Abstract
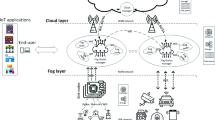
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of tens of billions of physical devices that are all connected to each other. These devices often have sensors or actuators, small microprocessors and ways to communicate. With the expansion of the IoT, the number of portable and mobile devices has increased significantly. Due to resource constraints, IoT devices are unable to complete tasks in full. To overcome this challenge, IoT devices must transfer tasks created in the IoT environment to cloud or fog servers. Fog computing (FC) is a computing paradigm that bridges the gap between the cloud and IoT devices and has lower latency compared to cloud computing. An algorithm for task offloading should have smart ways to make the best use of FC resources and cut down on latency. In this paper, an improved multi-objective Aquila optimizer (IMOAO) equipped with a Pareto front is proposed to task offloading from IoT devices to fog nodes with the aim of reducing the response time. To improve the MOAO algorithm, opposition-based learning (OBL) is used to diversify the population and discover optimal solutions. The IMOAO algorithm has been evaluated by the number of tasks and the number of fog nodes in order to reduce the response time. The results show that the average response time and failure rate obtained by IMOAO algorithm are lower compared to particle swarm optimization (PSO) and firefly algorithm (FA). Also, the comparisons show that the IMOAO model has a lower response time compared to multi-objective bacterial foraging optimization (MO-BFO), ant colony optimization (ACO), particle swarm optimization (PSO) and FA.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Seyfollahi, A., Abeshloo, H., Ghaffari, A.: Enhancing mobile crowdsensing in Fog-based internet of things utilizing Harris hawks optimization,. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 13(9), 4543–4558 (2022)
Mohammadi, R., Ghaffari, A.: Optimizing reliability through network coding in wireless multimedia sensor networks. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 8(9), 834–841 (2015)
Cheng, B., Wang, M., Zhao, S., Zhai, Z., Zhu, D., Chen, J.: Situation-aware dynamic service coordination in an IoT environment. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 25(4), 2082–2095 (2017)
Lv, Z., Qiao, L., Li, J., Song, H.: Deep-learning-enabled security issues in the internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 8(12), 9531–9538 (2020)
Li, B., Zhou, X., Ning, Z., Guan, X., Yiu, K.-F.C.: Dynamic event-triggered security control for networked control systems with cyber-attacks: A model predictive control approach. Inf. Sci. 612, 384–398 (2022)
Cao, K., et al.: Achieving reliable and secure communications in wireless-powered NOMA systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 70(2), 1978–1983 (2021)
Dai, X., et al.: Task co-offloading for d2d-assisted mobile edge computing in industrial internet of things. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 19(1), 480–490 (2022)
Jiang, H., Xiao, Z., Li, Z., Xu, J., Zeng, F., Wang, D.: An energy-efficient framework for internet of things underlaying heterogeneous small cell networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 21(1), 31–43 (2020)
Yao, Y., Zhao, J., Li, Z., Cheng, X., Wu, L.: Jamming and eavesdropping defense scheme based on deep reinforcement learning in autonomous vehicle networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 18, 1211–1224 (2023)
Lv, Z., Song, H.: Mobile internet of things under data physical fusion technology. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(5), 4616–4624 (2019)
Zhang, K., et al.: Training effective deep reinforcement learning agents for real-time life-cycle production optimization. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 208, 109766 (2022)
Xiong, Z., et al.: A comprehensive confirmation-based selfish node detection algorithm for socially aware networks. J. Signal Process. Syst. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-023-01868-6
Kamalinia, A., Ghaffari, A.: Hybrid task scheduling method for cloud computing by genetic and DE algorithms. Wireless Personal Commun 97(4), 6301–6323 (2017)
Li, J., et al.: Resource orchestration of cloud-edge–based smart grid fault detection. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. (TOSN) 18(3), 1–26 (2022)
Cao, B., Sun, Z., Zhang, J., Gu, Y.: Resource allocation in 5G IoV architecture based on SDN and fog-cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(6), 3832–3840 (2021)
Wang, S., Sheng, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, D., Shen, J., Chen, R.: Blockchain-empowered distributed multi-camera multi-target tracking in edge computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2023.3261890
Ni, Q., Guo, J., Wu, W., Wang, H.: Influence-based community partition with sandwich method for social networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 10(2), 819–830 (2022)
She, Q., Hu, R., Xu, J., Liu, M., Xu, K., Huang, H.: Learning high-DOF reaching-and-grasping via dynamic representation of gripper-object interaction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.13998, 2022.
