Abstract
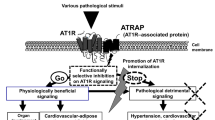
We cloned a novel molecule, AT1 receptor-associated protein (ATRAP), which is expressed in many tissues but specifically interacts with the AT1 receptor carboxylterminal. In the kidney, ATRAP was broadly distributed along the renal tubules; salt intake modulated its expression. In cardiovascular cells, angiotensin II (Ang II) stimulation made ATRAP co-localized with AT1 receptor in cytoplasm; ATRAP overexpression decreased cell surface AT1 receptor. In downstream signaling pathways, ATRAP suppressed Ang II-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase, activation of c-fos gene transcription, and enhancement of amino acid or bromodeoxyuridine incorporation in cardiovascular cells. Thus, cardiovascular ATRAP may promote AT1 receptor internalization and attenuate Ang II-mediated cardiovascular remodeling. We would expect ATRAP to become a new therapeutic target molecule to treat and prevent cardiovascular remodeling in hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Chobanian AV, Alexander RW: Exacerbation of atherosclerosis by hypertension. Potential mechanisms and clinical implications. Arch Intern Med 1996, 156:1952–1956.
Tunon J, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J: Regulation of matrix proteins and impact on vascular structure. Curr Hypertens Rep 2000, 2:106–113.
Dazu VJ, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Sedding DG: Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: new perspectives and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med 2002, 8:1249–1256.
Dzau VJ: Tissue renin-angiotensin system in myocardial hypertrophy and failure. Arch Intern Med 1993, 153:937–942.
Kim S, Iwao H: Molecular and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated cardiovascular and renal diseases. Pharmacol Rev 2000, 52:11–34.
Ruiz-Ortega M, Ruperez M, Esteban V, et al.: Molecular mechanisms of angiotensin II-induced vascular injury. Curr Hypertens Rep 2003, 5:73–79.
Mehta PK, Griendling KK: Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2007, 292:C82–97.
Tamura K, Umemura S, Nyui N, et al.: Activation of angiotensinogen gene in cardiac myocytes by angiotensin II and mechanical stretch. Am J Physiol 1998, 275:R1–R9.
Tamura K, Nyui N, Tamura N, et al.: Mechanism of angiotensin II-mediated regulation of fibronectin gene in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 1998, 273:26487–26496.
Tamura K, Chen YE, Lopez-Ilasaca M, et al.: Molecular mechanism of fibronectin gene activation by cyclic stretch in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2000, 275:34619–34627.
Nyui N, Tamura K, Mizuno K, et al.: Stretch-induced MAP kinase activation in cardiomyocytes of angiotensinogen-deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997, 235:36–41.
Nyui N, Tamura K, Mizuno K, et al.: gp130 is involved in stretch-induced MAP kinase activation in cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998, 245:928–932.
Baker KM, Chernin MI, Wixson SK, et al.: Renin-angiotensin system involvement in pressure-overload cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Am J Physiol 1990, 259:H324–H332.
Schunkert H, Dzau VJ, Tang SS, et al.: Increased rat cardiac angiotensin converting enzyme activity and mRNA expression in pressure overload left ventricular hypertrophy. Effects on coronary resistance, contractility, and relaxation. J Clin Invest 1990, 86:1913–1920.
Rakugi H, Jacob HJ, Krieger JE, et al.: Vascular injury induces angiotensinogen gene expression in the media and neointima. Circulation 1993, 87:283–290.
Tamura K, Umemura S, Nyui N, et al.: Tissue-specific regulation of angiotensinogen gene expression in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1996, 27:1216–1223.
Tamura K, Umemura S, Yamakawa T, et al.: Modulation of tissue angiotensinogen gene expression in genetically obese hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol 1997, 272:R1704–R1711.
Tamura K, Chiba E, Yokoyama N, et al.: Renin-angiotensin system and fibronectin gene expression in Dahl Iwai salt-sensitive and salt-resistant rats. J Hypertens 1999, 17:81–89.
Cohn JN, Tognoni G, for the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial Investigators: A randomized trial of the angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan in chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001, 345:1667–1675.
Dahlof B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, et al.: Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002, 359:995–1003.
Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K, Granger CB, et al.: Effects of candesartan on mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic heart failure: the CHARM-Overall programme. Lancet 2003, 362:759–766.
Navar LG, Kobori H, Prieto-Carrasquero M: Intrarenal angiotensin II and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 2003, 5:135–143.
Dzau VJ, Lopez-Ilasaca M: Searching for transcriptional regulators for Ang II-induced vascular pathology. J Clin Invest 2005, 115:2319–2322.
Ruiz-Ortega M, Esteban V, Ruperez M, et al.: Renal and vascular hypertension-induced inflammation: role of angiotensin II. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2006, 15:159–166.
