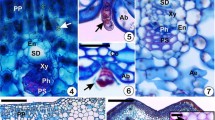
Abstract
The phytohormone production hypothesis suggests that organisms, including insects, induce galls by producing and secreting plant growth hormones. Auxins and cytokinins are classes of phytohormones that induce cell growth and cell division, which could contribute to the plant tissue proliferation which constitutes the covering gall. Bacteria, symbiotic with insects, may also play a part in gall induction by insects through the synthesis of phytohormones or other effectors. Past studies have shown that concentrations of cytokinins and auxins in gall-inducing insects are higher than in their host plants. However, these analyses have involved whole-body extractions. Using immunolocalization of cytokinin and auxin, in the gall-inducing stage of Eurosta solidaginis, we found both phytohormones to localize almost exclusively to the salivary glands. Co-localization of phytohormone label with a nucleic acid stain in the salivary glands revealed the absence of Wolbachia sp., the bacterial symbiont of E. solidaginis, which suggests that phytohormone production is symbiont independent. Our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that phytohormones are synthesized in and secreted from the salivary glands of E. solidaginis into host-plant tissues for the purpose of manipulating the host plant.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Negative Control Images, Single and Dual Channel Images, and Protocol for Immunolocalization of Phytohormones are available through the Figshare repository Figshare Link: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.c.5338007.
References
Abrahamson WG, Weis AE (1997) Evolutionary ecology across three trophic levels: goldenrods, gallmakers, and natural enemies. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.12987/9780691209432
Albertson R, Tan V, Leads RR, Reyes M, Sullivan W, Casper-Lindley C (2013) Mapping Wolbachia distributions in the adult Drosophila brain. Cell Microbiol 15:1527–1544. https://doi.org/10.1111/cmi.12136
Andreas P, Kisiala A, Emery RJN, De Clerck-Floate R, Tooker JF, Price PW, Miller DG III, Chen MS, Connor EF (2020) Cytokinins are abundant and widespread among insect species. Plants 9(2):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020208
Angra-Sharma R, Sharma DK (1999) Cytokinins in pathogenesis and disease resistance of Pyrenophora teres-barley and Dreschslera maydis-maize interactions during early stages of infection. Mycopathologia 148:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007126025955
Barash I, Manulis-Sasson S (2007) Virulence mechanisms and host-specificity of gall forming Pantoea agglomerans. Trends Microbiol 15:538–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2007.10.009
Barash I, Manulis-Sasson S (2009) Recent evolution of bacterial pathogens: The gall-forming Pantoea agglomerans case. Ann Rev Phytopath 47:133–152. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081803
Barbosa P, Berry D, Kary CK (2014) Insect Histology: Practical Laboratory Techniques. Oxford, UK: John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org.https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118876114.
Bartlett L, Connor EF (2014) Exogenous phytohormones and the induction of plant galls by insects. Arthropod-Plant Inter 8:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081803
Birol I, Jackman SD, Nielsen CB, Qian JQ, Varhol R, Stazyk G, Morin RD, Zhao Y, Hirst M, Schein JE, Horsman E, Connors JM, Gascoyne RD, Marra MA, Jones SJM (2009) De novo transcriptome assembly with ABySS. Bioinformatics 25:2872–2877. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp367
Body M, Kaiser W, Dubreuil G, Casas J, Giron D (2013) Leaf-miners co-opt microorganisms to enhance their nutritional environment. J Chem Ecol 39:969–977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-013-0307-y
Bruce SA, Saville BJ, Emery RJN (2011) Ustilago maydis produces cytokinins and abscisic acid for potential regulation of tumor formation in maize. J Plant Growth Regul 30:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-010-9166-8
Brütting C, Crava CM, Schäfer M, Schuman MC, Meldau S, Adam N, Baldwin IT (2018) Cytokinin transfer by a free-living mirid to Nicotiana attenuate recapitulates a strategy of endophytic insects. eLife 7:e36268. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36268
Cambier S, Ginis O, Moreau SJM, Gayral P, Hearn J, Stone GN, Giron D, Huguet E, Drezen JM (2019) Gall wasp transcriptomes unravel potential effectors involved in molecular dialogues with oak and rose. Front Physiol 10:926. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00926
