Abstract
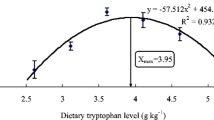
A 56-day feeding trial was conducted to examine the dietary leucine requirement of juvenile Japanese seabass in seawater floating net cages (1.5 m × 1.5 m × 2.0 m). Six isonitrogenous (crude protein 40%) and isoenergetic (gross energy 20 kJ g−1) diets were formulated to contain different concentrations of leucine (0.9%, 1.49%, 2.07%, 2.70%, 3.30% and 3.88% of dry matter). Crystalline L-amino acids were supplemented to simulate the whole body amino acid pattern of Japanese seabass except for leucine. Three groups (30 fish individuals each, 8.0 g ± 0.20 g in initial weight) were fed to apparent satiation at 5:00 and 17:30 every day. During the experimental period, the water temperature ranged from 26 to 32δC and salinity from 26 to 30, and the dissolved oxygen was maintained at 7 mg L−1. The results showed that weight gain (WG), nitrogen retention (NR), feed efficiency (FE) and protein efficiency ratio (PER) were significantly increased when dietary leucine was increased from 0.90% to 2.70% of dry matter, and then declined. WG was the highest when fish were fed D4 containing 2.70% of leucine. No significant differences were observed in body composition among dietary treatments (P > 0.05). Considering the change of WG, the optimum dietary leucine requirement of juvenile Japanese seabass was either 2.39% of dry matter or 5.68% of dietary protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidi, S. F., and Khan, M. A., 2007. Dietary leucine requirement of fingerling Indian major carp, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Aquaculture Research, 38: 478–486, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2007.01687.x.
Ai, Q. H., Mai, K. S., Li, H. T., Zhang, C. X., Zhang, L., Duan, Q. Y., Tan, B. P., Xu, W., Ma, H. M., Zhang, W. B., and Liufu, Z. G., 2004a. Effects of dietary protein to energy ratios on growth and body composition of juvenile Japanese seabass, Lateolabrax japonicus. Aquaculture, 230: 507–516, DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2003.09.040.
Ai, Q. H., Mai, K. S., Zhang, C. X., Xu, W., Duan, Q. Y., Tan, B. P., and Liufu, Z. G., 2004b. Effects of dietary vitamin C on growth and immune response of Japanese seabass, Lateolabrax japonicus. Aquaculture, 242: 489–500, DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.08.016.
Alliot, E., Febvre, A., Metailler, R., and Pastoureaud, A., 1974. Besoins nutritifs du bar (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Etude du taux de protéine et du taux de lipide dans le régime. Actes Colloq, CNEXO, 1: 215–228.
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC), 1995. Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International. 16th edition. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA.
Balage, M., Dupont, J., Mothe-Satney, I., Tesseraud, S., Mosoni, L., and Dardevet, D., 2011. Leucine supplementation in rats induced a delay in muscle IR/PI3K signaling pathway associated with overall impaired glucose tolerance. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 22: 219–226.
Chance, R. E., Mertz, E. T., and Halver, J. E., 1964. Nutrition of salmonid fishes: XII Isoleucine, leucine, valine and phenylalanine requirements of chinook salmon and interrelation between isoleucine and leucine for growth. Journal of Nutrition, 83: 177–185.
Choo, P. S., Smith, T. K., Cho, C. Y., and Ferguson, H. W., 1991. Dietary excesses of leucine influence growth and body composition of rainbow trout. Journal of Nutrition, 121: 1932–1939.
Crozier, S. J., Kimball, S. R., Emmert, S. W., Anthony, J. C., and Jefferson, L. S., 2005. Oral leucine administration stimulates protein synthesis in rat skeletal muscle. Journal of Nutrition, 135: 376–382.
de la Higuera, M., 2001. Effcts of nutritional factors and feed characteristics on feed intake. In: Food Intake in Fish. Houlihan, D., et al., eds., Blackwell, Oxford, 250–268.
Dardevet, D., Sornet, C., Bayle, G., Prugnaud, J., Pouyet, C., and Grizard, J., 2002. Postprandial stimulation of muscle protein synthesis in old rats can be restored by a leucine-supplemented meal. Journal of Nutrition, 132: 95–100.
D’Mello, J. P. F., 2003. Adverse effects of amino acids. In: Amino Acids in Animal Nutrition. 2nd edition. D’Mello, J. P. F., ed., CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK, 125–142.
Donato Jr., J., Pedrosa, R. G., de Araujo Jr., J. A., Pires, I. S., and Tirapegui, J., 2007. Effects of leucine and phenylalanine supplementation during intermittent periods of food restriction and refeeding in adult rats. Life Science, 81: 31–39.
Eller, L. K., Saha, D. C., Shearer, J., and Reimer, R. A., 2013. Dietary leucine improve whole-body insulin sensitivity independent of body fat in diet-induced obese Sprague-Dawley rats. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 24(7): 1285–1294, DOI: org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.10.004.
Forster, I., and Ogata, H. Y., 1998. Lysine requirement of juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys oliíaceus and juvenile red sea bream Pagrus major. Aquaculture, 161: 131–142.
Freudenberg, A., Petzke, K. J., and Klaus, P. S., 2012. Comparison of high-protein and leucine supplementation in the prevention of metabolic syndrome and related disorders in mice. Journal of Nutrtional Biochemistry, 23: 1524–1530, DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.10.005.
Garlick, P. J., 2005. The role of leucine in the regulation of protein metabolism. Journal of Nutrition, 135(6 Suppl): 1553S–1556S.
Hughes, S. G., Rumsey, G. L., and Nesheim, M. C., 1984. Effects of dietary excess of branched-chain amino acids on the metabolism and tissue composition of lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 78A: 413–418.
