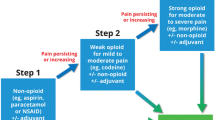
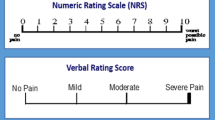
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory disease of synovial joints, and pain is the predominant problem for people with RA. Pain in RA is distressing in its own right and adversely affects disability and psychosocial outcomes. RA pain may be due to joint inflammation and also augmented by central sensitization and structural joint damage. Noninflammatory pain mechanisms may confound the assessment of disease activity in RA, and treatment should aim to both suppress inflammatory disease and relieve pain symptoms. Effective treatment stratification requires a full assessment of pain mechanisms by clinical history and examination, as well as objective assessment of synovitis and joint damage. Biologic therapies and joint replacement surgery have major impacts on RA pain, but may only be available to those with most severe or advanced disease. Holistic approaches to pain management are indicated, including pharmacologic analgesia where randomized controlled trials (RCTs) offer evidence of efficacy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Heiberg T, Kvien TK. Preferences for improved health examined in 1024 patients with rheumatoid arthritis: pain has highest priority. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;47(4):391–7.
Taylor P, Manger B, Alvaro-Gracia J, Johnstone R, Gomez-Reino J, Eberhardt E, et al. Patient perceptions concerning pain management in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Int Med Res. 2010;38:1213–24.
Courvoisier N, Dougados M, Cantagrel A, Goupille P, Meyer O, Sibilia J, et al. Prognostic factors of 10-year radiographic outcome in early rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10:R106.
Odegard S, Finset A, Mowinckel P, Kvien TK, Uhlig T. Pain and psychological health status over a 10-year period in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:1195–201.
Sokka T, Kankainen A, Hannonen P. Scores for functional disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are correlated at higher levels with pain scores than with radiographic scores. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:386–9.
Hakkinen A, Kautiainen H, Hannonen P, Ylinen J, Arkela-Kautiainen M, Sokka T. Pain and joint mobility explain individual subdimensions of the health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) disability index in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:59–63.
Hakkinen A, Kautiainen H, Hannonen P, Ylinen J, Makinen H, Sokka T. Muscle strength, pain, and disease activity explain individual subdimensions of the Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index, especially in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:30–4.
Covic T, Tyson G, Spencer D, Howe G. Depression in rheumatoid arthritis patients: demographic, clinical, and psychological predictors. J Psychosom Res. 2006;60:469–76.
Drewes AM, Svendsen L, Taagholt SJ, Bjerregard K, Nielsen KD, Hansen B. Sleep in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with healthy subjects and studies of sleep/wake interactions. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37:71–81.
Irwin MR, Olmstead R, Carrillo C, Sadeghi N, Fitzgerald JD, Ranganath VK, et al. Sleep loss exacerbates fatigue, depression, and pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Sleep. 2012;35:537–43.
Nicassio PM, Ormseth SR, Kay M, Custodio M, Irwin MR, Olmstead R, et al. The contribution of pain and depression to self-reported sleep disturbance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pain. 2012;153:107–12.
Wolfe F, Michaud K, Li T. Sleep disturbance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation by medical outcomes study and visual analog sleep scales. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:1942–51.
• McWilliams DF, Zhang W, Mansell JS, Kiely PD, Young A, Walsh DA. Predictors of change in bodily pain in early rheumatoid arthritis: the ERAN study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012. doi:10.1002/acr.21723. Data analysis from an inception cohort of early RA which derives the DAS28-P index and suggests that patient-reported components of disease activity may be associated with future pain.
Forslind K, Hafstrom I, Ahlmen M, Svensson B. Sex: a major predictor of remission in early rheumatoid arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:46–52.
Finckh A, Choi HK, Wolfe F. Progression of radiographic joint damage in different eras: trends towards milder disease in rheumatoid arthritis are attributable to improved treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1192–7.
Schipper LG, Fransen J, den Broeder AA, Van Riel PL. Time to achieve remission determines time to be in remission. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R97.
Soubrier M, Lukas C, Sibilia J, Fautrel B, Roux F, Gossec L, et al. Disease activity score-driven therapy vs routine care in patients with recent-onset active rheumatoid arthritis: data from the GUEPARD trial and ESPOIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.137695.
van der Bijl AE, Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Ten Wolde S, Han KH, van Krugten MV, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate as induction therapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2129–34.
Wolfe F, Michaud K. Assessment of pain in rheumatoid arthritis: minimal clinically significant difference, predictors, and the effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:1674–83.
