Abstract
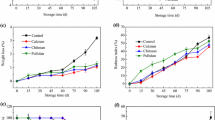
Rapid quality deterioration after harvest restricts the shelf life of broccoli, and reduces its commercial value. In this study, the effects of combined edible coating with chitosan and tea polyphenol (CTS + TP) on the post-harvest quality of broccoli were investigated. Results showed that the combined treatment of chitosan and tea polyphenol had better effects on the decay rate, weight loss rate, and respiratory intensity of broccoli than the single chitosan treatment and control. CTS + TP treatment mitigated the severity of broccoli yellowing, which was demonstrated by the higher hue angle, chlorophyll level, and strong red fluorescence emission of the treated samples, as well as delayed yellowing time compared to that observed in controls. Moreover, CTS + TP treatment better protected the sensory quality of the product, such as odor, hardness, and chewiness, and prevented evident changes. The vitamin C level in the treated samples was extremely higher, and the higher antioxidant capacity was also noted. The content of sulforaphane, the typical bioactive substance of broccoli, declined conspicuously in the yellowed broccoli, while the change was noticeably relieved by CTS + TP coating. The significantly upregulated expressions of BoCYP83A1, BoMYB28, and BoMYR in treated samples may have played an important role in the improvement of sulforaphane contents. These findings indicated that the edible coating with CTS + TP alleviated yellowing symptoms, improved the sensory quality, and enhanced the nutraceutical value of broccoli.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ali, A., Muhammad, M., Sijam, K., & Siddiqui, Y. (2011). Effect of chitosan coatings on the physicochemical characteristics of Eksotika II papaya (Carica papaya L.) fruit during cold storage. Food Chemistry, 124, 620–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.06.085
Alvarez, M. V., Ponce, A. G., del Moreira, M., & R. (2013). Antimicrobial efficiency of chitosan coating enriched with bioactive compounds to improve the safety of fresh cut broccoli. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 50, 78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.06.021
Alvarez-Jubete, L., Valverde, J., Kehoe, K., Reilly, K., Rai, D. K., & Barry-Ryan, C. (2014). Development of a novel functional soup rich in bioactive sulforaphane using broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. ssp. italica) florets and byproducts. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 1310–1321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1113-9
Bautista-Baños, S., Hernández-Lauzardo, A. N., Velázquez-del Valle, M. G., Hernández-López, M., Ait Barka, E., Bosquez-Molina, E., & Wilson, C. L. (2006). Chitosan as a potential natural compound to control pre and postharvest diseases of horticultural commodities. Crop Protection, 25, 108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2005.03.010
Cai, J. H., Cheng, S. C., Luo, F., Zhao, Y. B., Wei, B. D., Zhou, Q., Zhou, X., & Ji, S. J. (2019). Influence of ethylene on morphology and pigment changes in harvested broccoli. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12, 883–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02267-1
Cazón, P., Velazquez, G., Ramírez, J. A., & Vázquez, M. (2016). Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocolloids, 68, 136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.09.009
Chen, J., Zhang, S., & Yang, X. (2013). Control of brown rot on nectarines by tea polyphenol combined with tea saponin. Crop Protection, 45, 29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2012.11.006
Conversa, G., Lazzizera, C., Chiaravalle, A. E., Miedico, O., Bonasia, A., La Rotonda, P., & Elia, A. (2019). Selenium fern application and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi soil inoculation enhance Se content and antioxidant properties of green asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) spears. Scientia Horticulturae, 252, 176–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.03.056
Di Pentima, J. H., Rios, J. J., Clemente, A., & Olias, J. M. (1995). Biogenesis of off-odor in broccoli storage under low-oxygen atmosphere. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 43, 1310–1313. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00053a035
Eason, J. R., Ryan, D., Page, B., Watson, L., & Coupe, S. A. (2007). Harvested broccoli (Brassica oleracea) responds to high carbon dioxide and low oxygen atmosphere by inducing stress-response genes. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 43, 358–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.10.001
Falcó, I., Flores-Meraz, P. L., Randazzo, W., Sánchez, G., López-Rubio, A., & Fabra, M. J. (2019). Antiviral activity of alginate-oleic acid based coatings incorporating green tea extract on strawberries and raspberries. Food Hydrocolloids, 87, 611–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.08.055
Fang, H. X., Luo, F., Li, P. X., Zhou, Q., Zhou, X., Wei, B. D., Cheng, S. C., Zhou, H. S., & Ji, S. J. (2020). Potential of jasmonic acid (JA) in accelerating postharvest yellowing of broccoli by promoting its chlorophyll degradation. Food Chemistry, 309, 125737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125737
Franck, F., Juneau, P., & Popovic, R. (2002). Resolution of the photosystem I and photosystem II contributions to chlorophyll fluorescence of intact leaves at room temperature. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics, 1556, 239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(02)00366-3
Freitas, P. M., López-Gálvez, F., Tudela, J. A., Gil, M. I., & Allende, A. (2015). Postharvest treatment of table grapes with ultraviolet-C and chitosan coating preserves quality and increases stilbene content. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 105, 51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.03.011
