Abstract
Purpose
To gain insight into the association of physical activity (PA), chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) and health-related quality of life among colorectal cancer survivors, up to 11 years after diagnosis.
Methods
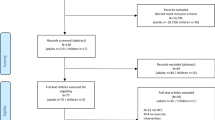
Data of the second data wave of a Dutch prospective population-based survey among colorectal cancer survivors diagnosed between 2000 and 2009 as registered by the Eindhoven Cancer Registry was used. Eighty-three percent (n = 1648) of patients filled out the EORTC QLQ-C30 and the EORTC QLQ-CIPN20 of which 506 patients (31 %) were treated with chemotherapy.
Results
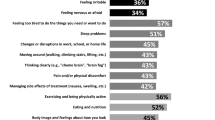
Treatment with chemotherapy was associated with a higher percentage of patients reporting CIPN symptoms regardless of PA. Furthermore, not meeting the Dutch PA guideline of 150 min of moderate to vigorous PA a week was associated with more CIPN among patients treated with chemotherapy. Also patients not treated with chemotherapy reported CIPN-like symptoms, especially when not meeting the PA guideline. Statistically significant and clinically relevant worse scores on almost all EORTC QLQ-C30 subscales were reported by those not meeting the PA guideline compared to those who did meet the guideline, regardless of CIPN symptoms. However, these differences were more pronounced in the group with many CIPN symptoms (e.g. upper 30 %).
Implications for Cancer Survivors
Alertness among health care professionals and patients for the importance of PA is warranted, as meeting the PA guideline was associated with less CIPN-like symptoms and a higher health-related quality of life regardless of treatment with chemotherapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiegel RND, Jemal A. Cancer statistics 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29.
Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(23):2343–51.
Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, Lavoie Smith EM, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014.
Park SB, Lin CS, Krishnan AV, Goldstein D, Friedlander ML, Kiernan MC. Long-term neuropathy after oxaliplatin treatment: challenging the dictum of reversibility. Oncologist. 2011;16(5):708–16.
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(16):2938–47.
Land SR, Kopec JA, Cecchini RS, Ganz PA, Wieand HS, Colangelo LH, et al. Neurotoxicity from oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(16):2205–11.
Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez G, Sereno M, Miralles A, Casado-Sáenz E, Gutiérrez-Rivas E. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: clinical features, diagnosis, prevention and treatment strategies. Clin Transl Oncol. 2010;12(2):81–91.
Kannarkat G, Lasher E, Schiff D. Neurologic complications of chemotherapy agents. Curr Opin Neurol. 2007;20(6):719–25.
Quasthoff S, Hartung H. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol. 2002;249(1):9–17.
Ocean AJ, Vahdat LT. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: pathogenesis and emerging therapies. Support Care Cancer. 2004;12(9):619–25.
Windebank AJ. Chemotherapeutic neuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol. 1999;12(5):565–71.
LoMonaco M, Milone M, Batocchi AP, Padua L, Restuccia D, Tonali P. Cisplatin neuropathy: clinical course and neurophysiological findings. J Neurol. 1992;239(4):199–204.
Simons CC, Hughes LA, van Engeland M, Goldbohm RA, van den Brandt PA, Weijenberg MP. Physical activity, occupational sitting time, and colorectal cancer risk in the Netherlands cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2013;177(6):514–30.
Johnson CM, Wei C, Ensor JE, Smolenski DJ, Amos CI, Levin B, et al. Meta-analyses of colorectal cancer risk factors. Cancer Causes Control. 2013. doi:10.1007/s10552-013-0201-5.
Vrieling A, Kampman E. The role of body mass index, physical activity, and diet in colorectal cancer recurrence and survival: a review of the literature. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92(3):471–90.
Je Y, Jeon JY, Giovannucci EL, Meyerhardt JA. Association between physical activity and mortality in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Cancer. 2013.
Lynch BM, Cerin E, Owen N, Hawkes AL, Aitken JF. Prospective relationships of physical activity with quality of life among colorectal cancer survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(27):4480–7.
Peddle CJ, Au HJ, Courneya KS. Associations between exercise, quality of life, and fatigue in colorectal cancer survivors. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51(8):1242–8.
Thraen-Borowski KM, Trentham-Dietz A, Edwards DF, Koltyn KF, Colbert LH. Dose-response relationships between physical activity, social participation, and health-related quality of life in colorectal cancer survivors. J Cancer Surviv. 2013.
Buffart LM, Thong MS, Schep G, Chinapaw MJ, Brug J, van de Poll-Franse LV. Self-reported physical activity: its correlates and relationship with health-related quality of life in a large cohort of colorectal cancer survivors. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36164.
Grimmett C, Bridgewater J, Steptoe A, Wardle J. Lifestyle and quality of life in colorectal cancer survivors. Qual Life Res. 2011;20(8):1237–45.
Streckmann F, Kneis S, Leifert JA, Baumann FT, Kleber M, Ihorst G, et al. Exercise program improves therapy-related side-effects and quality of life in lymphoma patients undergoing therapy. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(2):493–9.
Stevinson C, Steed H, Faught W, Tonkin K, Vallance JK, Ladha AB, et al. Physical activity in ovarian cancer survivors: associations with fatigue, sleep, and psychosocial functioning. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009;19(1):73–8.
Tofthagen C, Visovsky C, Berry DL. Strength and balance training for adults with peripheral neuropathy and high risk of fall: current evidence and implications for future research. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2012;39(5):E416–24.
Mols F, Beijers T, Vreugdenhil G, van de Poll-Franse L. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and its association with quality of life: a systematic review. Support Care Cancer. 2014;22(8):2261–9.