Chanclud E, Kisiala A, Emery RJN, Chalvon V, Ducasse A, Romiti-Michel C, Gravot A, Kroj T, Morel J (2016) Cytokinin production by the rice blast fungus is a pivotal requirement for full virulence. PloS Pathog 12(2):e1005457. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005457
Connor EF, Bartlett L, O’Toole S, Byrd S, Biskar K, Orozco J (2012) The mechanism of gall induction makes galls red. Arthropod-Plant Inter 6:489–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-012-9210-7
Dewitte W, van Onckelen H (2001) Probing the distribution of plant hormones by immunocytochemistry. Plant Growth Regul 33:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010729703354
Dewitte W, Chiappetta A, Azmi A, Witters A, Strnad M, Rembur J, Noin M, Chriqui D, van Onckelen HA (1999) Dynamics of cytokinins in apical shoot meristems of a day neutral tobacco during floral transition and flower formation. Plant Physiol 119:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.119.1.111
Dodueva IE, Lebedeva MA, Kuznetsova KA, Gancheva MS, Papononva SS, Lutova LL (2020) Plant tumors: a hundred years of study. Planta 251:82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03375-5
Doehlemann G, Wahl R, Horst RJ, Voll LM, Usadel B, Poree F, Stitt M, Pons-Kühnemann J, Sonnewald U, Kahmann R, Kämper J (2008) Reprogramming a maize plant: transcriptional and metabolic changes induced by the fungal biotroph Ustilago maydis. Plant J 56:181–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03590.x
Dorchin N, Hoffman J, Stirk W, Novak O, Strnad M, van Staden J (2009) Sexually dimorphic gall structures correspond to differential phytohormone contents in male and female wasps. Physiol Entomol 34:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3032.2009.00702.x
Doyle D, Laufer H (1969) Sources of larval salivary gland secretion in the dipteran Chironomus tentans. J Cell Biol 40:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.40.1.61
Eberle J, Wang TL, Cook S, Wells B, Weiler EW (1987) Immunoassay and ultrastructural localization of isopentenyladenine and related cytokinins using monoclonal antibodies. Planta 172:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398657
Erb M, Meldau S, Howe GA (2012) Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends Plant Sci 17:250–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.01.003
Frébort I, Kowalska M, Hluska T, Frébortová J, Galuszka T (2011) Evolution of cytokinin biosynthesis and degradation. J Exp Bot 62:2431–2452. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err004
Galuszka P, Spíchal L, Kopečný D, Tarkowski P, Frébortová J, Šebela M, Frébort I (2008) Metabolism of plant hormones cytokinins and their function in signaling, cell differentiation and plant development. In: In Rahman AU (ed) Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, Vol. 34. New York: Elsevier, pp 203-264, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1572-5995(08)80024-5
Giron D, Glevarec GJ (2014) Cytokinin-Induced phenotypes in plant-insect interactions: learning from the bacterial world. J Chem Ecol 40:826–835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-014-0466-5
Giron D, Kaiser W, Imbault N, Casas J (2007) Cytokinin-mediated leaf manipulation by a leafminer caterpillar. Biol Lett 3:340-343, https:// doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2007.0051
Giron D, Frago E, Glevarec G, Pieterse CMJ, Dicke M (2013) Cytokinins as key regulators in plant–microbe–insect interactions: connecting plant growth and defense. Funct Ecol 27:599–609. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12042
Gordon SA, Buess E (1967) Observations on the physiology and radiation response of auxin. Ann NY Acad Sci 144:136–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb34008.x
Hammer TJ, De Clerck-Floate R, Tooker JF, Price PW, Miller DG III, Connor EF (2020) Are bacterial symbionts associated with gall induction in insects? Arthropod-Plant Inter 15:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-020-09800-6
Hearn J, Blaxter M, Schonrögge K, Nieves-Aldrey JL, Pujade-Villar J, Huguet E, Drezen JM, Shorthouse JD, Stone GN (2019) Genomic dissection of an extended phenotype: Oak galling by a cynipid gall wasp. PLoS Genet 15(11):e1008398. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008398
Hou HQ, Zhao GZ, Su CY, Zhu DH (2020) Wolbachia prevalence patterns: horizontal transmission, recombination, and multiple infections in chestnut gall wasp-parasitoid communities. Entomol Exp Appl 168:752–765. https://doi.org/10.1111/eea.12962
Jameson P (2000) Cytokinins and auxins in plant pathogen interactions – an overview. Plant Growth Regul 32:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010733617543
