Abstract
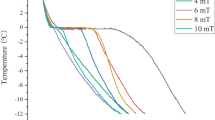
A number of novel freezing systems have been developed that claim to improve the quality of frozen foods by enhancing supercooling in the food prior to ice nucleation and consequently controlling ice crystal formation. One of these is the Cells Alive System (CAS) produced by ABI of Japan, which applies oscillating magnetic fields (OMF) during freezing. This study was carried out to investigate what effect applying OMF (0.04 to 0.53 mT) during freezing had on the freezing characteristics of pork loin samples when compared to freezing under the same conditions without OMF. Overall, the results of this study clearly indicate that freezing under the OMF conditions used in these experiments had no significant effect on the freezing characteristics of pork, in comparison with freezing under the same conditions without OMF.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedini, S., Kaku, M., Kawata, T., Koseki, H., Kojima, S., Sumi, H., Motokawa, M., Fujita, T., Ohtani, J., Ohwada, N., & Tanne, K. (2011). Effects of cryopreservation with a newly-developed magnetic field programmed freezer on periodontal ligament cells and pulp tissues. Cryobiology, 62, 181–187.
Choi, Y. S., Ku, S. K., Jeong, J. Y., Jeon, K. H., & Kim, Y. B. (2015). Changes in ultrastructure and sensory characteristics on electro-magnetic and air blast freezing of beef during frozen storage. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 35, 27–34.
Commission Internationale de L’Éclairage (1976). CIE Colorimetry — Part 4: 1976 L*a*b* Color Space. Commission Internationale de L’Éclairage.
Cowell, N. D., & Namor, M. S. S. (1974). Heat transfer coefficients in plate freezing—effect of packaging materials. Proc. of I.I.R. Meetings of Commissions B1, C1 and C2. Bressanone, Italy, Sept., 17–20.
Huff-Lonergan, E., & Lonergan, S. M. (2005). Mechanisms of water-holding capacity of meat: the role of post-mortem biochemical and structural changes. Meat Science, 71, 194–204.
James, C., Purnell, G., & James, S. J. (2015a). A review of novel and innovative freezing technologies. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 1616–1634.
James, C., Reitz, B. G., & James, S. J. (2015b). The freezing characteristics of garlic bulbs (Allium sativum L.) frozen conventionally or with the assistance of an oscillating weak magnetic field. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(3), 702–708.
James, C., Purnell, G., & James, S. J. (2015c). Can magnetism improve the storage of foods. New Food, 18(2), 40–43.
Jiang, S. T., & Lee, T. C. (2005). Freezing seafood and seafood products: principles and applications. In Y. H. Hui (Ed.), Handbook of food science, technology, and Engineering (pp. 39-1–39-35). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kaku, M., Kamada, H., Kawata, T., Koseki, H., Abedini, S., Kojima, S., Motokawa, M., Fujita, T., Ohtani, J., Tsuka, N., Matsuda, Y., Sunagawa, H., Hernandes, R. A. M., Ohwada, N., & Tanne, K. (2010). Cryopreservation of periodontal ligament cells with magnetic field for tooth banking. Cryobiology, 61, 73–78.
Kaku, M., Kawata, T., Abedini, S., Koseki, H., Kojima, S., Sumi, H., Shikata, H., Motokawa, M., Fujita, T., Ohtani, J., Ohwada, N., Kurita, M., & Tanne, K. (2012). Electric and magnetic fields in cryopreservation: a response. Cryobiology, 64, 304–305.
Kim, Y. B., Jeong, J. Y., Ku, S. K., Kim, E. M., Park, K. J., & Jang, A. (2013a). Effects of various thawing methods on the quality characteristics of frozen beef. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 33(6), 723–729.
Kim, Y. B., Woo, S. M., Jeong, J. Y., Ku, S. K., Jeong, J. W., Kum, J. S., & Kim, E. M. (2013b). Temperature changes during freezing and effect of physicochemical properties after thawing on meat by air blast and magnetic resonance quick freezing. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 33(6), 763–771.
