Abstract
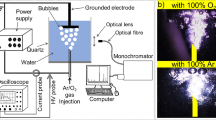
In this study, a gliding arc discharge (GAD) microplasma system was designed, and its decontamination effect was investigated on stainless steel (SS), silicone (Si), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) surfaces artificially contaminated with 8.15 ± 0.28 log cfu/mL of Escherichia coli and 6.18 ± 0.21 log cfu/mL of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Each of the contaminated surfaces was treated with high purity air (79% nitrogen and 21% oxygen) or nitrogen plasmas for 1–10 min at varying rates of gas flow. Significant reductions of 3.76 ± 0.28, 3.19 ± 0.31, and 2.95 ± 0.94 log cfu/mL in S. epidermidis, and 2.72 ± 0.82, 4.43 ± 0.14, and 3.18 ± 0.96 log cfu/mL in E. coli on SS, Si, and PET surfaces, respectively, were achieved after 5 min of plasma treatment by using nitrogen as the plasma forming gas (p < 0.05). The temperature changes of each surface during plasma generation were lower than 35 °C and were not affected by the type of plasma forming gas. Additionally, morphological changes in the structure of E. coli and S. epidermidis after GAD plasma treatments were demonstrated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramzon, N., Joaquin, J. C., Bray, J., & Brelles-Marino, G. (2006). Biofilm destruction by RF high-pressure cold plasma jet. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 34(4), 1304–1309.
Akdogan, E., & Mutlu, M. (2012). Generation of amphoteric surfaces via glow-discharge technique with single precursor and the behavior of bovine serum albumin at the surface. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces, 89, 289–294.
Atlas, R. M. (1995). Principles of microbiology. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book, Inc.
Bayliss, D. L., Walsh, J. L., Iza, F., Shama, G., Holah, J., & Kong, M. G. (2012). Complex responses of microorganisms as a community to a flowing atmospheric plasma. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 9(6), 597–611.
Biederman, H., Boyaci, I. H., Bilkova, P., Slavinska, D., Mutlu, S., Zemek, J., et al. (2001). Characterization of glow-discharge-treated cellulose acetate membrane surfaces for single-layer enzyme electrode studies. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 81(6), 1341–1352.
Boudam, M. K., Moisan, M., Saoudi, B., Popovici, C., Gherardi, N., & Massines, F. (2006). Bacterial spore inactivation by atmospheric-pressure plasmas in the presence or absence of UV photons as obtained with the same gas mixture. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 39(16), 3494–3507.
Burlica, R., Grim, R. G., Shih, K. Y., Balkwill, D., & Locke, B. R. (2010). Bacteria inactivation using low power pulsed gliding arc discharges with water spray. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 7(8), 640–649.
Cokeliler, D., Caner, H., Zemek, J., Choukourov, A., Biederman, H., & Mutlu, M. (2007). A plasma polymerization technique to overcome cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections. Biomedical Materials, 2(1), 39–47.
Dasan, B. G., Boyaci, I. H., & Mutlu, M. (2016a). Inactivation of aflatoxigenic fungi (Aspergillus spp.) on granular food model, maize, in an atmospheric pressure fluidized bed plasma system. Food Control, 70, 1–8.
Dasan, B. G., Mutlu, M., & Boyaci, I. H. (2016b). Decontamination of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus spores on hazelnuts via atmospheric pressure fluidized bed plasma reactor. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 216, 50–59.
Diatczyk, J., Komarzyniec, G., & Stryczewska, H. D. (2011). Power consumption of gliding arc discharge plasma reactor. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5, 12–16.
Fernandez, A., & Thompson, A. (2012). The inactivation of Salmonella by cold atmospheric plasma treatment. Food Research International, 45(2), 678–684.
Fridman, A. (2008). Plasma biology and plasma medicine. In Plasma chemistry (pp. 848–913): Cambrigde University Press.
Graves, D. B. (2012). The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 45(26). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/45/26/263001.
Gunaydin, B., Sir, N., Kavlak, S., Guner, A., & Mutlu, M. (2010). A new approach for the electrochemical detection of phenolic compounds. Part I: modification of graphite surface by plasma polymerization technique and characterization by Raman spectroscopy. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3(3), 473–479.
Guven, B., Basaran-Akgul, N., Temur, E., Tamer, U., & Boyaci, I. H. (2011). SERS-based sandwich immunoassay using antibody coated magnetic nanoparticles for Escherichia coli enumeration. Analyst, 136(4), 740–748.