Wiles NJ, Scott DG, Barrett EM, Merry P, Arie E, Gaffney K, et al. Benchmarking: the five year outcome of rheumatoid arthritis assessed using a pain score, the Health Assessment Questionnaire, and the Short Form-36 (SF-36) in a community and a clinic based sample. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60:956–61.
Rupp I, Boshuizen HC, Roorda LD, Dinant HJ, Jacobi CE, van den Bos G. Course of patient-reported health outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of longitudinal and cross-sectional approaches. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:228–33.
Roche PA, Klestov AC, Heim HM. Description of stable pain in rheumatoid arthritis: a 6 year study. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:1733–8.
Ulus Y, Akyol Y, Tander B, Durmus D, Bilgici A, Kuru O. Sleep quality in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: associations with pain, fatigue, depression, and disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29(6 Suppl 69):S92–6.
Sokka T. Morning stiffness and other patient-reported outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 2011;125:23–7.
Konttinen YT, Tiainen VM, Gomez-Barrena E, Hukkanen M, Salo J. Innervation of the joint and role of neuropeptides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1069:149–54.
Schaible HG, Ebersberger A, Von Banchet GS. Mechanisms of pain in arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;966:343–54.
• Raychaudhuri SP, Raychaudhuri SK, Atkuri KR, Herzenberg LA, Herzenberg LA. Nerve growth factor: a key local regulator in the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:3243–52. Ex vivo study finding that NGF levels were raised in RA synovial fluid and that RA synoviocytes proliferated more rapidly in response to NGF-stimulation than normal cells or those from people with OA.
Aloe L, Tuveri MA, Carcassi U, Levi-Montalcini R. Nerve growth factor in the synovial fluid of patients with chronic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:351–5.
Pezet S, Onteniente B, Jullien J, Junier MP, Grannec G, Rudkin BB, et al. Differential regulation of NGF receptors in primary sensory neurons by adjuvant-induced arthritis in the rat. Pain. 2001;90:113–25.
Seidel MF, Herguijuela M, Forkert R, Otten U. Nerve growth factor in rheumatic diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;40:109–26.
Mapp PI, Walsh DA. Mechanisms and targets of angiogenesis and nerve growth in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8:390–8.
Suri S, Gill SE, Massena de Camin S, Wilson D, McWilliams DF, Walsh DA. Neurovascular invasion at the osteochondral junction and in osteophytes in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:1423–8.
• Walsh DA, McWilliams DF, Turley MJ, Dixon MR, Franses RE, Mapp PI, et al. Angiogenesis and nerve growth factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:1852–61. Histomorphometry study which found that NGF was expressed in vascular channels breaching the tidemark in RA and OA. NGF was associated with channels containing sensory nerve fibers.
Ashraf S, Wibberley H, Mapp PI, Hill R, Wilson D, Walsh DA. Increased vascular penetration and nerve growth in the meniscus: a potential source of pain in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:523–9.
Schaible HG, von Banchet GS, Boettger MK, Brauer R, Gajda M, Richter F, et al. The role of proinflammatory cytokines in the generation and maintenance of joint pain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1193:60–9.
Benemei S, Nicoletti P, Capone JG, Geppetti P. CGRP receptors in the control of pain and inflammation. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9:9–14.
Brenn D, Richter F, Schaible HG. Sensitization of unmyelinated sensory fibers of the joint nerve to mechanical stimuli by interleukin-6 in the rat: an inflammatory mechanism of joint pain. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:351–9.
• Zhang L, Berta T, Xu ZZ, Liu T, Park JY, Ji RR. TNF-alpha contributes to spinal cord synaptic plasticity and inflammatory pain: distinct role of TNF receptor subtypes 1 and 2. Pain. 2011;152:419–27. In vivo study of inflammatory arthritis using KO mice. TNFα evoked increased neuronal activity within the spinal cord and subsequent hyperalgesia.
Watkins LR, Maier SF. Beyond neurons: evidence that immune and glial cells contribute to pathological pain states. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:981–1011.
Richter F, Natura G, Loser S, Schmidt K, Viisanen H, Schaible HG. Tumor necrosis factor causes persistent sensitization of joint nociceptors to mechanical stimuli in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:3806–14.
Bekkelund SI, Mellgren SI, Proven A, Husby G. Quantified neurological examination with emphasis on motor and sensory functions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and controls. Br J Rheumatol. 1996;35:1116–21.
