Abstract
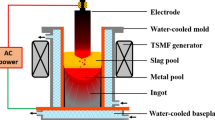
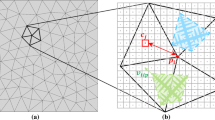
A transient, two-dimensional axisymmetric model was developed to understand the effect of the electromagnetic stirring (EMS) on the grain morphology of the electroslag remelting ingot. The cellular automaton-finite element technique was employed to describe the nucleation and growth of the grain. The Joule heating and Lorentz force created by the current of the furnace, as well as the Lorentz force induced by the EMS device, are included. The effect of the EMS current on the grain structure was investigated using the model. A reasonable agreement between the experiment and simulation was obtained. The growth direction of the upper grain without the EMS is approximately 45° with respect to the vertical axis, while changes to the radial were caused by EMS. The grain was considerably refined by the EMS, and the average area of the grain decreased from 9.381 × 10−7 m2 to 6.781 × 10−7 m2 with the current of the EMS ranging from 0 A to 500 A. Both the local solidification time and second dendrite arm spacing decreased with the increasing stirring intensity. The metal pool depth, however, increased with the EMS, which definitely contributed to the macrosegregation formation. The upper ingot with EMS was darker than that without EMS in the experiment. The EMS technique should be used with caution.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{B}} \) :
-
Thermal buoyancy (N m−3)
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{LS}} \) :
-
Lorentz force induced by the current of the furnace (N m−3)
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{LE}} \) :
-
Lorentz force created by the EMS device (N m−3)
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{D}} \) :
-
Damping force (N m−3)
- G :
-
Temperature gradient (K m−1)
- H :
-
Enthalpy (J kg−1)
- k eff :
-
Effective thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- L :
-
Latent heat (J kg−1)
- M :
-
Secondary dendrite arm spacing coefficient (m s−1)
- n :
-
Density of grain (1/m3)
- n max :
-
Maximum density of grain (1/m3)
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Q J :
-
Joule heating (W m−3)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u :
-
Solidification rate (m s−1)
- \( \vec{v} \) :
-
Velocity (m s−1)
- ΔT :
-
Temperature difference (K)
- ΔT σ :
-
Standard deviation of the temperature difference
- ΔT m :
-
Average temperature difference (K)
- ΔT max :
-
Maximum nucleation undercooling (K)
- λ 2 :
-
Secondary dendrite arm spacing (m)
- μ eff :
-
Effective viscosity (Pa s)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
References
A. Ludwig, A. Kharicha, and M. Wu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45B, 36 (2014).
B. Hernandez-Morales and A. Mitchell, Ironmaking Steelmaking 26, 423 (1999).
L. Nastac, S. Sundarraj, K.O. Yu, and Y. Pang, JOM 50, 30 (1998).
L.A. Bertram, P.R. Schunk, S.N. Kempka, F. Spadafora, and R. Minisandram, JOM 50, 18 (1998).
S. Iijima, Y. Kondo, and T. Saito, Tetsu-to-Hagané 67, S645 (1978).
K. Miyazawa, T. Fukaya, S. Asai, I. Muchi, M. Choudhary, and J. Szekely, Trans. ISIJ 25, 386 (1985).
A. Mitchell and B. Hernandez-Morales, Metall. Trans. B 21B, 723 (1990).
M. Murgaš, A.S. Chaus, A. Pokusa, and M. Pokusová, ISIJ Int. 40, 980 (2000).
V. Weber, A. Jardy, B. Dussoubs, D. Ablitzer, S. Rybéron, V. Schmitt, S. Hans, and H. Poisson, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 40B, 271 (2009).
B.K. Li, B. Wang, and F. Tsukihashi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45B, 1122 (2014).
H.P. Liu, M.G. Xu, S.T. Qiu, and H. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 43B, 1657 (2012).
Q. Wang, Z. He, B.K. Li, and F. Tsukihashi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45B, 2425 (2014).
Y.W. Dong, Z.H. Jiang, and Z.B. Li, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 14, 7 (2007).
Q. Wang, R.J. Zhao, M. Fafard, and B.K. Li, Appl. Therm. Eng. 80, 178 (2015).
K. Fezi, J. Yanke, and M.J.M Krane (Paper presented at Liquid Metal Processing and Casting 2013, Austin, TX, 2013), pp. 151–158.
D.R. Liu, G. Reinhart, N. Mangelinck-Noel, and Ch-A Gandin, ISIJ Int. 54, 392 (2014).
T. Takaki, ISIJ Int. 54, 437 (2014).
M.M. Franke, R.M. Hilbinger, C.H. Konrad, U. Glatzel, and R.F. Singer, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 42A, 1847 (2011).
B.K. Li, Q. Wang, F. Wang, and M.Q. Chen, JOM 66, 1153 (2014).
K.M. Kelkar, S.V. Patankar, S.K. Srivatsa, R.S. Minisandram, D.G. Evans, J.J. deBarbadillo, R.H. Smith, R.C. Helmink, A. Mitchell, and H.A. Sizek (Paper presented at Liquid Metal Processing and Casting 2013, Austin, TX, 2013), pp. 3–12.
Y. Natsume and K. Ohsasa, ISIJ Int. 54, 415 (2014).
S.J. Chen, G. Guillemot, and C.-A. Gandin, ISIJ Int. 54, 401 (2014).
H.J. Bai, Y. Li, and B.K. Li, Spec. Steel 29, 7 (2008).
B. Su, Z.Q. Han, and B.C. Liu, ISIJ Int. 53, 527 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The authors’ gratitude goes to National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51210007) and Fundamental Research Funds of People’s Republic of China for the Central Universities (N140206002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Yan, H., Wang, F. et al. Impact of Electromagnetic Stirring on Grain Structure of Electroslag Remelting Ingot. JOM 67, 1821–1829 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1479-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1479-4