Abstract
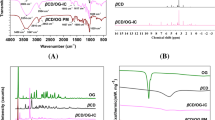
This work aimed to investigate the improvement of the performance of edible films based on tapioca starch containing natamycin and nisin, by the addition of zein. For that purpose, the effects on the physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of the developed films were evaluated. Results indicated that the addition of zein changed physicochemical properties, without altering the antimicrobial bioavailability of the films. The addition of zein improved the mechanical properties of the films, increasing the firmness at break and reducing the strain at break and also turned the films more yellow. Even more, in the presence of antimicrobials, the zein reduced water vapor permeability and water solubility and increased hydrophobicity.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article
References
Argüello-García, E., Solorza-Feria, J., Rendón-Villalobos, J. R., Rodríguez-Gonz, F., Jiménez-Pérez, A., & Flores-Huicochea, E. (2014). Properties of edible films based on oxidized starch and zein. International Journal of Polymer Science, 12(8), 773–781.
Balaguer, M., Fajardo, P., Gartner, H., Gomez-Estaca, J., Gavara, R., Almenar, E., & Hernandez-Munoz, P. (2014). Functional properties and antifungal activity of films based on gliadins containing cinnamaldehyde and natamycin. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 173, 62–71.
Basiak, E., Lenart, A., & Debeaufort, F. (2018). How glycerol and water contents affect the structural and functional properties of starch-based edible films. Polymers, 10(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040412.
Campos, C., Gerschenson, L., & Flores, S. (2011). Development of edible films and coatings with antimicrobial activity. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 4(6), 849–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0434-1.
Chen, X., Cui, F., Zi, H., Zhou, Y., Liu, H., & Xiao, J. (2019). Development and characterization of a hydroxypropyl starch/zein bilayer edible film. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 141, 1175–1182.
Choi, W., & Han, J. (2002). Film-forming mechanism and heat denaturation effects on the physical and chemical properties of pea-protein-isolate edible films. Journal of Food Science, 67(4), 1399–1406. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb10297.x.
Corradini, E., Souto, E., Carvalho, A., Curvelo, A., & Mattoso, L. (2006). Mechanical and morphological characterization of starch/zein blends plasticized with glycerol. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 101(6), 4133–4139.
Dean, K. M., Do, M. D., Petinakis, E., & Yu, L. (2008). Key interactions in biodegradable thermoplastic starch/poly(vinyl alcohol)/montmorillonite micro- and nanocomposites. Composites Science and Technology, 68(6), 1453–1462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.10.037
Dehnad, D., Emam-Djomeh, Z., Mirzaei, H., Jafari, S., & Dadashi, S. (2014). Optimization of physical and mechanical properties for chitosan-nanocellulose biocomposites. Carbohydrate Polymers, 105(1), 222–228.
Faradilla, R. H. F., Lee, G., Roberts, J., Martens, P., Stenzel, M., & Arcot, J. (2018). Effect of glycerol, nanoclay and graphene oxide on physicochemical properties of biodegradable nanocellulose plastic sourced from banana pseudo-stem. Cellulose, 25(1), 399–416.
Farajpour, R., Djomeh, Z. E., Moeini, S., Tavahkolipour, H., Safayan, S., Emam Djomeh, Z., et al. (2020). Structural and physico-mechanical properties of potato starch-olive oil edible films reinforced with zein nanoparticles. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 149, 941–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.175.
FDA. (2018). Food additive status list. In U. S. Food and Drug Administration.
Ge, L., Zhu, M., Xu, Y., Li, X., Li, D., & Mu, C. (2017). Development of antimicrobial and controlled biodegradable gelatin-based edible films containing nisin and amino-functionalized montmorillonite. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(9), 1727–1736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1941-0.
Gennadios, A., Weller, C., & Gooding, C. (1994). Measurement errors in water vapor permeability of highly permeable, hydrophilic edible films. Journal of Food Engineering, 21(4), 395–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/0260-8774(94)90062-0.
Gontard, N., Guilbert, S., & Cuq, J. (1992). Edible wheat gluten films: influence variables on film properties using methodology of the main process response surface. Journal of Food Science, 57(1), 190–195.
Guo, X., Lu, Y., Cui, H., Jia, X., Bai, H., & Ma, Y. (2012). Factors affecting the physical properties of edible composite film prepared from zein and wheat gluten. Molecules, 17(4), 3794–3804.
Habeych, E., van der Goot, A. J., & Boom, R. (2007). Prediction of permeation fluxes of small volatile components through starch-based films. Carbohydrate Polymers, 68(3), 528–536.
Han, J. (2014). A review of food packaging technologies and innovations. In J. Han (Ed.), Innovations in food packaging (Second Edi., pp. 3–12). San Diego, USA: Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394601-0.00001-1
Jiang, Y., Li, F., Li, D., Sun-Waterhouse, D., & Huang, Q. (2019). Zein/pectin nanoparticle-stabilized sesame oil pickering emulsions: sustainable bioactive carriers and healthy alternatives to sesame paste. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(12), 1982–1992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02361-4.
Jiménez, A., Fabra, M. J., Talens, P., & Chiralt, A. (2012). Edible and biodegradable starch films: a review. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(6), 2058–2076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0835-4.
Küçük, G. S., Çelik, Ö. F., Mazi, B. G., & Türe, H. (2020). Evaluation of alginate and zein films as a carrier of natamycin to increase the shelf life of kashar cheese. Packaging Technology and Science, 33(1), 39–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/pts.2483.