Leffler AS, Kosek E, Lerndal T, Nordmark B, Hansson P. Somatosensory perception and function of diffuse noxious inhibitory controls (DNIC) in patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pain. 2002;6:161–76.
Hodge MC, Nathan D, Bach TM. Plantar pressure pain thresholds and touch sensitivity in rheumatoid arthritis. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30:1–9.
Huskisson EC, Hart FD. Pain threshold and arthritis. Br Med J. 1972;4:193–5.
Agarwal V, Singh R, Wiclaf, Chauhan S, Tahlan A, Ahuja CK, et al. A clinical, electrophysiological, and pathological study of neuropathy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27:841–4.
Gerecz-Simon EM, Tunks ER, Heale JA, Kean WF, Buchanan WW. Measurement of pain threshold in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and healthy controls. Clin Rheumatol. 1989;8:467–74.
Lee YC, Chibnik LB, Lu B, Wasan AD, Edwards RR, Fossel AH, et al. The relationship between disease activity, sleep, psychiatric distress, and pain sensitivity in rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R160.
Konttinen YT, Honkanen VE, Gronblad M, Keinonen M, Santavirta N, Santavirta S. The relation of extraarticular tenderness to inflammatory joint disease and personality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992;19:851–5.
Hummel T, Schiessl C, Wendler J, Kobal G. Peripheral and central nervous changes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in response to repetitive painful stimulation. Int J Psychophysiol. 2000;37:177–83.
• Wolfe F, Hauser W, Hassett AL, Katz RS, Walitt BT. The development of fibromyalgia - I: examination of rates and predictors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Pain. 2011;152:291–9. Large US cohort study of incident fibromyalgia within the population of people with RA. Psychological factors, comorbidity, and RA severity were related to developing fibromyalgia. People with RA were reported to move in and out of fibromyalgia classification criteria throughout follow up.
Wolfe F. Fibromyalgianess. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:715–6.
Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Hauser W, Katz RS, et al. Fibromyalgia criteria and severity scales for clinical and epidemiological studies: a modification of the ACR Preliminary Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol. 2011;38:1113–22.
Wolfe F, Hauser W. Fibromyalgia diagnosis and diagnostic criteria. Ann Med. 2011;43:495–502.
Jolliffe VA, Anand P, Kidd BL. Assessment of cutaneous sensory and autonomic axon reflexes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995;54:251–5.
Jones AK, Cunningham VJ, Ha-Kawa S, Fujiwara T, Luthra SK, Silva S, et al. Changes in central opioid receptor binding in relation to inflammation and pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1994;33:909–16.
• Hess A, Axmann R, Rech J, Finzel S, Heindl C, Kreitz S, et al. Blockade of TNF-alpha rapidly inhibits pain responses in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:3731–6. Functional MRI study on human volunteers finding that central nervous activity is reduced rapidly after initiation of TNF-blockade. The investigators subsequently examined these findings in vivo and reported that overexpression of TNF in mice induced hyperalgesia.
Jones AK, Derbyshire SW. Reduced cortical responses to noxious heat in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997;56:601–7.
Schweinhardt P, Kalk N, Wartolowska K, Chessell I, Wordsworth P, Tracey I. Investigation into the neural correlates of emotional augmentation of clinical pain. NeuroImage. 2008;40:759–66.
• Gwilym SE, Filippini N, Douaud G, Carr AJ, Tracey I. Thalamic atrophy associated with painful osteoarthritis of the hip is reversible after arthroplasty: a longitudinal voxel-based morphometric study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2930–40. Volunteer study using subjects with hip OA. Altered gray matter volumes were detected in people with hip OA, which “reverted” to normal levels after joint replacement.
Wager TD, Rilling JK, Smith EE, Sokolik A, Casey KL, Davidson RJ, et al. Placebo-induced changes in FMRI in the anticipation and experience of pain. Science. 2004;303:1162–7.
Lampa J. Pain modulation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) - Influence of Adalimumab (PARADE). Available at: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01197144. Accessed 30 Aug 2012.
Clarke AE, St-Pierre Y, Joseph L, Penrod J, Sibley JT, Haga M, et al. Radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis correlates with functional disability but not direct medical costs. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:2416–24.
Sarzi-Puttini P, Fiorini T, Panni B, Turiel M, Cazzola M, Atzeni F. Correlation of the score for subjective pain with physical disability, clinical, and radiographic scores in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2002;3:18.