Hertwig, C., Reineke, K., Ehlbeck, J., Knorr, D., & Schlüter, O. (2015). Decontamination of whole black pepper using different cold atmospheric pressure plasma applications. Food Control, 55, 221–229.
Hury, S., Vidal, D. R., Desor, F., Pelletier, J., & Lagarde, T. (1998). A parametric study of the destruction efficiency of Bacillus spores in low pressure oxygen-based plasmas. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 26(6), 417–421.
Ibis, F., Oflaz, H., & Ercan, U. K. (2016). Biofilm inactivation and prevention on common implant material surfaces by non-thermal DBD plasma treatment. Plasma Medicine, 6(1), 33–45.
Kamgang-Youbi, G., Herry, J. M., Meylheuc, T., Brisset, J. L., Bellon-Fontaine, M. N., Doubla, A., et al. (2009). Microbial inactivation using plasma-activated water obtained by gliding electric discharges (vol 48, pg 13, 2009). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 49(2), 292–292.
Komarzyniec, G., Diatczyk, J., & Stryczewska, H. D. (2006). Arc plasma reactor power system with 5-limb transformer. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 9(2), 178–181.
Korachi, M., & Aslan, N. (2013). Low temperature atmospheric plasma for microbial decontamination. In A. Méndez-Vilas (Ed.), Microbial pathogens and strategies for combating them: science, technology and education (Vol. 1, pp. 453–459). Badajoz: Formatex.
Laroussi, M. (2002). Nonthermal decontamination of biological media by atmospheric-pressure plasmas: review, analysis, and prospects. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 30(4), 1409–1415.
Laroussi, M., & Leipold, F. (2004). Evaluation of the roles of reactive species, heat, and UV radiation in the inactivation of bacterial cells by air plasmas at atmospheric pressure. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 233(1–3), 81–86.
Laroussi, M., Mendis, D. A., & Rosenberg, M. (2003). Plasma interaction with microbes. New Journal of Physics, 5, 1–41.
Laroussi, M., Richardson, J. P., & Dobbs, F. C. Biochemical pathways in the interaction of non-equilibrium plasmas with bacteria. In Proc. Electromed, Portsmouth, VA, 2001 (pp. 33–34.)
Laroussi, M., Sayler, G. S., Glascock, B. B., McCurdy, B., Pearce, M. E., Bright, N. G., et al. (1999). Images of biological samples undergoing sterilization by a glow discharge at atmospheric pressure. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 27(1), 34–35.
Ma, Y., Zhang, G. J., Shi, X. M., Xu, G. M., & Yang, Y. (2008). Chemical mechanisms of bacterial inactivation using dielectric barrier discharge plasma in atmospheric air. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), 1615–1620.
Mai-Prochnow, A., Murphy, A. B., McLean, K. M., Kong, M. G., & Ostrikov, K. (2014). Atmospheric pressure plasmas: infection control and bacterial responses. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 43(6), 508–517.
Menashi, W. P. (1968). Treatment of surfaces. US.
Misra, N. N., Tiwari, B. K., Raghavarao, K. S. M. S., & Cullen, P. J. (2011). Nonthermal plasma inactivation of food-borne pathogens. Food Engineering Reviews, 3(3–4), 159–170.
Moisan, M., Barbeau, J., Crevier, M. C., Pelletier, J., Philip, N., & Saoudi, B. (2002). Plasma sterilization. Methods mechanisms. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 74(3), 349–358.
Moisan, M., Barbeau, J., Moreau, S., Pelletier, J., Tabrizian, M., & Yahia, L. H. (2001). Low-temperature sterilization using gas plasmas: a review of the experiments and an analysis of the inactivation mechanisms. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 226(1–2), 1–21.
Montie, T. C., Kelly-Wintenberg, K., & Roth, J. R. (2000). An overview of research using the one atmosphere uniform glow discharge plasma (OAUGDP) for sterilization of surfaces and materials. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 28(1), 41–50.
Moreau, M., Feuilloley, M. G. J., Orange, N., & Brisset, J. L. (2005). Lethal effect of the gliding arc discharges on Erwinia spp. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 98(5), 1039–1046.
Moreau, M., Feuilloley, M. G. J., Veron, W., Meylheuc, T., Chevalier, S., Brisset, J. L., et al. (2007). Gliding arc discharge in the potato pathogen Erwinia carotovora subsp atroseptica: mechanism of lethal action and effect on membrane-associated molecules. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(18), 5904–5910.
Mutlu, M., Mutlu, S., Boyaci, I. H., Alp, B., & Piskin, E. (1998). High-linearity glucose enzyme electrodes for food industries: preparation by a plasma polymerization technique. Polymers in Sensors, 690, 57–65.
