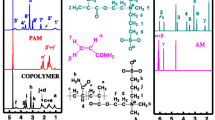
Abstract
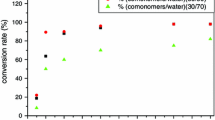
Molecular weight distribution of copolyacrylonitrile, which was obtained from precipitation copolymerization without and with using dispersants in mixed solution, is studied. The contribution ratio of liquid phase polymerization and solid phase polymerization under different polymerization conditions could be worked out through the formula, which has been deduced in literature. From the calculated results, common points of each reaction system are, i) contribution ratio (r) of solid phase to liquid phase decreases with the increase of water content; thus the solid phase polymerization is gradually strengthened, which is apt to form chain of high molecular weight, ii) the higher temperature leads to higher compatibility between water and DMSO; thus the solid phase polymerization contribution would decrease, while the value of r is considerably larger. The limit molecular weight distribution of the system without dispersants in 100% water is approaching to 2; thus the corresponding r becomes larger, the molecular weight distribution ratio (Q) decreases in the system with dispersants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. W. Liu, S. K. Zhang, J. Wang, S. K. Ryu and R. G. Jin, Carbon Lett., 13, 133 (2012).
W. S. Lyoo and J. P. Kim, Colloid Polym. Sci., 276, 951 (1998).
V. D. Keshav, Synth. Fibers, 10, 5 (1997).
A. K. Gupta, D. K. Paliwal and P. Bajaj, Polymer Reviews, 31, 1 (1991).
J. S. Tsai and C. H. Lin, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 42, 3045 (1991).
J. Zhang, F. J. Bu, Y. Q. Dai, L. W. Xue, Z. X. Xu, S. K. Ryu and R. G. Jin, Carbon Lett., 11, 22 (2010).
R. Devasia, C. P. Reghunadhan Nair and K. N. Ninan, European Polymer J., 38, 2003 (2002).
S. X. Zhou, Z. X. Weng and Z. M. Huang, J. Appl. Polymer Sci., 8, 1431 (2001).
Y. Z. Wang, C. F. Sun, C. G. Wang and B. Zhu, J. Shandong Univ., 33, 362 (2003).
Toray, J9-412269 Pat. 1997.2.10.
Mitsubishi Rayon, J9-13220 Pat. 1997.1.14.
Q. F. Qin, Y. Q. Dai, K. Yi, L. Zhang, S. K. Ryu and R. G. Jin, Carbon Lett., 11, 176 (2010).
S. S. Moghadam and S. H. Bahrami, Iran Polym. J., 14, 1032 (2005).
M. A. Ali, E. A. A. Ajbar and K. Alhumaiji, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27(1), 364 (2010).
A. K. Kashyap and V. Kalpagam, J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem., 17, 225 (1979).
C. G. Wang and B. Zhu, Polyacrylonitrile Based Carbon Fibers, Science Press, Beijing (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S.K., Liu, W.W., Zhang, H.B. et al. Contribution of the solid phase polymerization to the molecular weight distribution in acrylonitrile precipitation copolymerization. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 30, 746–750 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-012-0183-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-012-0183-0