Abstract
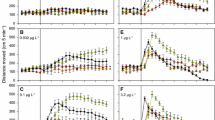
In this research, the toxic effects of deltamethrin (DM) on the behavior responses of Zebra fish (Danio rerio) in the characteristic of behavior strength were investigated followed by an assessment of an in situ remediation of the DMpollution using sodium percarbonate. Behavior strength of Danio rerio was approximately 0.83 in the control group and was slightly higher than 0.83 in the sublethal treatment (0.1 TU (toxic unit)), which suggested that sublethal DMexposure could induce a stimulation effect in 48 h of exposure. In lower DM concentration treatments (0.5 and 1.0 TU), behavior strength could be inhibited significantly. Behavior responses of Danio rerio showed a gradually increased tendency when they were exposed to higher concentration of DM, and the declining amplitudes of behavior strength changed with the increase of DMconcentrations. These results suggested that DM had evident acute toxicity effects on the behavior responses of Danio rerio with a good dose-effect relationship. The in situ remediation of the DM pollution using sodium percarbonate showed that the toxic effect of DM on behavior responses of Danio rerio could be eliminated even in the highest concentration of DM (5.0 TU). Meanwhile, the behavior response of Danio rerio in the treatment of sodium percarbonate was the same as in the control, which indicated that sodium percarbonate had no evident toxic effects on the behavior of Danio rerio in the current concentration. This study suggested that adding sodium percarbonate in situ might be a good way to eliminate the DM toxic effects.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang S, Zhao X, Sun Y, Ma J, Gao X, Xie T, Xu D, Yu Y, Zhao Y. Pollution of hazardous substances in industrial construction and demolition wastes and their multi-path risk within an abandoned pesticide manufacturing plant. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2017, 11(1): 12
Wiles J A, Jepson P C. Substrate-mediated toxicity of deltamethrin residues to aphid predators: estimation of toxicity factors to aid risk assessment. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1994, 27(3): 384–391
Liu P, Liu Y, Liu Q, Liu J. Photodegradation mechanism of deltamethrin and fenvalerate. Journal of Environmental Sciences- China, 2010, 22(7): 1123–1128
Al-Makkawy H K, Madbouly MD. Persistence and accumulation of some organic insecticides in Nile water and fish. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 1999, 27(1–2): 105–115
Cui J T, Zhang W, Yang X T. Isolating and degrading features of deltamethrin-degrading bacteria. Journal of Safety & Environment, 2009, 9(6): 59–62 (in Chinese)
Gómez M V, Caballero R, Vázquez E, Moreno A, de la Hoz A, Díaz-Ortiz ÁGreen and chemoselective oxidation of sulfides with sodium perborate and sodium percarbonate: nucleophilic and electrophilic character of the oxidation system. Green Chemistry, 2007, 9(4): 331–336
Chantarasuwan C, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W. Effects of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate on yield and characteristics of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Food Science & Technology International, 2011, 17(4): 403–414
Bjørsvik H R, Merinero J A V, Liguori L. Nitroarene catalyzed oxidation with sodium percarbonate or sodium perborate as the terminal oxidant. Tetrahedron Letters, 2004, 45(47): 8615–8620
Zhang Y H, Xue CM, Guo C H. Application sodium percarbonate to oxidative degradation trichloroethylene contamination in groundwater. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2011, 10(2): 1668–1673
Wang L, Qian H, Zhang M. Study on the degradation of pyrethroids pesticides by sodium percarbonate. Chemical Industry Times, 2009, 23(2): 10–13 (in Chinese)
Zhang G, Chen L, Chen J, Ren Z, Wang Z, Chon T S. Evidence for the stepwise behavioral response model (SBRM): the effects of carbamate pesticides on Medaka (Oryzias latipes) in an online monitoring system. Chemosphere, 2012, 87(7): 734–741
Ren Z, Zhang X, Wang X, Qi P, Zhang B, Zeng Y, Fu R, Miao M. AChE inhibition: one dominant factor for swimming behavior changes of Daphnia magna under DDVP exposure. Chemosphere, 2015, 120(1): 252–257