Nehra, V., Kumar, A., & Dwivedi, H. K. (2008). Atmospheric non-thermal plasma sources. International Journal of Engineering (IJE), 2(1), 53–68.
Niemira, B. A., & Sites, J. (2008). Cold plasma inactivates Salmonella stanley and Escherichia coli O157: H7 inoculated on golden delicious apples. Journal of Food Protection, 71(7), 1357–1365.
Pawlat, J. (2013). Atmospheric pressure plasma jet for decontamination purposes. European Physical Journal-Applied Physics, 61(2). doi:10.1051/Epjap/2012120431.
Pawlat, J., Samon, R., Stryczewska, H. D., Diatczyk, J., & Gizewski, T. (2013). RF-powered atmospheric pressure plasma jet for surface treatment. European Physical Journal-Applied Physics, 61(2). doi:10.1051/Epjap/2012120428.
Prysiazhnyi, V., Zaporojchenko, V., Kersten, H., & Cernak, M. (2012). Influence of humidity on atmospheric pressure air plasma treatment of aluminium surfaces. Applied Surface Science, 258(14), 5467–5471.
Rose, M. J., Aron, S. A., & Janicki, B. W. (1966). Effect of various nonionic surfactants on growth of Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology, 91(5), 1863–1868.
Schluter, O., Ehlbeck, J., Hertel, C., Habermeyer, M., Roth, A., Engel, K. H., et al. (2013). Opinion on the use of plasma processes for treatment of foods*. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 57(5), 920–927.
Schnabel, U., Niquet, R., Krohmann, U., Winter, J., Schlüter, O., Weltmann, K. D., et al. (2012). Decontamination of microbiologically contaminated specimen by direct and indirect plasma treatment. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 9(6), 569–575.
Sen, Y., Bagci, U., Gulec, H. A., & Mutlu, M. (2012). Modification of food-contacting surfaces by plasma polymerization technique: reducing the Biofouling of microorganisms on stainless steel surface. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(1), 166–175.
Sen, Y., & Mutlu, M. (2013). Sterilization of food contacting surfaces via non-thermal plasma treatment: a model study with Escherichia coli-contaminated stainless steel and polyethylene surfaces. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(12), 3295–3304.
Solon, J. G., & Killeen, S. (2015). Decontamination and sterilization. Surgery (Oxford), 33(11), 572–578.
Stryczewska, H. D., Diatczyk, J., & Pawlat, J. (2011). Temperature distribution in the gliding arc discharge chamber. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 14(2), 276–281.
Stryczewska, H. D., Jakubowski, T., Kalisiak, S., Gizewski, T., & Pawlat, J. (2013). Power systems of plasma reactors for non-thermal plasma generation. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 16(1), 52–62.
Vitrac, H., Guespin-Michel J.F., Brisset J.L. A microbiological investigation of the gliding arc treatment of aqueous media. In Proc. 7th Int. Symp. on High Pressure Low Temperature Plasma Chemistry, HAKONE VII, Greifswald, Germany, 2000 (Vol. 2, pp. 393–397)
von Keudell, A., Awakowicz, P., Benedikt, J., Raballand, V., Yanguas-Gil, A., Opretzka, J., et al. (2010). Inactivation of bacteria and biomolecules by low-pressure plasma discharges. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 7(3–4), 327–352.
von Woedtke, T., Reuter, S., Masur, K., & Weltmann, K. D. (2013). Plasmas for medicine. Physics Reports-Review Section of Physics Letters, 530(4), 291–320.
Yao, M., Mainelis, G., & An, H. R. (2005). Inactivation of microorganisms using electrostatic fields. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(9), 3338–3344.
Ziuzina, D., Han, L., Cullen, P. J., & Bourke, P. (2015). Cold plasma inactivation of internalised bacteria and biofilms for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 210, 53–61.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) (Project number: MAG 112M740), the Korean Scientific Cooperation Network, the European Research Area (KORANET) Joint Call on Green Technologies project: KORANET (ENV-BIO-GA), and COST Actions (MP1101 and TD1208) and LUT research fund.
We would like to thank Prof. H. Stryczewska for her kind guidance and management of the KORANET ENV-BIO-GA network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dasan, B.G., Onal-Ulusoy, B., Pawlat, J. et al. A New and Simple Approach for Decontamination of Food Contact Surfaces with Gliding Arc Discharge Atmospheric Non-Thermal Plasma. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 650–661 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1847-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1847-2