Khanna D, Ranganath VK, Fitzgerald J, Park GS, Altman RD, Elashoff D, et al. Increased radiographic damage scores at the onset of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis in older patients are associated with osteoarthritis of the hands, but not with more rapid progression of damage. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2284–92.
Hagglund KJ, Haley WE, Reveille JD, Alarcon GS. Predicting individual differences in pain and functional impairment among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32:851–8.
Edwards RR, Cahalan C, Mensing G, Smith M, Haythornthwaite JA. Pain, catastrophizing, and depression in the rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:216–24.
• Hewlett S, Sanderson T, May J, Alten R, 3rd Bingham CO, Cross M, et al. “I’m hurting, I want to kill myself’: rheumatoid arthritis flare is more than a high joint count–an international patient perspective on flare where medical help is sought. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:69–76. Qualitative study of RA flares, highlighting a need for improved assessment.
Rupp I, Boshuizen HC, Dinant HJ, Jacobi CE, van den Bos GA. Disability and health-related quality of life among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: association with radiographic joint damage, disease activity, pain, and depressive symptoms. Scand J Rheumatol. 2006;35:175–81.
Nicassio PM, Wallston KA. Longitudinal relationships among pain, sleep problems, and depression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Abnorm Psychol. 1992;101:514–20.
Prevoo ML, van ’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:44–8.
van der Heijde DM, van’t Hof MA, van Riel PL, van Leeuwen MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB. Validity of single variables and composite indices for measuring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992;51:177–81.
Van Riel PL. Disease activity score in Rheumatoid arthritis. Available from: http://www.reuma-nijmegen.nl/www.das-score.nl/index.html. Accessed 30 Aug 2012.
Leeb BF, Andel I, Sautner J, Nothnagl T, Rintelen B. The DAS28 in rheumatoid arthritis and fibromyalgia patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43:1504–7.
• Pollard LC, Kingsley GH, Choy EH, Scott DL. Fibromyalgic rheumatoid arthritis and disease assessment. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:924–8. When tender joint counts greatly out-number swollen joint counts, people with RA show more pain, disability, and disease activity. This supports a role for central sensitization in RA severity.
Dhir V, Lawrence A, Aggarwal A, Misra R. Fibromyalgia is common and adversely affects pain and fatigue perception in North Indian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:2443–8.
Ranzolin A, Brenol JC, Bredemeier M, Guarienti J, Rizzatti M, Feldman D, et al. Association of concomitant fibromyalgia with worse disease activity score in 28 joints, health assessment questionnaire, and short form 36 scores in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:794–800.
Schumacher HR, Pessler F, Chen LX. Diagnosing early rheumatoid arthritis (RA). What are the problems and opportunities? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21(5 Suppl 31):S15–9.
Kiely P, Walsh D, Williams R, Young A. Outcome in rheumatoid arthritis patients with continued conventional therapy for moderate disease activity–the early RA network (ERAN). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50:926–31.
• Liu SS, Buvanendran A, Rathmell JP, Sawhney M, Bae JJ, Moric M, et al. A cross-sectional survey on prevalence and risk factors for persistent postsurgical pain 1 year after total hip and knee replacement. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2012;37:415–22. A cross-sectional survey of post-operative pain after joint replacement. 40%–50% of respondents reported persistent pain.
Clarke H, Woodhouse LJ, Kennedy D, Stratford P, Katz J. Strategies aimed at preventing chronic post-surgical pain: comprehensive perioperative pain management after total joint replacement surgery. Physiother Can. 2011;63:289–304.
Calder JD, Ashwood N, Hollingdale JP. Survivorship analysis of the “Performance” total knee replacement-7-year follow-up. Int Orthop. 1999;23:100–3.
Kennedy D, Stratford PW, Pagura SM, Walsh M, Woodhouse LJ. Comparison of gender and group differences in self-report and physical performance measures in total hip and knee arthroplasty candidates. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:70–7.
Walsh M, Woodhouse LJ, Thomas SG, Finch E. Physical impairments and functional limitations: a comparison of individuals 1 year after total knee arthroplasty with control subjects. Phys Ther. 1998;78:248–58.
Emery P. Optimizing outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to anti-TNF treatment. Rheumatology. 2012;51 Suppl 5:v22–30.
Kirwan JR, Hallgren R, Mielants H, Wollheim F, Bjorck E, Persson T, et al. A randomized placebo controlled 12 week trial of budesonide and prednisolone in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:688–95.
NICE. Rheumatoid arthritis - the management of rheumatoid arthritis in adults. HMSO. 2009.
