Abstract
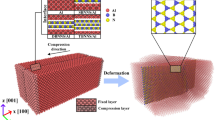
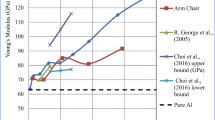
The recently discovered hybrid boron nitride-carbon (BN-C) nanostructures have triggered enormous attention in the research on innovative nanocomposite design. Molecular dynamics simulation is conducted in this study to analyze the load-carrying capacity of aluminum nanocomposites reinforced with different types of BN-C nanosheets. By adopting a realistic loading condition in actual composites, the study found that the mechanical performance of the nanocomposite is predominantly affected by the interfacial mechanics between the nanosheet and the inner surface of the matrix. The computed Young’s modulus of Al matrix reinforced by graphene, BN and BN-C nanofiber are 74.61 GPa, 74.65 GPa and 76.48 GPa respectively by using the realistic loading condition. The tensile loading behavior of the nanocomposite is also strongly dependent on the angle of recline of the nanosheet relative to the loading direction. The nanocomposite with a nanofiber reinforcement aligned at 0° to the principal loading axis exhibited maximum tensile resistance compared to that of nanofiber reinforcements aligned at 15° or 30°. The maximum load-carrying capacity under tension decreases with increasing temperature. However, increasing the BN concentration in the reinforcing nanosheet improves the thermal stability of the nanocomposite.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, and A.A. Firsov, Science 306, 666 (2004).
H. Zeng, C. Zhi, Z. Zhang, X. Wei, X. Wang, W. Guo, Y. Bando, and D. Golberg, Nano Lett. 10, 5049 (2010).
C. Lee, X. Wei, J.W. Kysar, and J. Hone, Science 321, 385 (2008).
C.H. Wong and V. Vijayaraghavan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 556, 420 (2012).
Y. Chen, J. Zou, S.J. Campbell, and G.L. Caer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2430 (2004).
T. Han, Y. Luo, and C. Wang, J. Phys. D 47, 025303 (2014).
J. Che, M. Jing, D. Liu, K. Wang, and Q. Fu, Compos. Part A 112, 32 (2018).
B. Zhong, Y. Cheng, M. Wang, Y. Bai, X. Huang, Y. Yu, H. Wang, and G. Wen, Compos. Part A 112, 515 (2018).
T. Li, X. Jiao, T. You, F. Dai, P. Zhang, F. Yu, L. Hu, L. Ding, L. Zhang, Z. Wen, and Y. Wu, Ceram. Int. 45, 4283 (2019).
A. Merlo, V.R.S.S. Mokkapati, S. Pandit, and I. Mijakovic, Biomater. Sci.-UK 6, 2298 (2018).
Y. Fan, Z. Yang, W. Hua, D. Liu, T. Tao, M.M. Rahman, W. Lei, S. Huang, and Y. Chen, Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602380 (2017).
K.Q. Xiao, L.C. Zhang, and I. Zarudi, Compos. Sci. Technol. 67, 177 (2007).
L.C. Zhang, I. Zarudi, and K.Q. Xiao, Wear 261, 806 (2006).
K.Q. Xiao and L.C. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 39, 4481 (2004).
M.W. Ahmad, B. Dey, G. Sarkhel, D.S. Bag, and A. Choudhury, Mater. Chem. Phys. 223, 426 (2019).
M. Basso, W. Azoti, H. Elmarakbi, and A. Elmarakbi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 136, 47664 (2019).
J. Zhang and X. Peng, Mater. Chem. Phys. 198, 250 (2017).
V. Guerra, C. Wan, and T. McNally, Prog. Mater Sci. 100, 170 (2019).
J. Zhang and C. Wang, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 49, 155305 (2016).
J. Zhang and C. Wang, Comput. Mater. Sci. 127, 270 (2017).
H. Alsanat, S. Gunalan, H. Guan, P. Keerthan, and J. Bull, Thin Walled Struct. 141, 460 (2019).
F. Khodabakhshi and A.P. Gerlich, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 759, 688 (2019).
Y. Mishin, D. Farkas, M.J. Mehl, and D.A. Papaconstantopoulos, Phys. Rev. B 59, 3393 (1999).
M.I. Mendelev, M.J. Kramer, C.A. Becker, and M. Asta, Philos. Mag. 88, 1723 (2008).
A. KinacI, J.B. Haskins, C. Sevik, and T. ÇağIn, Phys. Rev. B 86, 115410 (2012).
J. Tersoff, Phys. Rev. B 39, 5566 (1989).
K.N. Kudin, G.E. Scuseria, and B.I. Yakobson, Phys. Rev. B 64, 235406 (2001).
B.K. Choi, G.H. Yoon, and S. Lee, Compos. Part B 91, 119 (2016).
Z. Cong and S. Lee, Compos. Struct. 194, 80 (2018).
S. Plimpton, J. Comput. Phys. 117, 1 (1995).
Y.G. Wang, Z.X. Jiang, and L.L. Wang, Strain 49, 335 (2013).
M. Bokdam, G. Brocks, M.I. Katsnelson, and P.J. Kelly, Phys. Rev. B 90, 085415 (2014).
T. Olsen and K.S. Thygesen, Phys. Rev. B 87, 075111 (2013).
R. Rezaei, Comput. Mater. Sci. 151, 181 (2018).
N. Silvestre, B. Faria, and J.N. Canongia Lopes, Compos. Sci. Technol. 90, 16 (2014).
V. Vijayaraghavan and L. Zhang, Comput. Mater. Sci. 159, 376 (2019).
H. Zhao, K. Min, and N.R. Aluru, Nano Lett. 9, 3012 (2009).
T. Mori and K. Tanaka, Acta Metall. Mater. 21, 571 (1973).
D. Golberg, Y. Bando, Y. Huang, T. Terao, M. Mitome, C. Tang, and C. Zhi, ACS Nano 4, 2979 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vijayaraghavan, V., Zhang, L. Tensile Properties of Boron Nitride-Carbon Nanosheet-Reinforced Aluminum Nanocomposites Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation. JOM 72, 2305–2311 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04031-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04031-9