Abstract
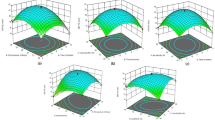
The aim of this research was to study the effect of furfural production from rice husk by hydrolysis accompanying supercritical CO2 (SC-CO2) extraction. The two-level fractional factorial design method was used to investigate the production process carried out with respect to furfural yield. The process variables are temperature range of 373–453 K, pressure 9.1–18.2 MPa, CO2 flow rate 8.3 × 10−5–1.7 × 10−4 kg/s (5–10 g/min), sulfuric acid concentration 1 to 7 (%wt) and ratio of liquid to solid (L/S) 5 : 1 to 15 : 1 (vol/wt). The results obtained from the experimental design showed that increasing temperature, pressure, CO2 flow rate and sulfuric acid concentration but decreasing ratio of liquid to solid would improve furfural yield. Moreover, furfural production by two-stage process (pre-hydrolysis and dehydration) can improve furfural yield further to be around 90% of theoretical maximum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. P. Dunlop, Furfural, Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, vol 11, 3rd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York (1984).
D. R. Arnold and J. L. Buzzard, A novel process for furfural production, Proceedings of South African Chemical Engineering Congress (2003).
K. J. Zeitsch, The chemistry and technology of furfural and its many by-products, Elsevier (2000).
H. D. Mansilla, J. Baeza, S. Urzua, G. Maturana, J. Villasenor and N. Duran, Bioresour. Technol., 66, 189 (1998).
B. P. Lavarack, G. J. Griffin and D. Rodman, Biomass Bioenerg., 23, 367 (2002).
C. Y. Park, Y. W. Ryu and C. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18, 475 (2001).
T. Sako, T. Sugeta, N. Nakazawa, T. Okubo and M. Sako, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 25, 372 (1992).
T. Sako, T. Sugeta, N. Nakazawa, K. Otake, M. Sato, K. Ishihara and M. Kato, Fluid Phase Equilib., 108, 293 (1995).
T. Gamse and R. Marr, Sep. Sci. Technol., 32, 355 (1997).
M. Sihvonen, E. Jarvenpaa, V. Hietaniemi and R. Huopalahti Trends Food Sci. Technol., 10, 217 (1999).
A. Demirbas, Energy Conv. Manag., 42, 279 (2001).
H. L. Dinsmore and S. Nagy, J. Assoc. Off. Ana. Chem., 57, 332 (1974).
D. C. Montgomery, Design and analysis of experiments, 5th ed., John Wiley & Sons New York (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sangarunlert, W., Piumsomboon, P. & Ngamprasertsith, S. Furfural production by acid hydrolysis and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction from rice husk. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 24, 936–941 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0101-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0101-z