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury on Systemic Inflammation: A Pilot Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471, 2815–2821 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-2908-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-2908-8