Horiuchi M, Akishita M, Dzau VJ: Recent progress in angiotensin II type 2 receptor research in the cardiovascular system. Hypertension 1999, 33:613–621.
Carey RM: Cardiovascular and renal regulation by the angiotensin type 2 receptor: the AT2 receptor comes of age. Hypertension 2005, 45:840–844.
Inagami T: Molecular biology and signaling of angiotensin receptors: an overview. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999, 10:S2–S7.
Miura S, Saku K, Karnik SS: Molecular analysis of the structure and function of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Hypertens Res 2003, 26:937–943.
Gaborik Z, Hunyady L: Intracellular trafficking of hormone receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2004, 15:286–293.
Hunyady L: Molecular mechanisms of angiotensin II receptor internalization. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999, 10:S47–S56.
Ushio-Fukai M, Alexander RW: Caveolin-dependent angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling in vascular smooth muscle. Hypertension 2006, 48:797–803.
Hein L, Meinel L, Pratt RE, et al.: Intracellular trafficking of angiotensin II and its AT1 and AT2 receptors: evidence for selective sorting of receptor and ligand. Mol Endocrinol 1997, 11:1266–1277.
Ohtsu H, Suzuki H, Nakashima H, et al.: Angiotensin II signal transduction through small GTP-binding proteins: mechanism and significance in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 2006, 48:534–540.
Daviet L, Lehtonen JY, Tamura K, et al.: Cloning and characterization of ATRAP, a novel protein that interacts with the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem 1999, 274:17058–17062.
Cui T, Nakagami H, Iwai M, et al.: ATRAP, novel AT1 receptor associated protein, enhances internalization of AT1 receptor and inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000, 279:938–941.
Lopez-Ilasaca M, Liu X, Tamura K, et al.: The angiotensin II type I receptor-associated protein, ATRAP, is a transmembrane protein and a modulator of angiotensin II signaling. Mol Biol Cell 2003, 14:5038–5050.
Tsurumi Y, Tamura K, Tanaka Y, et al.: Interacting molecule of AT1 receptor, ATRAP, is co-localized with AT1 receptor in the mouse renal tubules. Kidney Int 2006, 69:488–494.
Guo S, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Dzau VJ: Identification of calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand (CAML) as transducer of angiotensin II-mediated nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) activation. J Biol Chem 2005, 280:12536–12541.
Tanaka Y, Tamura K, Koide Y, et al.: The novel angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R)-associated protein ATRAP downregulates AT1R and ameliorates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. FEBS Lett 2005, 579:1579–1586.
Azuma K, Tamura K, Sakai M, et al.: A novel regulatory effect of AT1 receptor-interacting molecule vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 2006:48:e27.
Rodriguez-Vita J, Sanchez-Lopez E, Esteban V, et al.: Angiotensin II activates the Smad pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells by a transforming growth factor-beta-independent mechanism. Circulation 2005, 111:2509–2517.
Border WA, Noble NA: Interactions of transforming growth factor-beta and angiotensin II in renal fibrosis. Hypertension 1998, 31:181–188.
Zacchigna L, Vecchione C, Notte A, et al.: Emilin1 links TGF-beta maturation to blood pressure homeostasis. Cell 2006, 124:929–942.
August P, Suthanthiran M: Transforming growth factor beta signaling, vascular remodeling, and hypertension. N Engl J Med 2006, 354:2721–2723.
Oshita A, Iwai M, Chen R, et al.: Attenuation of inflammatory vascular remodeling by angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein. Hypertension 2006, 48:671–676.
Guo DF, Tardif V, Ghelima K, et al.: A novel angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein induces cellular hypertrophy in rat vascular smooth muscle and renal proximal tubular cells. J Biol Chem 2004, 279:21109–21120.
Ushio-Fukai M, Zuo L, Ikeda S, et al.: cAbl tyrosine kinase mediates reactive oxygen species-and caveolin-dependent AT1 receptor signaling in vascular smooth muscle: role in vascular hypertrophy. Circ Res 2005, 97:829–836.
Guo DF, Chenier I, Lavoie JL, et al.: Development of hypertension and kidney hypertrophy in transgenic mice overexpressing ARAP1 gene in the kidney. Hypertension 2006, 48:453–459.
Zou Y, Akazawa H, Qin Y, et al.: Mechanical stress activates angiotensin II type 1 receptor without the involvement of angiotensin II. Nat Cell Biol 2004, 6:499–506.
Miura S, Fujino M, Hanzawa H, et al.: Molecular mechanism underlying inverse agonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem 2006, 281:19288–19295.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamura, K., Tanaka, Y., Tsurumi, Y. et al. The role of angiotensin AT1 receptor-associated protein in renin-angiotensin system regulation and function. Current Science Inc 9, 121–127 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-007-0022-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-007-0022-6