Abstract
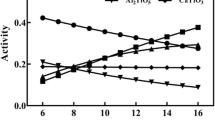
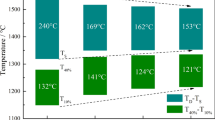
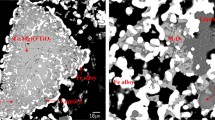
The complicated reduction behaviors of iron, vanadium and titanium oxides must be accurately controlled for the successful smelting of vanadium titanomagnetite. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of the binary basicity, MgO content, smelting temperature, duration and reductants on the reduction of iron, vanadium and titanium oxides during the electric furnace smelting of vanadium titanomagnetite metallized pellets. The results demonstrate that the recovery ratios of both iron and vanadium increase as the binary basicity increases from 0.9 to 1.2, whereas the reduction of titanium oxides is mitigated when the basicity is maintained at 1.1. Compared to its weak effect on the recovery ratio of iron, increasing MgO content improves the vanadium recovery ratio. A low content of titanium in molten iron is obtained when the MgO content in the slag is lower than 11%, whereas the titanium content in the molten iron increases as the MgO content increases further. Moreover, the iron and vanadium recovery ratios, and the Ti content in the molten iron, increase with increasing smelting temperature, duration and reductant content.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.W. Lv, Z.G. Lun, J.Q. Yin, and C.G. Bai, ISIJ Int. 53, 1115 (2013).
Y.F. Guo, S.S. Liu, T. Jiang, G.Z. Qiu, and F. Chen, Hydrometallurgy 147–148, 134 (2014).
F.Q. Zheng, F. Chen, Y.F. Guo, T. Jiang, A.Y. Travyanov, and G.Z. Qiu, JOM 68, 1476 (2016).
P.R. Taylor, S.A. Shuey, E.E. Vidal, and J.C. Gomez, Miner. Metall. Process. 23, 80 (2006).
W.G. Fu, Y.C. Wen, and H.E. Xie, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 18, 7 (2011).
D.S. Chen, L.S. Zhao, Y.H. Liu, T. Qi, J.C. Wang, and L.N. Wang, J. Hazard. Mater. 244–245, 588 (2013).
S.Y. Chen and M.S. Chu, J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 114, 481 (2014).
Y. Sun, H.Y. Zheng, Y. Dong, X. Jiang, Y.S. Shen, and F.M. Shen, Int. J. Miner. Process. 142, 119 (2015).
L. Zhao, L. Wang, D. Chen, H. Zhao, Y. Liu, and T. Qi, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25, 1325 (2015).
S. Samanta, S. Mukherjee, and R. Dey, JOM 67, 467 (2015).
M.Y. Wang, S.F. Zhou, X.W. Wang, B.F. Chen, H.X. Yang, S.K. Wang, and P.F. Luo, JOM 68, 2698 (2016).
Z. Peng and J.Y. Hwang, Int. Mater. Rev. 60, 30 (2015).
Y.L. Zhen, G.H. Zhang, and K.C. Chou, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46, 155 (2015).
W. Geyser, W.S. Steinberg, and J. Nell, J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 111, 707 (2011).
V.E. Roshchin, A.V. Asanov, and A.V. Roshchin, Russ. Metall. 11, 1001 (2010).
J. Wang, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Master Thesis (2014).
E.H. Wu, University of Science and Technology, Beijing, Ph.D Thesis (2016).
L. Zhang, L.N. Zhang, M.Y. Wang, T.P. Lou, Z.T. Sui, and J.S. Jang, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 352, 123 (2006).
E. Wearing, J. Mater. Sci. 18, 1629 (1983).
S. Ren, Q.C. Liu, J.L. Zhang, M. Chen, X.D. Ma, and B.J. Zhao, Ironmak. Steelmak. 42, 117 (2015).
T. Jiang, S. Wang, Y.F. Guo, F. Chen, and F.Q. Zheng, Metals 6, 107 (2016).
C.W. Bale, E. Bélisle, P. Chartrand, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, K. Hack, I.H. Jung, Y.B. Kang, J. Melançon, A.D. Pelton, C. Robelin, and S. Petersen, Calphad 33, 295 (2009).
T. Hu, X.W. Lv, C.G. Bai, Z.G. Lun, and G.B. Qiu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44, 252 (2013).
H.G. Du, Principles of Blast Furnaces Melting Vanadium-Titanium Magnetite (Beijing: Science Press, 1996), p. 108.
X.H. Huang, Principles of Iron and Steel Metallurgy, 4th ed. (Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013), pp. 61, 296, 439.
M.X. Fang and H.S. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. Powder Metall. 11, 329 (2006).
A. Shankar, M.R.G. Rnerup, A.K. Lahiri, and S. Seetharaman, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 38, 911 (2007).
P.C. Li and X.J. Ning, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 446 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Guo, Y., Jiang, T. et al. Reduction Behaviors of Iron, Vanadium and Titanium Oxides in Smelting of Vanadium Titanomagnetite Metallized Pellets. JOM 69, 1646–1653 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2367-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2367-x