Abstract
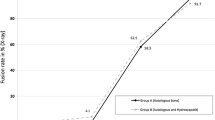
It is unclear whether using artificial cages increases fusion rates compared with use of bone chips alone in posterior lumbar interbody fusion for patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis. We hypothesized artificial cages for posterior lumbar interbody fusion would provide better clinical and radiographic outcomes than bone chips alone. We assumed solid fusion would provide good clinical outcomes. We clinically and radiographically followed 34 patients with spondylolisthesis having posterior lumbar interbody fusion with mixed autogenous and allogeneic bone chips alone and 42 patients having posterior lumbar interbody fusion with implantation of artificial cages packed with morselized bone graft. Patients with the artificial cage had better functional improvement in the Oswestry disability index than those with bone chips alone, whereas pain score, patient satisfaction, and fusion rate were similar in the two groups. Postoperative disc height ratio, slip ratio, and segmental lordosis all decreased at final followup in the patients with bone chips alone but remained unchanged in the artificial cage group. The functional outcome correlated with radiographic fusion status. We conclude artificial cages provide better functional outcomes and radiographic improvement than bone chips alone in posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis, although both techniques achieved comparable fusion rates.
Level of Evidence: Level III, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agazzi S, Reverdin A, May D. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cages: an independent review of 71 cases. J Neurosurg. 1999;91:186–192.
Akamaru T, Kawahara N, Tim Yoon S, Minamide A, Su Kim K, Tomita K, Hutton WC. Adjacent segment motion after a simulated lumbar fusion in different sagittal alignments: a biomechanical analysis. Spine. 2003;28:1560–1566.
Arai Y, Takahashi M, Kurosawa H, Shitoto K. Comparative study of iliac bone graft and carbon cage with local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2002;10:1–7.
Blumenthal SL, Gill K. Can lumbar spine radiographs accurately determine fusion in postoperative patients? Correlation of routine radiographs with a second surgical look at lumbar fusions. Spine. 1993;18:1186–1189.
Brantigan JW, Neidre A. Achievement of normal sagittal plane alignment using a wedged carbon fiber reinforced polymer fusion cage in treatment of spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2003;3:186–196.
Brantigan JW, Steffee AD, Lewis ML, Quinn LM, Persenaire JM. Lumbar interbody fusion using the Brantigan I/F cage for posterior lumbar interbody fusion and the variable pedicle screw placement system: two-year results from a Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption clinical trial. Spine. 2000;25:1437–1446.
Chen D, Fay LA, Lok J, Yuan P, Edwards WT, Yuan HA. Increasing neuroforaminal volume by anterior interbody distraction in degenerative lumbar spine. Spine. 1995;20:74–79.
Chen L, Tang T, Yang H. Complications associated with posterior lumbar interbody fusion using Bagby and Kuslich method for treatment of spondylolisthesis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2003;116:99–103.
Cloward RB. Spondylolisthesis: treatment by laminectomy and posterior interbody fusion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981;154:74–82.
Csecsei G, Klekner A, Sikula J. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) using the bony elements of the dorsal spinal segment. Acta Chir Hung. 1997;36:54–56.
Csecsei GI, Klekner AP, Dobai J, Lajgut A, Sikula J. Posterior interbody fusion using laminectomy bone and transpedicular screw fixation in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis. Surg Neurol. 2000;53:2–6; discussion 6–7.
Diedrich O, Perlick L, Schmitt O, Kraft CN. Radiographic characteristics on conventional radiographs after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: comparative study between radiotranslucent and radiopaque cages. J Spinal Disord. 2001;14:522–532.
Elias WJ, Simmons NE, Kaptain GJ, Chadduck JB, Whitehill R. Complications of posterior lumbar interbody fusion when using a titanium threaded cage device. J Neurosurg. 2000;93:45–52.
Enker P, Steffee AD. Interbody fusion and instrumentation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;300:90–101.
Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine. 2000;25:2940–2952; discussion 2952.
Fernyhough JC, White JI, LaRocca H. Fusion rates in multilevel cervical spondylosis comparing allograft fibula with autograft fibula in 126 patients. Spine. 1991;16(10 suppl):S561–S564.
Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM, Kurz LT. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies: Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine. 1997;22:2807–2812.
Fleiss JL. Significance tests have a role in epidemiologic research: reactions to A. M. Walker. Am J Public Health. 1986;76:559–560.
Groth AT, Kuklo TR, Klemme WR, Polly DW, Schroeder TM. Comparison of sagittal contour and posterior disc height following interbody fusion: threaded cylindrical cages versus structural allograft versus vertical cages. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18:332–336.
Hashimoto T, Shigenobu K, Kanayama M, Harada M, Oha F, Ohkoshi Y, Tada H, Yamamoto K, Yamane S. Clinical results of single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion using the Brantigan I/F carbon cage filled with a mixture of local morselized bone and bioactive ceramic granules. Spine. 2002;27:258–262.
