Abstract
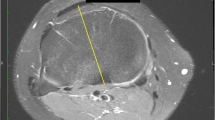
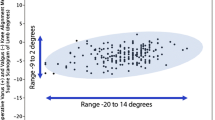
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the femoral component rotation in a small subset of patients who had developed arthrofibrosis after mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Arthrofibrosis was defined as flexion less than 90° or a flexion contracture greater than 10° following TKA. From a consecutive cohort of 3,058 mobile-bearing TKAs, 49 (1.6%) patients were diagnosed as having arthrofibrosis, of which 38 (86%) could be recruited for clinical assessment. Femoral rotation of a control group of 38 asymptomatic TKA patients matched for age, gender, and body mass index was also evaluated. The surgical epicondylar axis was compared with the posterior condylar axis for the femoral prosthesis. Femoral components in the arthrofibrosis group were significantly internally rotated by a mean of 4.7° (SD 2.2°, range 10° internal to 1° external). In the control group, the femoral component had a mean 0.3° internal rotation (SD 2.3°, range 4° internal to 6° external). Following mobile-bearing TKA, there is a significant correlation between internal femoral component rotation and chronic arthrofibrosis.
Résumé
Le propos de cette étude est d’évaluer la rotation du composant fémoral des sujets ayant développé une raideur du genou après prothèse à plateau mobile. La raideur du genou se définit comme une flexion inférieure à 90° avec un défaut d’extension de 10°. Sur une cohorte consécutive de 3 058 prothèses du genou à plateau mobile 1,6% ont présenté une raideur. 86% de ces patients ont pu être évalués cliniquement. La rotation du composant fémoral, outre le contrôle de 38 patients évalués, de même que l’âge, le sexe, le BMI. L’axe épicondylien a été comparé à l’axe du condyle postérieur, les composants fémoraux chez les sujets présentant une raideur du genou étaient, de manière significative, une rotation interne en moyenne de 4,7° (10° de rotation interne à 1° de rotation externe). Dans le groupe contrôle, le composant fémoral ne présentait que 0,3° de rotation interne (4° interne, 6° externe). Il existe donc une corrélation significative chez ces patients après prothèse à plateau mobile du genou entre la raideur du genou et la rotation du composant fémoral.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anouchi YS, Whiteside LA, Kaiser AD, Milliano MT (1983) The effects of axial rotational alignment of the femoral component on knee stability and patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty demonstrated on autopsy specimens. Clin Orthop 287:170–177
Arima J, Whiteside LA, McCarthy DS, White SE (1995) Femoral rotational alignment, based on the anteroposterior axis, in total knee arthroplasty in a valgus knee. A technical note. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:1331–1334
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L (2001) Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 392:46–55
Berger RA, Crossett LS (1998) Determining the rotation of the femoral and tibial components in total knee arthroplasty: a computed tomography technique. Oper Tech Orthop 8:128–133
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Rotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 356:144–153
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop 286:40–47
Boldt JG, Stiehl JB, Thuemler P (2002) Femoral rotation based on tibial axis. In: Hamelynck KJ, Stiehl JB (eds) LCS mobile bearing knee arthroplasty. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 175–182
Bong MR, Di Cesare PE (2004) Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 12:164–171
Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Stiehl JB, Walker SA, Dennis KN (1998) Range of motion following total knee arthroplasty: the effect of implant design and weight-bearing conditions. J Arthroplasty 13:748–752
Eckhoff DG, Metzger RG, Vandewalle MV (1995) Malrotation associated with implant alignment technique in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 321:28–31
Fehring TK (2000) Rotational malalignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 380:72–79
Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR (2000) Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 15:970–973
Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR (1998) The posterior condylar angle in osteoarthritic knees. J Arthroplasty 13:812–815
Harvey IA, Barry K, Kirby SP, Johnson R, Elloy MA (1993) Factors affecting the range of movement of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 75:950–955
Healy WL, Wasilewski SA, Takei R et al (1995) Patellofemoral complications following total knee arthroplasty: correlation with implant design and patient risk factors. J Arthroplasty 10:197–201
Katz MA, Beck TD, Silber JS, Seldes RM, Lotke PA (2001) Determining femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty: reliability of techniques. J Arthroplasty 16:301–305
Krackow AK, Mihalko WM (1999) The effect of medial release on flexion and extension gaps in cadaveric knees. Am J Knee Surg 12:222–228
Olcott CW, Scott RD (1999) The Ranawat Award. Femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 367:39–42
Olcott CW, Scott RD (2000) A comparison of 4 intraoperative methods to determine femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 15:22–26
Poilvache PL, Insall JN, Scuderi GR, Font-Rodriguez DE (1996) Rotational landmarks and sizing of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 331:35–46
Rhoads DD, Noble PC, Reuben JD, Mahoney OM, Tullos HS (1990) The effect of femoral component position on patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 260:43–51
Romero J, Duronio JF, Sohrabi A, Alexander N, MacWilliams BA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS (2002) Varus and valgus flexion laxity of total knee alignment methods in loaded cadaveric knees. Clin Orthop 394:243–253
Stiehl JB (2003) Patellar instability in total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 16:229–235
Whiteside LA, Arima J (1995) The anteroposterior axis for femoral rotational alignment in valgus total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 321:168–172
Winemaker MJ (2001) Perfect balance in total knee arthroplasty. The elusive compromise. J Arthroplasty 17:2–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boldt, J.G., Stiehl, J.B., Hodler, J. et al. Femoral component rotation and arthrofibrosis following mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 30, 420–425 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0085-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0085-z