Ku, S. K., Jeong, J. Y., Park, J. D., Jeon, K. H., Kim, E. M., & Kim, Y. B. (2014). Quality evaluation of pork with various freezing and thawing methods. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 34(5), 597–603.
Mok, J. H., Choi, W., Park, S. H., Lee, S. H., & Jun, S. (2015). Emerging pulsed electric field (PEF) and static magnetic field (SMF) combination technology for food freezing. International Journal of Refrigeration, 50, 137–145.
Naito, M., Hirai, S., Mihara, M., Terayama, H., Hatayama, N., Hayashi, S., Matsushita, M., & Itoh, M. (2012). Effect of a magnetic field on drosophila under supercooled conditions. PloS One, 7.
Nakagawa, T., Mihara, M., Noguchi, S., Fujii, K., Ohwada, T., Niino, T., Sato, I., Yamashita, H., Masamune, K., & Dohi, T. (2012). Development of pathology specimen preparation method by supercooling cryopreservation under magnetic field. Academic Collaborations for Sick Children, 5, 21–27.
Ngapo, T. M., Babare, I. H., Reynolds, J., & Mawson, R. F. (1999). Freezing and thawing rate effects on drip loss from samples of pork. Meat Science, 53(3), 149–158.
Otero, L., Rodríguez, A. C., Pérez-Mateos, M., & Sanz, P. D. (2016). Effects of magnetic fields on freezing: application to biological products. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 15(3), 646–667.
Otero, L., Pérez-Mateos, M., Rodríguez, A. C., & Sanz, P. D. (2017). Electromagnetic freezing: effects of weak oscillating magnetic fields on crab sticks. Journal of Food Engineering, 200, 87–94.
Owada, N. (2007). Highly-efficient freezing apparatus and highly-efficient freezing method. United States Patent US 7,237,400B2.
Owada, N., & Kurita, S. (2001). Super-quick freezing method and apparatus therefor. United States Patent US 2001/6250087B1.
Pérez Chabela, M. L., & Mateo-Oyague, J. (2006). Frozen meat: Quality and shelf life. In Y. H. Hui (Ed.), Handbook of food science, technology, and Engineering (pp. 115-1–115-9). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Suzuki, T., Takeuchi, Y., Masuda, K., Watanabe, M., Shirakashi, R., Fukuda, Y., Tsuruta, T., Yamamoto, K., Koga, N., Hiruma, N., Ichioka, J., & Takai, K. (2009). Experimental investigation of effectiveness of magnetic field on food freezing process. Transactions of the Japan Society of Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers, 26, 371–386.
Watanabe, M., Kanesaka, N., Masuda, K., & Suzuki, T. (2011). Effect of oscillating magnetic field on supercooling in food freezing. Proceedings of the 23 rd IIR International Congress of Refrigeration; refrigeration for sustainable development, August 21–26, Prague, Czech Republic. 1, 2892–2899.
Woo, M. W., & Mujumdar, A. S. (2010). Effects of electric and magnetic field on freezing and possible relevance in freeze drying. Drying Technology, 28, 433–443.
Wowk, B. (2012). Electric and magnetic fields in cryopreservation. Cryobiology, 64, 301–303.
Yamamoto, N., Tamura, S., Matsushita, J., & Ishimura, K. (2005). Fracture properties and microstructure of chicken breasts frozen by electromagnetic freezing. Journal of Home Economics of Japan, 56(3), 141–151.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Spanish MINECO through the Project AGL2012-39756-C02-01. A. C. Rodríguez has been supported by a grant from Spanish MINECO for the carrying out of a brief stay in a R & D centre, as an additional action to the pre-doctoral contract BES-2013-065942 from MINECO, jointly financed by the European Social Fund, in the framework of the National Program for the Promotion of Talent and its Employability (National Sub-Program for Doctors Training). We would also like to acknowledge Air Products for supporting the supervisory costs of C. James and S. J. James at FRPERC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, A.C., James, C. & James, S.J. Effects of Weak Oscillating Magnetic Fields on the Freezing of Pork Loin. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 1615–1621 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1931-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1931-2