Abstract
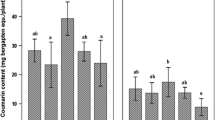
Cell suspension cultures of Linum album were developed from internode portions of in vitro germinated plant in Gamborg’s B5 medium supplemented with 0.4 mg naphthalene acetic acid/l. The highest biomass was 8.5 g/l with podophyllotoxin and 6-methoxypodophyllotoxin at 29 and 1.9 mg/l, respectively after 12 d cultivation. Co-cultures of L. album cells with axenically cultivable arbuscular mycorrhiza-like fungi, Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera, were established for the first time. These enhanced podophyllotoxin and 6-methoxypodophyllotoxin production by about four- and eight-fold, respectively, along with a 20% increase in biomass compared to the control cultures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldi A, Bisaria VS, Srivastava AK (2007) Biotechnological approaches for production of some plant based chemotherapeutics. In: Kayser O, Quax WJ (eds) Medicinal plant biotechnology—from basic research to industrial applications. Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim, Germany, pp 117–156
Barazani O, Benderoth M, Groten K, Kuhlemeier C, Baldwin IT (2005) Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera increase growth performance at the expense of herbivore resistance in Nicotiana attenuate. Oecologia 146:234–243
Chattopadhyay S, Srivastava AK, Bhojwani SS, Bisaria VS (2001) Development of suspension culture of Podophyllum hexandrum for the production of podophyllotoxin. Biotechnol Lett 23:2063–2066
Chauhan AK, Das A, Kharkwal AC, Varma A (2006) Impact of micro-organisms on environment and health. In: Chauhan AK, Varma A (eds) Microbiology series—microbes: health and environment, I.K. International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, pp 1–12
Dixon RA (2001) Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature 411:843–847
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Roberts PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Federolf K, Alfermann AW, Fuss E (2007) Aryltetralin–lignan formation in two different cell suspension cultures of Linum album: deoxypodophyllotoxin 6-hydroxylase, a key enzyme for the formation of 6-methoxypodophyllotoxin. Phytochem 68:1397–1406
Grayer RJ, Kokubun T (2001) Plant–fungal interactions: the search of phytoalexins and other antifungal compounds from higher plants. Phytochem 56:253–263
Harley JL, Smith SE (1983) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic Press, New York, p 483
Kaefer E (1977) Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv Genet 19:33–131
Kumari R, Pham GH, Sachdev M, Garg AP, Varma A (2004) Symbiotic fungi for eco-friendly environment: a perspective. Nat Prod Rad 3:396–400
Morton JB, Benny GL (1990) Revised classification of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Zygomycetes); A new order, Glomales, two new suborders, Glomineae and Gigasporineae, with an emendation of Glomaceae. Mycotaxon 37:471–491
Nicholas JB, John OW, Meromit A, Hassar TN (1994) Quantitative relationship between phenylalanine ammonia-lyase levels and phenylpropanoid accumulation in transgenic tobacco identifies a rate-determining step in natural product synthesis. Plant Biol 91:7608–7612
Rai MK, Singh An, Arya D, Varma A (2001) Positive growth responses of the medicinal plants Withania somnifera and Spilanthes calva to inoculation by Piriformospora indica in a field trial. Mycorrhizae 11:123–128
Rai MK, Varma A (2005) Arbuscular mycorrhizae—like biotechnological potential of Piriformospora indica, which promotes the growth of Adhatoda vasica. Electron J Biotechnol ISSN 8:107–112
Safir GR, Boyer JS, Gerdemann JW (1971) Mycorrhizal enhancement of water transports in soybean. Science 172:581–583
Sahay NS, Varma A (1999) Piriformospora indica: a new biological hardening tool for micropropogated plants. FEMS Microbiol Lett 181:297–302
Sahay NS, Varma A (2000) Biological approach towards increasing the survival rates of micropropogated plants. Curr Sci 78:126–129
Singh AN, Singh AR, Kumari M, Rai MK, Varma A (2003) Biotechnology importance of Piriformospora indica—a novel symbiotic mycorrhiza-like fungus: an overview. Indian J Biotechnol 2:65–75
Singh AN, Singh AR, Varma A (2002) Piriformospora indica—in vitro raised leguminous plants: a new dimension in establishment and phyto-promotion. Indian J Biotechnol 1:372–376
Smith RL, Gilkerson E (1979) Quantitation of glycosaminoglycan hexosamine using 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolone hydrazone hydrochloride. Anal Biochem 98:478–480
Smith SE, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Smollny T, Wichers H, Kalenberg S, Shahsavari A, Petersen M, Alfermann AW (1998) Accumulation of podophyllotoxin and related lignans in cell suspension cultures of Linum album. Phytochem 48:575–579
Tiwari P, Adholeya A (2002) In-vitro coculture of two AMF isolates—Gigaspora margarita and Glomus intraredices on Ri-T DNA transformed roots. FEMS Microbiol Lett 206:39–43
van Furden B, Hamburg A, Fuss E (2005) Influence of methyl jasmonate on podophyllotoxin and 6-methoxypodophyllotoxin accumulation in Linum album cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep 24:312–317
Verma S, Varma A, Rexer KH, Kost G, Sarbhoy A, Bisen P, Butehorn B, Franken P (1998) Piriformospora indica, gen. et sp. nov., a new root-colonizing fungus. Mycologia 95:896–903
Warcup JH, Talbot PHB (1967) Perfect states of Rhizoctonias associated with orchids. New Phytologists 66:631–641
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to Prof. Ajit Varma, Amity Institute of Herbal and Microbial Studies, Noida, India for providing fungal cultures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Intellectual property rights of the work is covered under Patent application no. 1266/DEL/2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldi, A., Jain, A., Gupta, N. et al. Co-culture of arbuscular mycorrhiza-like fungi (Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera) with plant cells of Linum album for enhanced production of podophyllotoxins: a first report. Biotechnol Lett 30, 1671–1677 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9736-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9736-z