Abstract
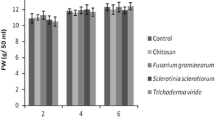
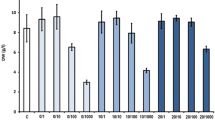
Linum album accumulates anti-tumor podophyllotoxin (PTOX) and its related lignans, which were originally isolated from an endangered species Podophyllum. In the present study, we examined the effects of five fungal extracts on the production of lignans in L. album cell cultures. Fusarium graminearum extract induced the highest increase of PTOX [143 μg g−1 dry weight (DW) of the L. album cell culture], while Rhizopus stolonifer extract enhanced the accumulation of lariciresinol up to 364 μg g−1 DW, instead of PTOX. Typical elicitors, such as chitin, chitosan, or methyl jasmonate (MeJA), were shown to be less effective in lignan production in L. album cell cultures. These results verified the advantages of fungal extracts to increase lignan production in L. album cell culture, and suggested potential on-demand metabolic engineering of lignan biosynthesis using differential fungal extracts.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldi A, Jain A, Bisaria VC (2008) Co-culture of arbuscular mycorrhiza-like fungi (Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera) with plant cells of Linum album for enhanced production of podophyllotoxins: a first report. Biotechnol Lett 30:1671–1677
Berim A, Spring O, Conrad J, Maitrejean M, Boland W, Petersen M (2005) Enhancement of lignan biosynthesis in suspension cultures of Linum nodiflorum by coronalon, indanoyl-isoleucine and methyl jasmonate. Planta 222:769–776
Canel C, Moraes RM, Dayan FE, Ferreira D (2000) Molecules of interest: podophyllotoxin. Phytochemistry 54:115–120
Farkya S, Bisaria VS, Sirvastava AK (2004) Biotechnological aspects of the production of the anticancer drug podophyllotoxin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:504–519
Farkya S, Julka A, Mehra R, Datta V, Srivastava AK, Bisaria VS (2005) Enhanced production of secondary metabolites by biotic elicitors in plant cell suspension cultures. In: 5th Asia Pacific Biochemical Engineering Conference. Jeju Island, Korea
Federolf K, Alfermann AW, Fuss E (2004) Aryltetralin-lignan formation in two different cell lines of Linum album: deoxypodophyllotoxin 6-hydroxylase, a key enzyme for the formation of 6-methoxypodophyllotoxin. Phytochemistry 68:1397–1406
Figgitt DP, Denever SP, Dewick PM, Jackson DE, Willians P (1989) Topoisomerase II: a potential target for novel antifungal agents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 160:257–262
Fuss E (2003) Lignans in plant cell and organ cultures: an overview. Phytochem Rev 2:307–320
Hano C, Addi M, Bensaddek D, Cronier S, Laine E (2006) Differential accumulation of monolignol-derived compounds in elicited flax (Linum usitatissimum) cell suspension cultures. Planta 223:975–989
Imre E, Somssich IE, Hahlbrok K (1998) Pathogen defence in plant—a paradigm of biological complexity. Trends Plant Sci 3:86–90
Ionkova I (2007) Biotechnological approaches for the production of lignans. Phcog Rev 1:57–68
Muranaka T, Miyata M, Ito K, Tachibana S (1998) Production of podophyllotoxin in Juniperus chinensis callus cultures treated with oligosaccharides and a biogenetic precursor. Phytochemistry 49:491–496
Petersen M, Alfermann AW (2001) The production of cytotoxic lignans by plant cell cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:135–142
Van Fürden B, Humburg A, Fuss E (2005) Influence of methyl jasmonate on podophyllotoxin and 6-methoxypodophyllotoxin accumulation in Linum album cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep 24:312–317
Yousefzadi M, Sharifi M, Behmanesh M, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Cusido RM, Palazon J (2010a) An approach to the biotechnological production of podophyllotoxin: a potential natural product for clinical anticancer drugs. Eng Life Sci 4:281–292
Yousefzadi M, Sharifi M, Behmanesh M, Moyano E, Palazon J (2010b) Salicylic acid improves podophyllotoxin production in cell cultures of Linum album by increasing the expression of genes related with its biosynthesis. Biotechnol Lett 32:1739–1743
Zhao J, Davis LC, Verpoorte R (2005) Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 23:283–333
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Tarbiat Modares University and Suntory Foundation for Life Sciences, Bioorganic Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahabadi, S.E., Sharifi, M., Safaie, N. et al. Increased lignan biosynthesis in the suspension cultures of Linum album by fungal extracts. Plant Biotechnol Rep 5, 367–373 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-011-0190-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-011-0190-3