Abstract
Background
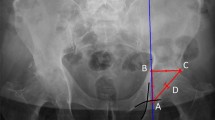
Pelvic radiographs are helpful in assessing limb-length discrepancy (LLD) before and after THA but are subject to variation. Different methods are used to determine LLDs. As a pelvic reference, both ischial tuberosities and the teardrops are used, and as a femoral reference, the lesser trochanter and center of the femoral head are used.
Questions/purposes
We validated the different methods for preoperative radiographic measurement of LLDs and evaluated their reliability.
Patients and Methods
LLDs were measured on full-leg radiographs for 52 patients (29 men, 23 women) with osteoarthritis (OA) of the hip and compared with different methods for measuring LLDs on AP radiographs of the pelvis.
Results
The true LLD varied from −8.0 to 9.1 mm. When the biischial line was used as a pelvic reference, the LLD measured on AP pelvis radiographs was different from the true LLD. No difference was found when the interteardrop line was used as a pelvic reference. There was substantial interobserver agreement when the lesser trochanter was used as a femoral reference (kappa = 0.66–0.70) and excellent interobserver and intraobserver agreement for all other measurements (kappa = 0.84–0.93).
Conclusions
Our data show use of the biischial line as a pelvic reference should be discouraged and the interteardrop line is a better alternative. The center of the femoral head is a more reliable femoral landmark compared with the lesser trochanter.
Level of Evidence
Level I, diagnostic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WD, Dimon JH 3rd. Leg length discrepancy in total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1992;23:201–209.
Austin MS, Hozack WJ, Sharkey PF, Rothman RH. Stability and leg length equality in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(3 suppl 1):88–90.
Bal BS. A technique for comparison of leg lengths during total hip replacement. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1996;25:61–62.
Blackley HR, Howell GE, Rorabeck CH. Planning and management of the difficult primary hip replacement: preoperative planning and technical considerations. Instr Course Lect. 2000;49:3–11.
Bono JV. Digital templating in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(suppl 2):118–122.
Bose WJ. Accurate limb-length equalization during total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2000;23:433–436.
Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH. Soft tissue balancing: the hip. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(4 suppl 1):17–22.
Clark CR, Huddleston HD, Schoch EP 3rd, Thomas BJ. Leg-length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14:38–45.
Cummings G, Scholz JP, Barnes K. The effect of imposed leg length difference on pelvic bone symmetry. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18:368–373.
Dolhain P, Tsigaras H, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Mac Donald S, Mc Calden R. The effectiveness of dual offset stems in restoring offset during total hip replacement. Acta Orthop Belg. 2002;68:490–499.
Edeen J, Sharkey PF, Alexander AH. Clinical significance of leg-length inequality after total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1995;24:347–351.
Eggli S, Pisan M, Müller ME. The value of preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80:382–390.
Friberg O. Clinical symptoms and biomechanics of lumbar spine and hip joint in leg length inequality. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8:643–651.
Giles LG, Taylor JR. Low-back pain associated with leg length inequality. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1981;6:510–521.
Gonzalez Della Valle A, Slullitel G, Piccaluga F, Salvati EA. The precision and usefulness of preoperative planning for cemented and hybrid total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:51–58.
Goodman SB, Adler SJ, Fyhrie DP, Schurman DJ. The acetabular teardrop and its relevance to acetabular migration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;236:199–204.
Gurney B, Mermier C, Robergs R, Gibson A, Rivero D. Effects of limb-length discrepancy on gait economy and lower-extremity muscle activity in older adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:907–915.
Hananouchi T, Sugano N, Nakamura N, Nishii T, Miki H, Yamamura M, Yoshikawa H. Preoperative templating of femoral components on plain X-rays: rotational evaluation with synthetic X-rays on ORTHODOC. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127:381–385.
Hofmann AA, Skrzynski MC. Leg-length inequality and nerve palsy in total hip arthroplasty: a lawyer awaits! Orthopedics. 2000;23:943–944.
Hoikka V, Santavirta S, Eskola A, Paavilainen T, Wirta J, Lindholm TS. Methodology for restoring functional leg length in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6:189–193.
Huddleston HD. An accurate method for measuring leg length and hip offset in hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 1997;20:331–332.
Jasty M, Webster W, Harris W. Management of limb length inequality during total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;333:165–171.
Khanduja V, Tek V, Scott G. The effect of a neck-retaining femoral implant on leg-length inequality following total hip arthroplasty: a radiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:712–715.
Konyves A, Bannister GC. The importance of leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:155–157.