Mols F, Beijers T, Lemmens V, van den Hurk CJ, Vreugdenhil G, van de Poll-Franse LV. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy and its association with quality of life among 2- to 11-year colorectal cancer survivors: results from the population-based PROFILES registry. J Clin Oncol. 2013.
van de Poll-Franse LV, Horevoorts N, van Eenbergen M, Denollet J, Roukema JA, Aaronson NK, et al. The patient reported outcomes following initial treatment and long term evaluation of survivorship registry: scope, rationale and design of an infrastructure for the study of physical and psychosocial outcomes in cancer survivorship cohorts. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(14):2188–94.
Janssen-Heijnen MLG, Louwman WJ, Van de Poll-Franse LV, Coebergh JWW. Results of 50 years cancer registry in the south of the Netherlands. 1955–2004 (in Dutch). Eindhoven: Eindhoven Cancer Regist. 2005.
Thong MS, Mols F, Lemmens VE, Creemers GJ, Slooter GD, van de Poll-Franse LV. Impact of chemotherapy on health status and symptom burden of colon cancer survivors: a population-based study. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(12):1798–807.
Thong MS, Mols F, Lemmens VE, Rutten HJ, Roukema JA, Martijn H, et al. Impact of preoperative radiotherapy on general and disease-specific health status of rectal cancer survivors: a population-based study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(3):e49–58.
Sangha O, Stucki G, Liang MH, Fossel AH, Katz JN. The self-administered comorbidity questionnaire: a new method to assess comorbidity for clinical and health services research. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49(2):156–63.
van Duijn C, Keij I. Sociaal-economische status indicator op postcode niveau. Maandstatistiek van de bevolking. 2002;50:32–5.
Niezgoda HE, Pater JL. A validation study of the domains of the core EORTC quality of life questionnaire. Qual Life Res. 1993;2(5):319–25.
Fayers P, Aaronson NK, Bjordal K, Group. ObotEQoL. The EORTC QLQ-C30 scoring manual. 3rd ed. Brussels: EORTC Publications; 2001.
Postma TJ, Aaronson NK, Heimans JJ, Muller MJ, Hildebrand JG, Delattre JY, et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: the QLQ-CIPN20. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41(8):1135–9.
Pols MA, Peeters PH, Ocke MC, Slimani N, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Collette HJ. Estimation of reproducibility and relative validity of the questions included in the EPIC Physical Activity Questionnaire. Int J Epidemiol. 1997;26 Suppl 1:S181–9.
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Leon AS, Jacobs Jr DR, Montoye HJ, Sallis JF, et al. Compendium of physical activities: classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993;25(1):71–80.
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, et al. Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32(9 Suppl):S498–504.
Boyette-Davis JA, Eng C, Wang XS, Cleeland CS, Wendelschafer-Crabb G, Kennedy WR, et al. Subclinical peripheral neuropathy is a common finding in colorectal cancer patients prior to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(11):3180–7.
Babyak MA. What you see may not be what you get: a brief, nontechnical introduction to overfitting in regression-type models. Psychosom Med. 2004;66(3):411–21.
Norman GR, Sloan JA, Wyrwich KW. Interpretation of changes in health-related quality of life: the remarkable universality of half a standard deviation. Med Care. 2003;41(5):582–92.
Cocks K, King MT, Velikova G, Martyn St-James M, Fayers PM, Brown JM. Evidence-based guidelines for determination of sample size and interpretation of the European Organisation for the Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(1):89–96.
White CM, Pritchard J, Turner-Stokes L. Exercise for people with peripheral neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;4, CD003904.
Streckmann F, Zopf EM, Lehmann HC, May K, Rizza J, Zimmer P et al. Exercise intervention studies in patients with peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2014.
Thraen-Borowski KM, Trentham-Dietz A, Edwards DF, Koltyn KF, Colbert LH. Dose-response relationships between physical activity, social participation, and health-related quality of life in colorectal cancer survivors. J Cancer Surviv. 2013;7(3):369–78.
Voskuil DW, van Nes JG, Junggeburt JM, van de Velde CJ, van Leeuwen FE, de Haes JC. Maintenance of physical activity and body weight in relation to subsequent quality of life in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(10):2094–101.
Statistiek CBv.
Je Y, Jeon JY, Giovannucci EL, Meyerhardt JA. Association between physical activity and mortality in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(8):1905–13.
http://www.sportzorg.nl/bibliotheek/nederlandse-norm-gezond-bewegen-nngb
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the patients and their doctors for their participation in the study. Special thanks go to Dr. M. van Bommel who was willing to function as an independent advisor and to answer questions of the patients. In addition, we want to thank the following hospitals for their cooperation: Amphia Hospital, Breda; Bernhoven Hospital, Veghel and Oss; Catharina Hospital, Eindhoven; Elkerliek Hospital, Helmond; Jeroen Bosch Hospital, ‘s Hertogenbosch; Maxima Medical Centre, Eindhoven and Veldhoven; Sint Anna Hospital, Geldrop; St. Elisabeth Hospital, Tilburg; Twee Steden Hospital, Tilburg and Waalwijk; and VieCury Hospital, Venlo and Venray.
Conflict of interest
None.
Funding
The present research was supported by a VENI grant (no. 451-10-041) from The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (The Hague, The Netherlands) awarded to Floortje Mols.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mols, F., Beijers, A.J.M., Vreugdenhil, G. et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, physical activity and health-related quality of life among colorectal cancer survivors from the PROFILES registry. J Cancer Surviv 9, 512–522 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-015-0427-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-015-0427-1