Zhang L, An J, Zhou Q. Single and joint effects of HHCB and cadmium on zebrafish (Danio rerio) in feculent water containing bedloads. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2012, 6(3): 360–372
Schulte C, Nagel R. Testing acute toxicity in the embryo of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio, as an alternative to the acute fish test: preliminary results. Alternatives to Laboratory Animals, 1994, 22 (1): 12–19
Huang Y, Zhang J, Han X, Huang T. The use of zebrafish (Danio rerio) behavioral responses in identifying sublethal exposures to deltamethrin. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2014, 11(4): 3650–3660
Ren Z, Wang Z. The differences in the behavior characteristics between Daphnia magna and Japanese madaka in an on-line biomonitoring system. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 2010, 22(5): 703–708
Kozińska A. Dominant pathogenic species of mesophilic aeromonads isolated from diseased and healthy fish cultured in poland. Journal of Fish Diseases, 2007, 30(5): 293–301
Sandbacka M, Christianson I, Isomaa B. The acute toxicity of surfactants on fish cells, Daphnia magna, and fish—A comparative study. Toxicology In Vitro, 2000, 14(1): 61–68
Villegas-Navarro A, Romero G M C, Rosas L E, Dominguez A R, Sachetin M W. Evaluation of Daphnia magna as an indicator of toxicity and treatment efficy of textile wastewaters. Environment International, 1999, 25(5): 619–624
El-Sayed Y S, Saad T T, El-Bahr S M. Acute intoxication of deltamethrin in monosex Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus with special reference to the clinical, biochemical and haematological effects. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2007, 24(3): 212–217
Viran R, Ünlü Erkoç F, Polat H, Koçak O. Investigation of acute toxicity of deltamethrin on guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2003, 55(1): 82–85
The Environmental Protection Administration of China. GB3838–2002 of China Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. Beijing: Environmental Science Press, 2002 (in Chinese)
Marigoudar S R, Nazeer Ahmed R, David M. Ultrastructural responses and oxidative stress induced by cypermethrin in the liver of Labeo rohita. Chemistry & Ecology, 2013, 29(4): 296–308
Stebbing A R. Hormesis–the stimulation of growth by low levels of inhibitors. Science of the Total Environment, 1982, 22(3): 213–234
Yin L, Yang H, Si G, Ren Q, Fu R, Zhang B, Zhang X, Wang X, Qi P, Xia C, Ren Z, Chon T S, Kim H. Persistence parameter: a reliable measurement for behavioral responses of medaka (Oryzias latipes) to environmental stress. Environmental Modeling and Assessment, 2016, 21(1): 159–167
Ren Z, Li Z, Ma M, Wang Z, Fu R. Behavioral responses of Daphnia magna to stresses of chemicals with different toxic characteristics. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2009, 82(3): 310–316
Ansari B A, Sharma D K. Toxic effect of synthetic pyrethroid deltamethrin and neem based formulation Achook on zebrafish, Danio rerio. Trends in Biosciences, 2009, 2(2): 18–20
Kabalka G W, Deshpande S M, Wadgaonkar P P, Chatla N. The transformation of nitriles into amides using sodium percarbonate. Synthetic Communications, 1990, 20(10): 1445–1451
Bonon A J, Mandelli D, Kholdeeva O A, Barmatova MV, Kozlov Y N, Shul’Pin G B. Oxidation of alkanes and olefins with hydrogen peroxide in acetonitrile solution catalyzed by a mesoporous titanium-silicate Ti-MMM-2. Applied Catalysis A, General, 2009, 365(1): 96–104
Hirahara Y, Nakamuro K, Sayato Y. Studies on behaviors of decomposition of pesticides. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2009, 12(1): E1–E4
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21107135) and the Ji’nan High-level Talent Plan (No. 2013041). The authors thank Dr. Li Shu for proofreading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ren, B., Li, S. et al. Is sodium percarbonate a good choice in situ remediation of deltamethrin pollution?. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 11, 3 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0931-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0931-9