Abstract
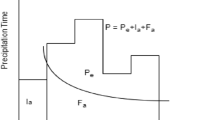
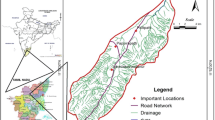
Soil Conservation Service (SCS) model, developed by U. S. Soil Conservation Service in 1972, has been widely applied in the estimation of runoff from an small watershed. In this paper, based on the remote sensing geo-information data of land use and soil classification all obtained from Landsat images in 1996 and 1997 and conventional data of hydrology and meteorology, the SCS model was investigated for simulating the surface runoff for single rainstorm in Wangdonggou watershed, a typical small watershed in the Loess Plateau, located in Changwu County of Shaanxi Province of China. Wangdonggou watershed was compartmentalized into 28 sub-units according to natural draining division, and the table of curve number (CN) values fitting for Wangdonggou watershed was also presented. During the flood period from 1996 to 1997, the hydrograph of calculated runoff process using the SCS model and the hydrograph of observed runoff process coincided very well in height as well as shape, and the model was of high precision above 75%. It is indicated that the SCS model is legitimate and can be successfully used to simulate the runoff generation and the runoff process of typical small watershed based on the remote sensing geo-information in the Loess Plateau.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandrmoha T, Durbude D G, 2001. Estimation of runoff using small watershed models. Hydrology Journal, 24(2): 45–53.
Delmar D F, William J E, Stephen R W, 2005. Soil and Water Conservation Engineering. Delhi: Standard Publishers Distributors.
Gert A S, 1988. Remote sensing in hydrology. Journal of Hydrology, 100(1–3): 239–265.
Greene R G, Cruise J F, 1995. Urban watershed modeling using geographic information system. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 121(4): 318–325.
Greene R G, Cruise J F, 1996. Development of a geographic information system for urban watershed analysis. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 62(7): 863–870.
Hassanuzzaman M K, 1993. Muskingum flood routing model for multiple tributaries. Water Resources Research, 4(1): 1057–1062.
Hawkins R H, 1993. Asymptotic determinations of runoff curve numbers from rainfall-runoff data. Journal of the Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, ASCE, 119(2): 334–345.
He C S, 2003. Integration of geographic information systems and simulation model for watershed management. Environmental Modelling & Software, 18(8): 809–813.
Hellweger F L, Maidment D R, 1999. Definition and connection of hydrologic elements using geographic data. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 4(1): 10–19.
Jin Hua, Sun Xihuan, Li Yangbin, 2003. Application of SCS model in Lanhe watershed. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 34(6): 735–762. (in Chinese)
Lewis M J, Singer M J, Tate K W, 2000. Applicability of SCS curve number method for a California Oak Woodlands Watershed. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 55(2): 226–230.
Li Yushan, Su Shanmin, 1996. Efficient Ecological and Economic System in Wangdong Watershed of Changwu County. Beijing: Scientific and Technical Documents Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Liu G C, Tian G L, Shu D C, 2004. Streamflow and soil moisture of agroforestry and grass watersheds in hilly area. Pedosphere, 14(2): 263–268.
Liu Xianzhao, Kang Shaozhong, Liu Delin, 2005. SCS model based on geographic information and its application to simulate rainfall-runoff relationship at typical small watershed level in Loess Plateau. Transaction of the CSAE, 21(5): 93–97. (in Chinese)
Mishra S K, Jain M K, Bhunya P K et al., 2005. Field applicability of the SCS-CN-based Mishra-Singh general model and its variants. Water Resources Management, 19(1): 37–62.
Pan Jianjun, 1996. Study on hydrological property and runoff of catchment’s by remote sensing. Journal of Soil Erosion and Soil and Water Conversation, 2(3): 88–92. (in Chinese)
Qi H W, 2001. Modelling urban growth effects on surface runoff with the integration of remote sensing and GIS. Environmental Management, 28(6): 737–748.
Sharma D, Kumar V, 2002. Application of SCS model with GIS database for estimation of runoff in arid watershed. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(2): 141–145.
Sharma T S, Kiran P V, Singh T H, 2001. Hydrologic response of a watershed to land use changes: A remote sensing and GIS approach. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(11): 2095–2108.
Shaanxi Province Civil Administration Bureau, 1971. Changwu County Map. Xi’an: Xi’an Map Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Tsihrintzis V A, Hamid R, 1997. Urban storm water quantity/quality modeling using the SCS method and empirical equation. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 33(3): 163–167.
United States Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service, 1972. Hydrology. In: National Engineering Handbook. Section 4. Washington D C: U S Govt. Printing office.
Xia J, Wang G S, Ye A Z, 2005. A distributed monthly water balance model for analyzing impacts of land cover change on flow regimes. Pedosphere, 15(6): 761–767.
Zepp H, Tang J L, Zhang B, 2005. Methodological framework for a multi-scale study on hydrological processes and soil erosion in subtropical southeast China. Pedosphere, 15(6): 695–706.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40101005)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Li, J. Application of SCS model in estimation of runoff from small watershed in Loess Plateau of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 18, 235–241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-008-0235-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-008-0235-x