Boers M, Verhoeven AC, Markusse HM, van de Laar MA, Westhovens R, van Denderen JC, et al. Randomized comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate, and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997;350:309–18.
Landewe RB, Boers M, Verhoeven AC, Westhovens R, van de Laar MA, Markusse HM, et al. COBRA combination therapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: long-term structural benefits of a brief intervention. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:347–56.
Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, Stamm TA, Uffmann M, Smolen JS. Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2004;43:906–14.
di Munno O, Sarchi C. Effectiveness of tolmetin in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation by means of a new method. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1982;4:203–6.
Solomon L, Abrams G. Voltaren in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. S Afr Med J. 1974;48:949–52.
Solomon L, Abrams G. Bumadizone calcium in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. S Afr Med J. 1977;52:391–3.
Thompson M, Fox H, Newell D. Ibuprofen in the treatment of arthritis. Med Proc. 1968;14:579–82.
Wienecke T, Gotzsche PC. Paracetamol vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;1:CD003789.
Seideman P. Additive effect of combined naproxen and paracetamol in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1993;32:1077–82.
Seideman P, Melander A. Equianalgesic effects of paracetamol and indomethacin in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1988;27:117–22.
Lee EY, Lee EB, Park BJ, Lee CK, Yoo B, Lim MK, et al. Tramadol 37.5-mg/acetaminophen 325-mg combination tablets added to regular therapy for rheumatoid arthritis pain: a 1-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Ther. 2006;28:2052–60.
Whittle SL, Richards BL, Husni E, Buchbinder R. Opioid therapy for treating rheumatoid arthritis pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;11:CD003113.
Emery P, Gibson T. A double-blind study of the simple analgesic nefopam in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1986;25:72–6.
Swinson DR, Booth J, Baker RD. Nefopam in rheumatoid arthritis. Results of a double-blind placebo controlled study. Clin Rheumatol. 1988;7:411–2.
Deal CL, Schnitzer TJ, Lipstein E, Seibold JR, Stevens RM, Levy MD, et al. Treatment of arthritis with topical capsaicin: a double-blind trial. Clin Ther. 1991;13:383–95.
Richards BL, Whittle SL, Buchbinder R. Antidepressants for pain management in rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;11:CD008920.
Noble M, Treadwell JR, Tregear SJ, Coates VH, Wiffen PJ, Akafomo C, et al. Long-term opioid management for chronic noncancer pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;1:CD006605.
• Atlas LY, Whittington RA, Lindquist MA, Wielgosz J, Sonty N, Wager TD. Dissociable influences of opiates and expectations on pain. J Neurosci. 2012;32:8053–64. Volunteer study finding that opioids and placebo expectancy both reduced experimental thermal pain. Functional MRI appears to suggest that both mechanisms operated independently.
• Bingel U, Wanigasekera V, Wiech K, Ni Mhuircheartaigh R, Lee MC, Ploner M, et al. The effect of treatment expectation on drug efficacy: imaging the analgesic benefit of the opioid remifentanil. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:7–4. Clinical volunteer study finding that negative expectations could remove pain-relieving effects of opioids. Functional MRI findings showed neural activity in brain regions associated with pain intensity.
Ramiro S, Radner H, van der Heijde D, van Tubergen A, Buchbinder R, Aletaha D, et al. Combination therapy for pain management in inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, other spondyloarthritis). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;10:CD008886.
Keefe FJ, Affleck G, Lefebvre JC, Starr K, Caldwell DS, Tennen H. Pain coping strategies and coping efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis: a daily process analysis. Pain. 1997;69:35–42.
Keefe FJ, Caldwell DS, Martinez S, Nunley J, Beckham J, Williams DA. Analyzing pain in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pain coping strategies in patients who have had knee replacement surgery. Pain. 1991;46:153–60.
Acknowledgments
Data for the Figure were prepared by Dr Sam Norton, Dept. Public Health & Primary Care, University of Cambridge, UK, and Professor Adam Young/Marie Hunt, University of West Hertfordshire, UK.
Disclosure
DAW has received grant funding from Pfizer Ltd. for work on pain in rheumatoid arthritis, and has provided consultancy to Pfizer Ltd. He receives grant funding from Arthritis Research UK, and is a Trustee of the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Network, UK Registered Charity No. 1102642; D.F. McWilliams is supported by a grant from Pfizer Ltd, UK (WS953552).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walsh, D.A., McWilliams, D.F. Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr Pain Headache Rep 16, 509–517 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-012-0303-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-012-0303-x