Kai S, Kumashiro S, Adachi S, Suzuki Y, Shiomi Y, Matsunaga K, Gyoutoku N, Asami T, Tokuda M (2017) Life history of Stenopsylla nigricornis (Hemiptera: Psylloidea: Triozidae) and phytohormones involved in gall induction. Arthropod-Plant Inter 11:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-016-9470-8
Kaiser W, Huguet E, Casas J, Commin C, Commin C, Giron D (2010) Plant green-island phenotype induced by leaf-miners is mediated by bacterial symbionts. P Roy Soc Lond B 277:2311–2319. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2010.0214
Karr TL, Yang W, Feder ME (1998) Overcoming cytoplasmic incompatibility in Drosophila. Proc Roy Soc. Lond. B 265:391–395. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1998.0307
Lichter A, Barash I, Valinsky L, Manulis-Sasson S (1995) The genes involved in cytokinin biosynthesis in Erwinia herbicola pv. gypsophilae: Characterization and role in gall formation. J Bacteriol 177:4457–4465. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.177.15.4457-4465
Limbourg B, Zalokar M (1973) Permeabilization of Drosophila eggs. Developmental Biol 35:382–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-1606(73)90034-1
MacDonald EMS, Powell GK, Regier DA, Glass NL, Roberto F, Kosuge T, Morris RO (1986) Secretion of zeatin, ribosylzeatin, and ribosyl-1”-methylzeatin by Pseudomonas savastanoi. Plant Physiol 82:742–747. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.82.3.742
Mapes CC, Davies PJ (2001) Cytokinins in the ball gall of Solidago altissima and in the gall forming larvae of Eurosta solidaginis. New Phytol 151:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00158.x
Mapes CC, Davies PJ (2001) Indole-3-acetic acid and ball gall development on Solidago altissima. New Phytol 151:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00161.x
Mashiguchi K, Tanaka K, Sajai T, Sugawara S, Kawaide H, Natsume M, Hanada A, Yaeno T, Shirasu K, Yao H, McSteen P, Zhao Y, Hayashi K, Kamiya Y, Kasahara H (2011) The main auxin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis. P Natl Acad Sci USA 108:18513–18517. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108434108
McCrea KD, Abrahamson WG, Weis AE (1985) Goldenrod ball gall effects on Solidago altissima: 14C translocation and growth. Ecology 66:1902–1907. https://doi.org/10.2307/2937386
Miles PW (1968) Insect secretions in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 6:137–164. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.06.090168.001033
Morrison EN, Emery RJN, Saville BJ (2015) Phytohormone involvement in the Ustilago maydis-Zea mays pathosystem: relationships between abscisic acid and cytokinin levels and strain virulence in infected cob tissue. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0130945. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130945
Morrsion EN, Knowles S, Thorn RG, Saville BJ, Emery RJN (2015) Detection of phytohormones in temperate forest fungi predicts consistent abscisic acid production and a common pathway for cytokinin biosynthesis. Mycologia 107:245–257. https://doi.org/10.3852/14-157
Müller H-AJ (2008) Immunolabeling of embryos. In: C. Dahmann (Ed.), Drosophila: Methods and Protocols (pp. 207–218). Humana Press. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-583-1_12
Naseem M, Wölfling M, Dandekar T (2014) Cytokinins for immunity beyond growth, galls and green islands. Trends Plant Sci 19:481–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.04.001
Nishii K, Wright F, Chen YY, Möller M (2018) Tangled history of a multigene family: the evolution of isopentenyltransferase genes. PLoS One 13(8):e0201198. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201198
Patten CL, Blakney AJC, Coulson TJD (2013) Activity, distribution and function of indole-3-acetic acid biosynthetic pathways in bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol 39:395–415. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2012.716819
Rand MD, Kearney AL, Dao J, Clason T (2010) Permeabilization of Drosophila embryos for introduction of small molecules. Insect Biochem Molec Biol 40:792–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.07.007
Redkar A, Hoser R, Schilling L, Zechmann B, Krzymowska M, Walbot V, Doehlemann G (2015) A secreted effector protein of Ustilago maydis guides maize leaf cells to form tumors. Plant Cell 27:1332–1351. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.131086
Reineke G, Heinze B, Schiraski J, Buettner H, Kahmann R, Basse CW (2008) Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) biosynthesis in the smut fungus Ustilago maydis and its relevance for increased IAA levels in infected tissue and host tumor formation. Mol Plant Pathol 9:339–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2008.00470.x