Kai Y, Oyama M, Morooka M. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using local facet joint autograft and pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 2004;29:41–46.
Kornblum MB, Fischgrund JS, Herkowitz HN, Abraham DA, Berkower DL, Ditkoff JS. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine. 2004;29:726–733; discussion 733–724.
Kroner AH, Eyb R, Lange A, Lomoschitz K, Mahdi T, Engel A. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 2006;31:1365–1371.
Kurz LT, Garfin SR, Booth RE Jr. Harvesting autogenous iliac bone grafts: a review of complications and techniques. Spine. 1989;14:1324–1331.
Kwon BK, Albert TJ. Adult low-grade acquired spondylolytic spondylolisthesis: evaluation and management. Spine. 2005;30(6 suppl):S35–S41.
La Rosa G, Cacciola F, Conti A, Cardali S, La Torre D, Gambadauro NM, Tomasello F. Posterior fusion compared with posterior interbody fusion in segmental spinal fixation for adult spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Focus. 2001;10:E9.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–174.
Lauber S, Schulte TL, Liljenqvist U, Halm H, Hackenberg L. Clinical and radiologic 2-4-year results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Spine. 2006;31:1693–1698.
Luczkiewicz P, Smoczynski A, Smoczynski M, Pankowski R, Piotrowski M. [The results of decompression and anterior lumbar interbody fusion with the use of interbody cages for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis] [in Polish]. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2006;71:173–175.
Ma GW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with specialized instruments. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;193:57–63.
Martin CR, Gruszczynski AT, Braunsfurth HA, Fallatah SM, O’Neil J, Wai EK. The surgical management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review. Spine. 2007;32:1791–1798.
Meyerding HW. Spondylolisthesis; surgical fusion of lumbosacral portion of spinal column and interarticular facets; use of autogenous bone grafts for relief of disabling backache. J Int Coll Surg. 1956;26:566–591.
Miura Y, Imagama S, Yoda M, Mitsuguchi H, Kachi H. Is local bone viable as a source of bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion? Spine. 2003;28:2386–2389.
Posner I, White AA 3rd, Edwards WT, Hayes WC. A biomechanical analysis of the clinical stability of the lumbar and lumbosacral spine. Spine. 1982;7:374–389.
Ray CD. Threaded fusion cages for lumbar interbody fusions: an economic comparison with 360 degrees fusions. Spine. 1997;22:681–685.
Ray CD. Threaded titanium cages for lumbar interbody fusions. Spine. 1997;22:667–679; discussion 679–680.
Santos ER, Goss DG, Morcom RK, Fraser RD. Radiologic assessment of interbody fusion using carbon fiber cages. Spine. 2003;28:997–1001.
Sarwat AM, O’Brien JP, Renton P, Sutcliffe JC. The use of allograft (and avoidance of autograft) in anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a critical analysis. Eur Spine J. 2001;10:237–241.
Sears W. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: restoration of sagittal balance using insert-and-rotate interbody spacers. Spine J. 2005;5:170–179.
Sears W. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lytic spondylolisthesis: restoration of sagittal balance using insert-and-rotate interbody spacers. Spine J. 2005;5:161–169.
Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: review of current trends and controversies. Spine. 2005;30:S71–S81.
Simmons JW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterior elements as chip grafts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;193:85–89.
Skowronski J, Wojnar J, Bielecki M. Interbody fusion and transpedicular fixation in the treatment of spondylolisthesis. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2007;9:149–155.
Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Lee JH, Cho KJ, Kim HG. Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1997;22:210–219; discussion 219–220.
Tullberg T, Brandt B, Rydberg J, Fritzell P. Fusion rate after posterior lumbar interbody fusion with carbon fiber implant: 1-year follow-up of 51 patients. Eur Spine J. 1996;5:178–182.
Umehara S, Zindrick MR, Patwardhan AG, Havey RM, Vrbos LA, Knight GW, Miyano S, Kirincic M, Kaneda K, Lorenz MA. The biomechanical effect of postoperative hypolordosis in instrumented lumbar fusion on instrumented and adjacent spinal segments. Spine. 2000;25:1617–1624.
Wimmer C, Krismer M, Gluch H, Ogon M, Stockl B. Autogenic versus allogenic bone grafts in anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;360:122–126.
Yamashita K, Hayashi J, Ohzono K, Hiroshima K. Correlation of patient satisfaction with symptom severity and walking ability after surgical treatment for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 2003;28:2477–2481.
Zhao J, Hou T, Wang X, Ma S. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using one diagonal fusion cage with transpedicular screw/rod fixation. Eur Spine J. 2003;12:173–177.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs.Yen for help with collecting the patient data, Dr. Tsai and Dr. Hsu for help in assessing the fusion status, and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors have received funding from NSC Grant NSC-2622 B 002-002 (PQC) and the Taiwan Spine Research Foundation (PQC).
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, CH., Wang, CT. & Chen, PQ. Instrumented Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Adult Spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466, 3034–3043 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0511-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0511-1