Abstract
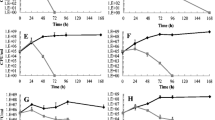
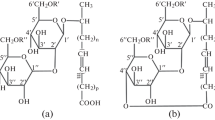
ε-Poly-L-lysine (ε-PL) is a natural antimicrobial cationic peptide. Antimicrobial activity of ε-PL is closely related to its molecular weight (Mw). However, the antimicrobial mechanisms of ε-PL with different Mws are still vague. In this study, Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used as the model system to analyze the mechanism from these three aspects: cell wall, cell membrane, and metabolism. The results showed that high-Mw ε-PL (1-3 kDa and >3 kDa) and commercial ε-PL product caused cell wall lesions, and significantly improved cell membrane permeability compared to low-Mw ε-PL (<1 kDa), resulting in leaking of the protoplasm through the pores and cell death. Furthermore, metabolomics analysis showed that high-Mw ε-PL (1-3 kDa and >3 kDa) and product displayed higher inhibition effect on the glycolysis pathway and tricarboxylic cycle than that of low-Mw ε-PL (<1 kDa).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Gould and N. Russell, Food preservatives, Springer (2003).
M. L. Ritchie and T. N. Romanuk, Plos One, 7, e34938 (2012).
C. Gao, Y. Tao, D. Jie, H. Fang, H. Luo and Y. Wan, Food Hydrocolloids, 36, 204 (2014).
Z. Xu, Z. Xu, X. Feng, D. Xu, J. Liang and H. Xu, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 100, 15 (2016).
J. Y. Miao, J. L. Zhou, G. Liu, F. L. Chen, Y. Chen, X. Gao, W. Dixon, M. Song, H. Xiao and Y. Cao, Food Control, 59, 609 (2016).
M. Hyldgaard, T. Mygind, B. S. Vad, M. Stenvang, D. E. Otzen and R. L. Meyer, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 80, 7759 (2014).
R. Su, T. Li, D. Fan, J. Huang, J. Zhao, B. Yan, W. Zhou, W. Zhang and H. Zhang, J. Sci. Food Agric., 99, 6 (2019).
S. Shima, H. Matsuoka, T. Iwamoto and H. Sakai, J. Antibiot., 37, 11 (1984).
M. Takehara, A. Hibino, M. Saimura and H. Hirohara, Biotechnol. Lett., 32, 9 (2010).
M. Wei, Y. Ge, C. Li, Y. Chen, W. Wang, B. Duan and X. Li, Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol., 103, 23 (2018).
R. Ye, H. Xu, C. Wan, S. Peng, L. Wang, H. Xu, Z. P. Aguilar, Y. Xiong, Z. Zeng and H. Wei, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 439, 1 (2013).
K. Liu, X. Zhou and M. Fu, Postharvest Biol. Tec., 123, 94 (2017).
H. Li, C. He, G. Li, Z. Zhang, B. Li and S. Tian, Postharvest Biol. Tec., 147, 1 (2019).
E. Wang, Y. Li, B. L. Maguy, Z. Lou, H. Wang, W. Zhao and X. Chen, Food Chem., 294, 533 (2019).
E. C. I. Veerman, M. Valentijn-Benz, W. van't Hof, K. Nazmi, J. van Marle and A. V. N. Amerongen, Biol. Chem., 391, 1 (2010).
S. Zhang, J. Xiong, W. Lou, Z. Ning, D. Zhang and J. Yang, Food Control, 98, 113 (2019).
M. Z. Ding, X. Zhou and Y. Yuan, Metabolomics, 6, 1 (2010).
I. L. Shih, M. H. Shen and Y. T. J. B. T. Van, Bioresour. Technol., 97, 9 (2006)
R. Song, R. B. Wei, H. Y. Luo and D. F. J. M. Wang, Molecules, 17, 3 (2012).
F. Guilhelmelli, N. Vilela, P. Albuquerque, L. S. Derengowski, I. Silva-Pereira and C. Kyaw, Front Microbiol., 4, 353 (2013).
M. R. Yeaman and N. Y. Yount, Pharmacol. Rev., 55, 1 (2003).
A. S. Ladokhin and S. H. J. B.-B. White, BBA-Biomembranes, 1514, 2 (2001).
V. Teixeira, M. J. Feio and M. Bastos, Prog. Lipid Res., 51, 2 (2012).
K. A. Brogden, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 3, 3 (2005).
M. A. Singer and S. Lindquist, Trends in Biotechnol., 16, 11 (1998).
S. C. Sharma, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 152, 11 (1997).
J. L. Parrou, M. A. Teste and J. Francois, J. Microbiol., 143, 6 (1997).
C. Godon, G. Lagniel, J. Lee, J. M. Buhler, S. Kieffer, R. Perrot, H. Boucherie, M. B. Toledano and J. Labarre, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 35 (1998).
V. Natera, L. Sobrevals, A. Fabra and S. Castro, Curr. Microbiol., 53, 6 (2006).
S. Yap and S. J. A. O. M. Lim, Arch Microbiol., 135, 3 (1983).
H. Takagi, F. Iwamoto and S. Nakamori, Appl. Microbiol. Biot., 47, 4 (1997).
S. Kubota, I. Takeo, K. Kume, M. Kanai, A. Shitamukai, M. Mizunuma, T. Miyakawa, H. Shimoi, H. Iefuji and D. Hirata, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 68, 4 (2004).
H. Li, M. Ma, S. Luo, R. Zhang, P. Han and W. Hu, Int. J. Biochem. Cell B., 44, 7 (2012).
M. Ding, X. Wang, Y. Yang and Y. Yuan, OMICS: J. Integrative Biol., 15, 10 (2011).
A. Barsch, H. G. Carvalho, J. V. Cullimore and K. Niehaus, J. Biotechnol., 127, 1 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (Project 2018YFD0400205), the Tianjin Municipal Commission of Education Research Plan (2017KJ011), Tianjin Engineering Research Center of Microbial Metabolism and Fermentation Process Control (ZXKF20180101), and Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (18JCQNJC78600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Wang, F., Tan, Z. et al. Antifungal mechanisms of ε-poly-L-Lysine with different molecular weights on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 37, 482–492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-019-0466-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-019-0466-9