Robischon M (2015) Do cytokinins function as two-way signals between plants and animals? BioEssays 37:356–363. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201400099
Sakakibara H (2006) Cytokinins: activity, biosynthesis, and translocation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:431–449. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105231
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nature Meth 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Seegobin M, Kisiala A, Noble A, Kaplan D, Brunetti C, Emery RJN (2018) Canis familiaris tissues are characterized by different profiles of cytokinins typical of the tRNA degradation pathway. FASEB J. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201800347
Sossountov L, Maldiney R, Sotta B, Sabbagh I, Habricot Y, Bonnet M, Miginiac E (1988) Immunocytochemical localization of cytokinins in Craigella tomato and a sideshootless mutant. Planta 175:291–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396334
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Remans R (2007) Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31:425–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00072.x
Spíchal L (2012) Cytokinins – recent news and views of evolutionally old molecules. Funct Plant Biol 39:267–284. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP11276
Stirk WA, van Staden J (2010) Flow of cytokinins through the environment. Plant Growth Regul 62:101–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9481-x
Stouthamer R, Breeuwer JAJ, Hurst GDD (1999) Wolbachia pipientis: microbial manipulator of arthropod reproduction. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:71–102. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.71
Straka JR, Hayward AR, Emery RJN (2010) Gall-inducing Pachypsylla celtidis (Psyllidae) infiltrate hackberry trees with high concentrations of phytohormones. J Plant Inter 5:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2010.484552
Sugio A, Dubreuil G, Giron D, Simon JC (2015) Plant–insect interactions under bacterial influence: ecological implications and underlying mechanisms. J Exp Bot 66:467–478. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru435
Suzuki H, Yokokura J, Ito T, Arai R, Yokoyama C, Toshima H, Nagata S, Asami T, Suzuki Y (2014) Biosynthetic pathway of the phytohormone auxin in insects and screening of its inhibitors. Insect Biochem Molec 53:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.07.008
Takei M, Yoshida S, Kawai T, Hasegawa M, Suzuki Y (2015) Adaptive significance of gall formation for a gall-inducing aphids on Japanese elm trees. J Insect Phys 72:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2014.11.006
Takei M, Kogure S, Yokoyama C, Kouzuma Y, Suzuki Y (2018) Identification of an aldehyde oxidase involved in indole-3-acetic acid synthesis in Bombyx mori silk gland. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 83:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2018.1525275
Tanaka Y, Okada K, Asami T, Suzuki Y (2013) Phytohormones in Japanese mugwort gall induction by a gall-inducing gall midge. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 9:1942–1948. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.130406
Thermo Fisher Scientific (2021) DAPI counterstaining protocols. https://www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/references/protocols/cell-and-tissue-analysis/dapi-protocol/basic-dapi-counterstaining-protocols.html
Tivendale ND, Ross JJ, Cohen JD (2014) The shifting paradigms of auxin biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci 19:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.09.012
Tooker JF, De Moraes CM (2011) Feeding by Hessian fly (Mayetiola destructor [Say]) larvae on wheat increases levels of fatty acids and indole-3-acetic acid but not hormones involved in plant defense signaling. J Plant Growth Regul 30:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-010-9177-5
Tooker JF, Helms AM (2014) Phytohormone dynamics associated with gall insects, and their potential role in the evolution of the gall-inducing habit. J Chem Ecol 40:742753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-014-0457-6
Walters DR, McRoberts N, Fitt BDL (2008) Are green islands red herrings? significance of green islands in plant interactions with pathogens and pests. Biol Rev 83:79–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2007.00033.x
Wang X, Lin S, Liu D, Gan L, McAvoy R, Ding J, Li Y (2020) Evolution and roles of cytokinin genes in angiosperms 1: Do ancient IPTs play housekeeping while non-ancient play regulatory roles? Hortic Res 7:28. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-019-0211-x