Krishnan SP, Carrington RW, Mohiyaddin S, Garlick N. Common misconceptions of normal hip joint relations on pelvic radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:409–412.
Lai KA, Lin CJ, Jou IM, Su FC. Gait analysis after total hip arthroplasty with leg-length equalization in women with unilateral congenital complete dislocation of the hip: comparison with untreated patients. J Orthop Res. 2001;19:1147–1152.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–174.
Machen MS, Stevens PM. Should full-length standing anteroposterior radiographs replace the scanogram for measurement of limb length discrepancy? J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005;14:30–37.
Maloney WJ, Keeney JA. Leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(4 suppl 1):108–110.
Matsuda K, Nakamura S, Matsushita T. A simple method to minimize limb-length discrepancy after hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:375–379.
McGee HM, Scott JH. A simple method of obtaining equal leg length in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;194:269–270.
Mihalko WM, Phillips MJ, Krackow KA. Acute sciatic and femoral neuritis following total hip arthroplasty: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:589–592.
Murphy SB, Ecker TM. Evaluation of a new leg length measurement algorithm in hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;463:85–89.
Nercessian OA, Piccoluga F, Eftekhar NS. Postoperative sciatic and femoral nerve palsy with reference to leg lengthening and medialization/lateralization of the hip joint following total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;304:165–171.
Parvizi J, Sharkey PF, Bissett GA, Rothman RH, Hozack WJ. Surgical treatment of limb-length discrepancy following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:2310–2317.
Ranawat CS. The pants too short, the leg too long! Orthopedics. 1999;22:845–846.
Ranawat CS, Rao RR, Rodriguez JA, Bhende HS. Correction of limb-length inequality during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16:715–720.
Ranawat CS, Rodriguez JA. Functional leg-length inequality following total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:359–364.
Rand JA, Ilstrup DM. Comparison of Charnley and T-28 total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;180:201–205.
Rösler J, Perka C. The effect of anatomical positional relationships on kinetic parameters after total hip replacement. Int Orthop. 2000;24:23–27.
Sarin VK, Pratt WR, Bradley GW. Accurate femur repositioning is critical during intraoperative total hip arthroplasty length and offset assessment. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:887–891.
Sathappan SS, Ginat D, Patel V, Walsh M, Jaffe WL, Di Cesare PE. Effect of anesthesia type on limb length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:203–209.
Schmalzried TP. Preoperative templating and biomechanics in total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2005;28(8 suppl):s849–851.
Shiramizu K, Naito M, Shitama T, Nakamura Y, Shitama H. L-shaped caliper for limb length measurement during total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:966–969.
Siebenrock KA, Kalbermatten DF, Ganz R. Effect of pelvic tilt on acetabular retroversion: a study of pelves from cadavers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;407:241–248.
Stone RG, Weeks LE, Hajdu M, Stinchfield FE. Evaluation of sciatic nerve compromise during total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;201:26–31.
Suh KT, Cheon SJ, Kim DW. Comparison of preoperative templating with postoperative assessment in cementless total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75:40–44.
Tannast M, Zheng G, Anderegg C, Burckhardt K, Langlotz F, Ganz R, Siebenrock KA. Tilt and rotation correction of acetabular version on pelvic radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;438:182–190.
Unnanuntana A, Wagner D, Goodman SB. The accuracy of preoperative templating in cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:180–186.
Weber ER, Daube JR, Coventry MB. Peripheral neuropathies associated with total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58:66–69.
Wedemeyer C, Quitmann H, Xu J, Heep H, von Knoch M, Saxler G. Digital templating in total hip arthroplasty with the Mayo stem. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128:1023–1029.
White AB. AAOS Committee on Professional Liability: Study of 119 closed malpractice claims involving hip replacement. AAOS Bulletin. July 1994.
White TO, Dougall TW. Arthroplasty of the hip: leg length is not important. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:335–338.
Williamson JA, Reckling FW. Limb length discrepancy and related problems following total hip joint replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978;134:135–138.
Wixson RL, MacDonald MA. Total hip arthroplasty through a minimal posterior approach using imageless computer-assisted hip navigation. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(7 suppl 3):51–56.
Woo RY, Morrey BF. Dislocations after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64:1295–1306.
Woolson ST. Leg length equalization during total hip replacement. Orthopedics. 1990;13:17–21.
Woolson ST, Hartford JM, Sawyer A. Results of a method of leg-length equalization for patients undergoing primary total hip replacement. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14:159–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Meermans, G., Malik, A., Witt, J. et al. Preoperative Radiographic Assessment of Limb-length Discrepancy in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469, 1677–1682 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1588-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1588-x