Abstract
Background
Proximal femoral nail antirotation devices (PFNAs) are considered biomechanically superior to dynamic hip screws for treating unstable peritrochanteric fractures and reportedly have a lower complication rate. The PFNA II was introduced to eliminate lateral cortex impingement encountered with the PFNA. However, it is unclear whether the new design in fact avoids lateral cortex impingement without compromising stability of fixation and fracture healing.
Questions/Purposes
We therefore asked whether the PFNA II: (1) eliminates the lateral cortex impingement and fracture displacement experienced with PFNA; and (2) provides stable fracture fixation with a low major complication rate for unstable fractures in European patients.
Methods
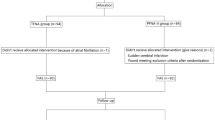
We retrospectively reviewed 108 patients with an unstable peritrochanteric fracture, 58 treated with PFNA and 50 with PFNA II. We compared nail positioning, major and minor complication rates, operative and fluoroscopy time, blood transfused, time to mobilization, hospital stay, fracture union, and Harris hip score. The minimum followup was 12 months (mean, 13 months; range, 12–18 months).
Results
In the PFNA II group we encountered no impingement on the lateral cortex and no patients with lateral fragment or loss of reduction at insertion, whereas with the PFNA group, we had 10 and five cases, respectively. Fracture union occurred in all patients treated with PFNA II without mechanical failures. PFNA II cases were associated with a slightly shorter surgical time than PFNA cases (23 minutes versus 27 minutes, respectively).
Conclusion
PFNA II avoided lateral cortex impingement experienced with PFNA, providing fast and stable fixation of the unstable peritrochanteric fractures.
Level of Evidence
Level III, retrospective comparative study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Yassari G, Langstaff RJ, Jones JWM, Al-Lami M. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN) for the treatment of unstable trochanteric femoral fracture. Injury. 2002;33:395–399.
Anglen JO, Weinstein JN; American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Research Committee. Nail or plate fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: changing pattern of practice. A review of the American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Database. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:700–707.
AO Foundation. Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation, PFNA®. Available at: www.aofoundation.org. Accessed June 2008.
Aros B, Tosteson AN, Gottlieb DJ, Koval KJ, Is a sliding hip screw or im nail the preferred implant for intertrochanteric fracture fixation? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:2827–2832.
Banan H, Al-Sabti A, Jimulia T, Hart AJ. The treatment of unstable, extracapsular hip fractures with the AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN): our first 60 cases. Injury. 2002;33:401–405.
Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, Keggi JM. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:1058–1064.
Butler M, Forte ML, Joglekar SB, Swiontkowski MF, Kane RL. Evidence summary: systematic review of surgical treatments for geriatric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:1104–1115.
Curtis MJ, Jinnah RH, Wilson V, Cunningham BW. Proximal femoral fractures: a biomechanical study to compare intramedullary and extramedullary fixation. Injury. 1994;25:99–104.
David A, von der HD, Pommer A. Therapeutic possibilities in trochanteric fractures. Safe–fast–stable. Orthopade. 2000;29:294–301.
Domingo LJ, Cecilia D, Herrera A, Resines C. Trochanteric fractures treated with a proximal femoral nail. Int Orthop. 2001;25:298–301.
Foulongne E, Gilleron M, Roussignol X, Lenoble E, Dujardin F. Mini-invasive nail versus DHS to fix pertrochanteric fractures: a case-control study. Injury. 2011;42:204–208.
Friedl W, Clausen J. [Experimental examination for optimized stabilisation of trochanteric femur fractures, intra- or extramedullary implant localisation and influence of femur neck component profile on cut-out risk] [in German]. Chirurg. 2001;72:1344–1352.
Gardenbroek TJ, Segers MJ, Simmermacher RK, Hammacher ER. The proximal femur nail antirotation: an identifiable improvement in the treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fractures? J Trauma. 2011;71:169–174.
Garg B, Marimuthu K, Kumar V, Malhotra R, Kotwal PP. Outcome of short proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw for fixation of unstable trochanteric fractures. A randomised prospective comparative trial. Hip Int. 2011;21:531–536.
Haidukewych GJ, Israel TA, Berry DJ. Reverse obliquity fractures of the intertrochanteric region of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:643–650.
Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51:737–755.
Kannus P, Parkkari J, Sievanen H, Heinonen A, Vuori I, Järvinen M. Epidemiology of hip fracture. Bone. 1996;18(Suppl):57S–63S.
Kokoroghiannis C, Aktselis I, Deligeorgis A, Fragkomichalos E, Papadimas D, Pappadas I. Evolving concepts of stability and intramedullary fixation of intertrochanteric fractures—a review. Injury. 2012;43:686–693.
Kuzyk PR, Bhandari M, McKee MD, Russell TA, Schemitsch EH. Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation for subtrochanteric femur fractures J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23:465–470.
Laros GS. The role of osteoporosis in intertrochanteric fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1980;11:525–537.