Ghaouth, A., Arul, J., Ponnampalam, R., & Boulet, M. (2010). Use of chitosan coating to reduce water loss and maintain quality of cucumber and bell pepper fruits. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 15, 359–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4549.1991.tb00178.x
Gillespie, K. M., & Ainsworth, E. A. (2007). Measurement of reduced, oxidized and total ascorbate content in plants. Nature Protocols, 2, 871–874. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.101
Guo, L., Yang, R., & Gu, Z. (2016). Cloning of genes related to aliphatic glucosinolate metabolism and the mechanism of sulforaphane accumulation in broccoli sprouts under jasmonic acid treatment. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 96, 4329–4336. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7629
Guo, L., Zhu, Y., & Wang, F. (2018). Calcium sulfate treatment enhances bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity in broccoli sprouts during growth and storage. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 139, 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.01.010
Han, C., Zuo, J., Wang, Q., Xu, L., Zhai, B., Wang, Z., Dong, H., & Gao, L. (2014). Effects of chitosan coating on postharvest quality and shelf life of sponge gourd (Luffa cylindrica) during storage. Scientia Horticulturae, 166, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.09.007
Hansen, M. E., Srensen, H., & Cantwell, M. (2001). Changes in acetaldehyde, ethanol and amino acid concentrations in broccoli florets during air and controlled atmosphere storage. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 22, 227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(01)00093-X
Hong, K., Xie, J., Zhang, L., Sun, D., & Gong, D. (2012). Effects of chitosan coating on postharvest life and quality of guava (Psidium guajava L.) fruit during cold storage. Scientia Horticulturae, 144, 172–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.07.002
Jin, P., Yao, D., Xu, F., Wang, H., & Zheng, Y. (2015). Effect of light on quality and bioactive compounds in postharvest broccoli florets. Food Chemistry, 172, 705–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.134
Ku, K. M., Choi, J. H., Kim, H. S., Kushad, M. M., Jeffery, E. H., & Juvik, J. A. (2013). Methyl jasmonate and 1-methylcyclopropene treatment effects on quinone reductase inducing activity and post-harvest quality of broccoli. PLoS ONE, 8, e77127. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077127
Liang, H., Yuan, Q. P., Dong, H. R., & Liu, Y. M. (2006). Determination of sulforaphane in broccoli and cabbage by high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 19(5), 473–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2005.11.005
Lichtenthaler, H. K. (1987). Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods in Enzymology, 148, 350–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Lv, J., Wu, J., Zuo, J., Fan, L., Shi, J., Gao, L., Li, M., & Wang, Q. (2017). Effect of Se treatment on the volatile compounds in broccoli. Food Chemistry, 216, 225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.005
Martín-Diana, A. B., Rico, D., & Barry-Ryan, C. (2008). Green tea extract as a natural antioxidant to extend the shelf-life of fresh-cut lettuce. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 9, 593–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2008.04.001
Matusheski, N. V., Swarup, R., Juvik, J. A., Mithen, R., Bennett, M., & Jeffery, E. H. (2006). Epithiospecifier protein from broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. ssp. italica) inhibits formation of the anticancer agent sulforaphane. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 2069–2076. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0525277
Molamohammadi, H., Pakkish, Z., Akhavan, H. R., & Saffari, V. R. (2020). Effect of salicylic acid incorporated chitosan coating on shelf life extension of fresh in-hull pistachio fruit. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13, 121–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02383-y
Möller, H., Grelier, S., Pardon, P., & Coma, V. (2004). Antimicrobial and physicochemical properties of chitosan−HPMC-based films. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52, 6585–6591. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0306690
Moreira, M. R., Ponce, A., Ansorena, R., & Roura, S. I. (2011a). Effectiveness of edible coatings combined with mild heat shocks on microbial spoilage and sensory quality of fresh cut broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.). Journal of Food Science, 76, M367–M374. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02210.x
Moreira, M. R., Roura, S. I., & Ponce, A. (2011b). Effectiveness of chitosan edible coatings to improve microbiological and sensory quality of fresh cut broccoli. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 44, 2335–2341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2011.04.009
Mustafa, M. A., Ali, A., Manickam, S., & Siddiqui, Y. (2014). Ultrasound-assisted chitosan–surfactant nanostructure assemblies: Towards maintaining postharvest quality of tomatoes. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 2102–2111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1173-x
Olivas, G. I., & Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V. (2005). Edible coatings for fresh-cut fruits. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 45, 657–670. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690490911837
Petriccione, M., Sanctis, F. D., Pasquariello, M. S., Mastrobuoni, F., Rega, P., Scortichini, M., & Mencarelli, F. (2015). The effect of chitosan coating on the quality and nutraceutical traits of sweet cherry during postharvest life. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 394–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1411-x
Pružinská, A., Anders, I., Aubry, S., Schenk, N., Tapernoux-Lüthi, E., Müller, T., Kräutler, B., & Hörtensteiner, S. (2007). In vivo participation of red chlorophyll catabolite reductase in chlorophyll breakdown. The Plant Cell, 19, 369–387. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.044404