Weissbach H, King W, Sjoerdsma A, Udenfriend S (1959) Formation of indole-3-acetic acid from tryptamine in animals: a method for the estimation of indole-3-acetic acid in tissues. J Biol Chem 234:81–86
Werren JH (1997) Biology of Wolbachia. Annu Rev Entomol 42:587–609. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.42.1.587
Witiak SM (2006) Hormonal and molecular investigations of phylloxera leaf gall development. Dissertation, Pennsylvania State University, http://etda.libraries.psu.edu/theses/approved/WorldWideIndex/ETD-1564/index.html
Woodward A, Bartel B (2005) Auxin: regulation, action, and interaction. Ann Bot 95:707–735. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci083
Wu J, Baldwin IT (2010) New insights into plant responses to the attack from insect herbivores. Annu Rev Genet 44:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163500
Xie G, Keyhani NO, Bonner CA, Jensen RA (2003) Ancient origin of the tryptophan operon and the dynamics of evolutionary change. Microbiol Mol Biol R 67:303–342. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.67.3.303-342.2003
Yamaguchi H, Tanaka H, Hasegawa M, Tokuda M, Asami T, Suzuki Y (2012) Phytohormones and willow gall induction by a gall-inducing sawfly. New Phytol 196:586–595. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04264.x
Yokoyama C, Takei M, Kouzuma Y, Nagata S, Suzuki Y (2017) Novel tryptophan metabolic pathways in auxin biosynthesis in silkworm. J Insect Physiol 101:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2017.07.006
Yue J, Hu X, Huang J (2014) Origin of plant auxin biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci 19:764–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.07.004
Zavala ME, Brandon DL (1983) Localization of a phytohormone using immunocytochemistry. J Cell Biol 97:1235–1239. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.97.4.1235
Zhang H, Guiget A, Dubreuil G, Kisiala A, Andreas P, Emery RJN, Huguet E, Body M, Giron D (2017) Dynamics and origin of cytokinins involved in plant manipulation by a leaf-mining insect. Insect Sci 24:1065–1078. https://doi.org/10.1111/eea.12681
Zhao C, Navarro Escalante L, Chen H, Benatti TR, Qu J, Chellapilla S, Waterhouse RM, Wheeler D, Andersson MN, Bao R, Batterton M, Behura SK, Blankenburg KP, Caragea D, Carolan JC, Coyle M, El-Bouhssini M, Francisco L, Friedrich M, Gill N, Grace T, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Han Y, Hauser F, Herndon N, Holder M, Ioannidis P, Jackson L, Javaid M, Jhangiani SN, Johnson AJ, Kalra D, Korchina V, Kovar CL, Lara F, Lee SL, Liu X, Lofstedt C, Mata R, Mathew T, Muzny DM, Nagar S, Nazareth LV, Okwuonu G, Ongeri F, Perales L, Peterson BF, Pu LL, Robertson HM, Schemerhorn BJ, Scherer SE, Shreve JT, Simmons D, Subramanyam S, Thornton RL, Xue K, Weissenberger JM, Williams CE, Worley KC, Zhu D, Zhu Y, Harris MO, Shukle RH, Werren JH, Zdobnov EM, Chen MS, Brown SJ, Stuart JJ, Richards S (2015) A massive expansion of effector genes underlies gall-formation in the wheat pest Mayetiola destructor. Curr Biol 25:613–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.12.057
Zhao C, Rispe C, Nabity PD (2019) Secretory RING finger proteins function as effectors in a grapevine galling insect. BMC Genomics 20:923. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6313-x
Zhu J, Oger PM, Schrammeijer B, Hooykaas PJJ, Farrand SK, Winans SC (2000) The bases of crown gall tumorigenesis. J Bacteriol 182:3885–3895. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.182.14.3885-3895.2000
Acknowledgements
We thank Lisa Galli, Dr. Sarah Witiak, Dr. Blake Riggs, and Dr. Gary Felton for technical advice and guidance. Dr. Tim Craig for collecting and shipping samples, Stephannie Seng and Natalie Fiutek for their assistance with lab work, and Dr. John Tooker for comments on an earlier version of this manuscript. The authors wish to thank the reviewers for their constructive and insightful remarks improving our manuscript. This research was supported by the ARCS Foundation: Northern California Chapter to GEP, National Science Foundation Grant DEB 0943263 to EFC, and National Institute of Health MS/PhD Bridges: R25-GM048972 to GEP
Funding
The ARCS Foundation: Northern California Chapter to GEP, National Science Foundation Grant DEB 0943263 to EFC and National Institute H MS/PhD Bridges: R25-GM048972 to GEP
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Heikki Hokkanen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponce, G.E., Fuse, M., Chan, A. et al. The localization of phytohormones within the gall-inducing insect Eurosta solidaginis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Arthropod-Plant Interactions 15, 375–385 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-021-09817-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-021-09817-5