Little NJ, Verma V, Fernando C, Elliott DS, Khaleel A. A prospective trial comparing the Holland nail with the dynamic hip screw in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90:1073–1078.
Liu M, Yang Z, Pei F, Huang F, Chen S, Xiang Z. A meta-analysis of the Gamma nail and dynamic hip screw in treating peritrochanteric fractures. Int Orthop. 2010;34:323–328.
Lv C, Fang Y, Liu L, Wang G, Yang T, Zhang H, Song Y. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation—Asia: early results. Orthopedics. 2011;34:351.
Madsen J, Næss L, Aune A, Alho A, Ekeland A, Strømsøe K. Dynamic hip screw with trochanteric stabilizing plate in the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures: a comparative study with the Gamma nail and compression hip screw. J Orthop Trauma. 1998;12:241–248.
Muller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J (1990) The Comprehensive Classification of Fractures of Long Bones. 1st ed. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, New York, NY, USA: Springer-Verlag;
Orthopaedic Trauma Association Committee for Coding and Classification. Fracture and dislocation compendium. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10(Suppl 1):v–ix, 1–154.
Pajarinen J, Lindahl J, Michelsson O, Savolainen V, Hirvensalo E. Pertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with a dynamic hip screw or a proximal femoral nail. A randomised study comparing post-operative rehabilitation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:76–81.
Panjabi MM, Lindsey RW, Walter SD, White AA 3rd. The clinician’s ability to evaluate the strength of healing fractures from plain radiographs. J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3:29–32.
Parker MJ, Handoll HH. Gamma and other cephalocondylic intramedullary nails versus extramedullary implants for extracapsular hip fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;4:CD000093.
Parker MJ, Handoll HH. Intramedullary nails for extracapsular hip fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;3:CD004961.
Parker MJ, Handoll HH. Gamma and other cephalocondylic intramedullary nails versus extramedullary implants for extracapsular hip fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;9:CD000093.
Radford PJ, Needoff M, Webb JK. A prospective randomized comparison of the dynamic hip screw and the gamma locking nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:789–793.
Sabin S, Ertürer E, Oztürk I, Toker S, Seçkin F, Akman S, Radiographic and functional results of osteosynthesis using the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44:127–134.
Schipper IB, Marti RK, van der Werken C. Unstable trochanteric femoral fractures: extramedullary or intramedullary fixation. Review of literature. Injury. 2004;35:142–151.
Sommers MB, Roth C, Hall H, Kam BC, Ehmke LW, Krieg JC, Madey SM, Bottlang M. A laboratory model to evaluate cutout resistance of implants for pertrochanteric fracture fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18:361–368.
Strauss E, Frank J, Lee J, Kummer FJ, Tejwani N. Helical blade versus sliding hip screw for treatment of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures. A biomechanical evaluation. Injury. 2006;37:984–989.
Streubel PN, Wong AH, Ricci WM, Gardner MJ. Is there a standard trochanteric entry site for nailing of subtrochanteric femur fractures? J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25:202–207.
Synthes. Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation, PFNA®. Available at: www.synthes.com. Accessed June 2008.
Tyagi V, Yang JH, Oh KJ. A computed tomography-based analysis of proximal femoral geometry for lateral impingement with two types of proximal femoral nail anterotation in subtrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2010;41:857–861.
Verettas DA, Ifantidis P, Chatzipapas CN, Drosos GI, Xarchas KC, Chloropoulou P, Kazakos KI, Trypsianis G, Ververidis A. Systematic effects of surgical treatment of hip fractures: gliding screw-plating vs intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2010;41:279–284.
Windolf M, Braunstein V, Dutoit C, Schwieger K. Is a helical shaped implant a superior alternative to the dynamic hip screw for unstable femoral neck fractures? A biomechanical investigation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24:59–64.
Xu YZ, Geng DC, Mao HQ, Zhu XS, Yang HL. A comparison of the proximal femoral nail antirotation device and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fracture. J Int Med Res. 2010;38:1266–1275.
Yoshimine F, Latta LL, Milne EL. Sliding characteristics of compression hip screws in the intertrochanteric fracture: a clinical study. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7:348–353.
Ziran BH, Heckman DS, Olarte CM, Chou K, Baranick J. Intramedullary hip screw versus standard compression hip screw: early postoperative rehabilitation comparisons. Orthopedics. 2009;32:83.
Zou J, Xu Y, Yang H. A comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw devices in trochanteric fractures. J Int Med Res. 2009;37:1057–1064.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she, or a member of their immediate family, has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article
Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research neither advocates nor endorses the use of any treatment, drug, or device. Readers are encouraged to always seek additional information, including FDA-approval status, of any drug or device prior to clinical use.
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Macheras, G.A., Koutsostathis, S.D., Galanakos, S. et al. Does PFNA II Avoid Lateral Cortex Impingement for Unstable Peritrochanteric Fractures?. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470, 3067–3076 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2445-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2445-x