Kaushik, S. J., 1998. Whole body amino acid composition of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax), gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and turbot (Psetta maxima) with an estimation of their IAA requirement profiles. Aquatic Living Resources, 11(5): 355–358, DOI: 10.1016/S0990-7440(98)80007-7.
Khan, M. A., and Abidi, S. F., 2007. Total aromatic amino acid requirement of Indian major carp Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fry. Aquaculture, 267: 111–118, DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture 2007.02.025.
Kimball, S. R., and Jefferson, L. S., 2006. Signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms through which branched-chain amino acids mediate translational control of protein synthesis. Journal of Nutrition, 136(1 Suppl): 227S–231S.
Li, A. J., 1996. Aquaculture Nutrition and Feeds. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, 21pp.
Luo, Z., Liu, Y. J., Mai, K. S., Tian, L. X., Yang, H. J., and Tan, X. Y., 2005. Dietary l-methionine requirement of juvenile grouper Epinephelus coioides at a constant dietary cystine level. Aquaculture, 249: 409–418, DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.04.030.
López, N., Sánchez, J., Picó, C., Palou, A., and Serra, F., 2010. Dietary L-leucine supplementation of lactation rats results in a tendency to increase lean/fat ratio associated to lower orexigenic neuropeptide expression in hypothalamus. Peptides, 31: 1361–1367, DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.03.028.
Macotela, Y., Emanuelli, B., Bang, A. M., Espinoza, D. O., Boucher, J., Beebe, K., Gall, W. C., and Kahn, R., 2011. Dietary leucine-An environmental modifier of insulin resistance acting on multiple levels of metabolism. PLoS One, 6: e21187, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021187.
Mai, K. S., Wan, J. L., Ai, Q. H., Xu, W., Liufu, Z. G., Zhang, L., Zhang, C. X., and Li, H. T., 2006. Dietary methionine requirement of large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea R. Aquacuture, 253: 564–572, DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.08.010.
Millamena, O. M., Bautista, M. N., Reyes, O. S., and Kanazawa, A., 1997. Threonine requirement of juvenile marine shrimp Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture, 151: 9–14, DOI: 10.1016/S0044-8486(96)01486-x.
Millamena, O. M., Teruel, M. B., Kananzawa, A., and Teshima, S., 1999. Quantitative dietary requirements of postlarval tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon, for histidine, isoleucine, phenylalanine and tryptophan. Aquaculture, 179: 169–179, DOI: 101016/S0044-8486(99)00160-x.
Ng, W. K., and Hung, S. S. O., 1995. Estimating the ideal dietary indispensable amino acid pattern for growth of white sturgeon. Aquacture Nutrition, 1: 85–94, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2095.1995.tb00023.x.
Rieu, I., Balage, M., Sornet, C., Giraudet, C., Pujos, E., Grizard, J., Mosoni, L., and Dardevet, D., 2006. Leucine supplementation improve smuscle protein synthesis in elderly men independently of hyperaminoacidaemia. Journal of Physiology, 575(1): 305–315, DOI: 10.1113/jphysio.2006.110742.
Rollin, X., 1999. Critical study of indispensable amino acids requirements of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fry. PhD thesis. Universitée catholique de Louvain, Louvain, Belgium, 17–30.
Tibaldi, E., and Tulli, F., 1999. Dietary threonine requirement of juvenile european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture, 175: 155–166, DOI: 10.1016/S0044-8486 (99)00029-0.
Toneto, A. T., Salomao, E. M., Sebinelli, M. C. C., and Gomes-Marcondes, 2012. Effects of leucine-rich diet and exercise on inflammatory response produced by the tumour growth in rats. Abstract/Cytokine, 59: P053, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2012.06.137.
Vianna, D., Resende, G. F. T., Torres-Leal, F. L., Pantaleāo, L. C., Donato, J., and Tirapegui, J., 2012. Long-term leucine supplementation reduces fat mass gain without changing body protein status of aging rats. Nutrition, 28: 182–189, DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2011.04.004.
Wilson, R. P., and Halver, J. E., 1986. Protein and amino acid requirements of fishes. Annual Review of Nutrition, 6: 225–244.
Wilson, R. P., William, E. P., and Robinson, E. H., 1980. Leucine, isoleucine, valine and hisidine requrirementf of fingerling channel catfish. Journal of Nutrition, 110(4): 627–633.
Yamamoto, T., Shima, T., and Furutia, H., 2004. Antagonistic effects of branched chain amino acids induced by excess protein bound leucine in diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture, 232: 539–550, DOI: 10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00543-X.
Zeitoun, I. H., Ullrey, D. E., and Magee, W. T., 1976. Quantifying nutrient requirements of fish. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 33: 167–172.
Zhang, C. X., Mai, K. S., Ai, Q. H., Zhang, W. B., Duan, Q. Y., Tan, B. P., Ma, H. M., Xu, W., Liufu, Z. G., and Wang, X. J., 2006. Dietary phosphorus requirement of juvenile Japanese seabass, Lateolabrax japonicus. Aquaculture, 255: 201–209, DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.11.040.
Zhang, Y., Guo, K., LeBlanc, R. E., Loh, D., Schwartz, G. J., and Yu, Y. H., 2007. Increasing dietary leucine intake reduces diet-induced obesity and improves glucose and cholesterol metabolism in mice via multimechanisma. Diabetes, 56(6): 1647–1654.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Cheng, Z., Mai, K. et al. Dietary leucine requirement of juvenile Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). J. Ocean Univ. China 14, 121–126 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2387-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2387-5