Raseetha, S., Leong, S. Y., Burritt, D. J., & Oey, I. (2013). Understanding the degradation of ascorbic acid and glutathione in relation to the levels of oxidative stress biomarkers in broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. italica cv. Bellstar) during storage and mechanical processing. Food Chemistry, 138, 1360–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.126
Ribeiro, A. M., Estevinho, B. N., & Rocha, F. (2020). Preparation and incorporation of functional ingredients in edible films and coatings. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14, 209–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02528-4
Romanazzi, G., Feliziani, E., Baños, S. B., & Sivakumar, D. (2015). Shelf life extension of fresh fruit and vegetables by chitosan treatment. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 57, 579–601. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2014.900474
Rybarczyk-Plonska, A., Hagen, S. F., Borge, G. I. A., Bengtsson, G. B., Hansen, M. K., & Wold, A.-B. (2016). Glucosinolates in broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica) as affected by postharvest temperature and radiation treatments. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 116, 16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.12.010
Sánchez-Vega, R., Elez-Martínez, P., & Martín-Belloso, O. (2014). Effects of high-intensity pulsed electric fields processing parameters on the chlorophyll content and its degradation compounds in broccoli juice. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 1137–1148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1152-2
Sarabandi, K., & Mahdi Jafari, S. (2019). Effect of chitosan coating on the properties of nanoliposomes loaded with flaxseed-peptide fractions: stability during spray-drying. Food Chemistry, 310, 125951.1–125951.10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125951
Shi, J., Gao, L., Zuo, J., Wang, Q., Wang, Q., & Fan, L. (2016). Exogenous sodium nitroprusside treatment of broccoli florets extends shelf life, enhances antioxidant enzyme activity, and inhibits chlorophyll-degradation. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 116, 98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.01.007
Soares, A., Carrascosa, C., & Raposo, A. (2017). Influence of different cooking methods on the concentration of glucosinolates and vitamin C in broccoli. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10, 1387–1411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1930-3
Tharanathan, R. N. (2003). Biodegradable films and composite coatings: Past, present and future. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 14, 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-2244(02)00280-7
Traka, M. H., Saha, S., Huseby, S., Kopriva, S., Walley, P. G., Barker, G. C., Moore, J., Mero, G., Bosch, F., Constant, H., Kelly, L., Schepers, H., Boddupalli, S., & Mithen, R. F. (2013). Genetic regulation of glucoraphanin accumulation in Beneforté® broccoli. New Phytologist, 198, 1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12232
Vilaplana, R., Guerrero, K., Guevara, J., & Valencia-Chamorro, S. (2020). Chitosan coatings to control soft mold on fresh blackberries (Rubus glaucus Benth.) during postharvest period. Scientia Horticulturae, 262, 109049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.109049
Wang, L., Yan, D., Men, H., Jin, T., & Jiang, Z. (2013). Preparation and characterization of active films based on chitosan incorporated tea polyphenols. Food Hydrocolloids, 32, 35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.11.034
Wang, Y., Wang, J. C., Zhu, G. P., Han, P. I., & Liu, Y. W. (2019). Research progress of application of tea polyphenols degradable composite films in food preservation. Packaging Engineering, 40, 97–103. https://doi.org/10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2019.13.014
Wu, H., Wang, D., Shi, J., Xue, S., & Gao, M. (2010). Effect of the complex of zinc (II) and cerium (IV) with chitosan on the preservation quality and degradation of organophosphorus pesticides in Chinese Jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Mill. cv. Dongzao). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 5757–5762. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf100537k
Yang, C. S., Lambert, J. D., & Sang, S. (2009). Antioxidative and anti-carcinogenic activities of tea polyphenols. Archives of Toxicology, 83, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0372-0
Zhang, X. T., Zhang, M., Devahastin, S., & Guo, Z. (2019). Effect of combined ultrasonication and modified atmosphere packaging on storage quality of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12, 1573–1583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02316-9
Zhao, B. (2006). The health effects of tea polyphenols and their antioxidant mechanism. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 38, 59–68. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.38.59
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China [grant number 2016YFD0400103].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huixin Fang: investigation, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, visualization. Qian Zhou: conceptualization, validation, resources. Qingxi Yang: conceptualization, methodology. Xin Zhou: investigation, supervision. Shunchang Cheng: resources, conceptualization. Baodong Wei: resources, software. Jiangkuo Li: resources. Shujuan Ji: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, H., Zhou, Q., Yang, Q. et al. Influence of Combined Edible Coating with Chitosan and Tea Polyphenol on the Quality Deterioration and Health-promoting Compounds in Harvested Broccoli. Food Bioprocess Technol 15, 407–420 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02751-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02751-7