Li, C., Wu, K., Su, Y., Riffat, S. B., Ni, X., & Jiang, F. (2019). Effect of drying temperature on structural and thermomechanical properties of konjac glucomannan-zein blend films. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 138, 135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.007.
Martins, J., Cerqueira, M., Souza, B., Carmo Avides, M., & Vicente, A. (2010). Shelf life extension of ricotta cheese using coatings of galactomannans from nonconventional sources incorporating nisin against Listeria monocytogenes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(3), 1884–1891. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf902774z.
Muscat, D., Adhikari, R., McKnight, S., Guo, Q., & Adhikari, B. (2013). The physicochemical characteristics and hydrophobicity of high amylose starch–glycerol films in the presence of three natural waxes. Journal of Food Engineering, 119(2), 205–219.
Ochoa, T. A., García-Almendárez, B. E., Reyes, A. A., Pastrana, D. M. R., López, G. F. G., Belloso, O. M., & González, C. R. (2017). Design and characterization of corn starch edible films including beeswax and natural antimicrobials. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(1), 103–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1800-4.
Ollé Resa, C. P., Gerschenson, L. N., & Jagus, R. J. (2013). Effect of natamycin on physical properties of starch edible films and their effect on Saccharomyces cerevisiae activity. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(11), 3124–3133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0960-0.
Ollé Resa, C. P., Gerschenson, L. N., & Jagus, R. J. (2014a). Natamycin and nisin supported on starch edible films for controlling mixed culture growth on model systems and Port Salut cheese. Food Control, 44, 146–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.03.054.
Ollé Resa, C. P., Jagus, R. J., & Gerschenson, L. N. (2014b). Effect of natamycin, nisin and glycerol on the physicochemical properties, roughness and hydrophobicity of tapioca starch edible films. Materials Science and Engineering C, 40, 281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.04.005.
Oymaci, P., & Altinkaya, S. A. (2016). Improvement of barrier and mechanical properties of whey protein isolate based food packaging films by incorporation of zein nanoparticles as a novel bionanocomposite. Food Hydrocolloids, 54, 1–9.
Rachtanapun, P., & Rattanapanone, N. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl cellulose powder and films from Mimosa pigra. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 122(5), 3218–3226.
Samsalee, N., & Sothornvit, R. (2019). Development and characterization of porcine plasma protein-chitosan blended films. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 22(April 2018), 100406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100406.
Samsalee, N., & Sothornvit, R. (2020). Characterization of food application and quality of porcine plasma protein–based films incorporated with chitosan or encapsulated turmeric oil. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(3), 488–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02411-2.
Sessa, J., Eller, F. J., Palmquist, D. E., & Lawton, J. W. (2003). Improved methods for decolorizing corn zein. Idustrial Crops and Products, 18(1), 55–65.
Shiroodi, S. G., Nesaei, S., Ovissipour, M., Al-Qadiri, H. M., Rasco, B., & Sablani, S. (2016). Biodegradable polymeric films incorporated with nisin: characterization and efficiency against Listeria monocytogenes. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9(6), 958–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1684-3.
Sothornvit, R., & Krochta, J. M. (2005). Plasticizers in edible films and coatings. Innovations in Food Packaging, 403–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012311632-1/50055-3.
Tang, C., & Jiang, Y. (2007). Modulation of mechanical and surface hydrophobic properties of food protein films by transglutaminase treatment. Food Research International, 40(4), 504–509.
Teklehaimanot, W., Taylor, J., & Emmambux, M. (2016). Formation and properties of aqueous compatible colloidal blends between pre-gelatinized maize starch and zein. Journal of Cereal Science, 68, 74–81.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2015). Chapter 1 Food and drugs administration, Subchapter B Food for human consumption, Part 184 Direct food substances affirmed as generally recognized as safe, Subpart B Listing of Specific Sub- stances Affirmed as GRAS, 184.1984-Zein. In Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 Food and Drugs.
Vu, H., & Lumdubwong, N. (2016). Starch behaviors and mechanical properties of starch blend films with different plasticizers. Carbohydrate Polymers, 154, 112–120.
Yemenicioğlu, A. (2016). Zein and its composites and blends with natural active compounds: development of antimicrobial films for food packaging. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging (pp. 503–513).
Zhang, S., & Zhao, H. (2017). Preparation and properties of zein–rutin composite nanoparticle/corn starch films. Carbohydrate Polymers, 169, 385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.044.
Zuo, G., Song, X., Chen, F., & Shen, Z. (2019). Physical and structural characterization of edible bilayer films made with zein and corn-wheat starch. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 18(3), 324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2017.09.005.
Soliman, E., Mohy Eldin, M., & Furuta, M. (2009). Biodegradable zein-based films: influence of gamma-irradiation on structural and functional properties. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57(6), 2529–35.
Trezza, T., & Krochta, J. (2000). Color Stability of Edible Coatings During Prolonged Storage. Journal of Food Science, 65(1), 1166–1169.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Industrias del Maíz S.A. (Argentina), DSM (Argentina), and Bill Driessen from ARTESA LLC (USA).
Funding
This study was financially supported by the University of Buenos Aires (UBACyT20020170100063BA and 20020170100229BA) and National Agency of Scientific and Technical Research (PICT2015 No. 2109 and PICT2015 No. 2742).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by all authors. The manuscript was written and commented by all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Code Availability
The software used for statistical calculus is open access: Apache OpenOffice Calc., SPSS version 15 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez, P.F., Ollé Resa, C.P., Gerschenson, L.N. et al. Addition of Zein for the Improvement of Physicochemical Properties of Antimicrobial Tapioca Starch Edible Film. Food Bioprocess Technol 14, 262–271 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02565-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02565-z