Dai, X., et al.: Task offloading for cloud-assisted fog computing with dynamic service caching in enterprise management systems. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 19(1), 662–672 (2022)
Xiao, Z., Shu, J., Jiang, H., Min, G., Chen, H., Han, Z.: Perception task offloading with collaborative computation for autonomous driving. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 41(2), 457–473 (2022)
Cao, B., et al.: Large-scale many-objective deployment optimization of edge servers. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(6), 3841–3849 (2021)
Wang, Y., Han, X., Jin, S.: MAP based modeling method and performance study of a task offloading scheme with time-correlated traffic and VM repair in MEC systems. Wireless Netw. 29(1), 47–68 (2023)
Deng, X., Liu, E., Li, S., Duan, Y., Xu, M.: Interpretable multi-modal image registration network based on disentangled convolutional sparse coding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 32, 1078–1091 (2023)
Liu, G.: Data collection in mi-assisted wireless powered underground sensor networks: directions, recent advances, and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 59(4), 132–138 (2021)
Lv, Z., Chen, D., Feng, H., Wei, W., Lv, H.: Artificial intelligence in underwater digital twins sensor networks. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. (TOSN) 18(3), 1–27 (2022)
Cao, B., Wang, X., Zhang, W., Song, H., Lv, Z.: A many-objective optimization model of industrial internet of things based on private blockchain. IEEE Netw. 34(5), 78–83 (2020)
Wang, J., et al.: Control of time delay force feedback teleoperation system with finite time convergence. Front. Neurorobot. 16, 877069 (2022)
Pan, S., Lin, M., Xu, M., Zhu, S., Bian, L.-A., Li, G.: A low-profile programmable beam scanning holographic array antenna without phase shifters. IEEE Internet Things J. 9(11), 8838–8851 (2021)
Salimian, M., Ghobaei-Arani, M., Shahidinejad, A.: An evolutionary multi-objective optimization technique to deploy the IoT services in Fog-enabled networks: an autonomous approach. Appl. Artificial Intell. 36(1), 2008149 (2022)
Li, R., et al.: Denoising method of ground-penetrating radar signal based on independent component analysis with multifractal spectrum. Measurement 192, 110886 (2022)
Li, X., Zang, Z., Shen, F., Sun, Y.: Task offloading scheme based on improved contract net protocol and beetle antennae search algorithm in fog computing networks. Mobile Netw. Appl. 25, 2517–2526 (2020)
Li, A., Masouros, C., Swindlehurst, A.L., Yu, W.: 1-bit massive MIMO transmission: embracing interference with symbol-level precoding. IEEE Commun. Mag. 59(5), 121–127 (2021)
Jiang, Y., Li, X.: Broadband cancellation method in an adaptive co-site interference cancellation system. Int. J. Electron. 109(5), 854–874 (2022)
Gong, J., Rezaeipanah, A.: A fuzzy delay-bandwidth guaranteed routing algorithm for video conferencing services over SDN networks,". Multimed. Tools and Appl. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14349-6
Guo, F., Zhou, W., Lu, Q., Zhang, C.: Path extension similarity link prediction method based on matrix algebra in directed networks. Comput. Commun. 187, 83–92 (2022)
Li, B., Zhang, M., Rong, Y., Han, Z.: Transceiver optimization for wireless powered time-division duplex MU-MIMO systems: non-robust and robust designs. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 21(6), 4594–4607 (2021)
Cao, B., Zhao, J., Gu, Y., Ling, Y., Ma, X.: Applying graph-based differential grouping for multiobjective large-scale optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 53, 100626 (2020)
Lu, Z., Cheng, R., Jin, Y., Tan, K.C., Deb, K.: Neural architecture search as multiobjective optimization benchmarks: problem formulation and performance assessment,". IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2022.3233364
Xiao, Z., et al.: Multi-objective parallel task offloading and content caching in D2D-aided MEC networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2022.3199876
Cao, B., et al.: Multiobjective 3-D topology optimization of next-generation wireless data center network. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 16(5), 3597–3605 (2019)
Cao, B., Zhang, W., Wang, X., Zhao, J., Gu, Y., Zhang, Y.: A memetic algorithm based on two_Arch2 for multi-depot heterogeneous-vehicle capacitated arc routing problem. Swarm Evol. Comput. 63, 100864 (2021)
Zheng, W., Yin, L.: Characterization inference based on joint-optimization of multi-layer semantics and deep fusion matching network. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 8, e908 (2022)
Movahedi, Z., Defude, B., Hosseininia, Am.: An efficient population-based multi-objective task scheduling approach in fog computing systems,". J. Cloud Comput. 10, 53 (2021)
Zhou, G., Zhang, R., Huang, S.: Generalized buffering algorithm. IEEE Access 9, 27140–27157 (2021)
Subbaraj, S., Thiyagarajan, R., Rengaraj, M.: A smart fog computing based real-time secure resource allocation and scheduling strategy using multi-objective crow search algorithm,". J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03354-y
Najafizadeh, A., Salajegheh, A., Rahmani, A.M., Sahafi, A.: Multi-objective task scheduling in cloud-fog computing using goal programming approach,". Cluster Comput. 25, 141–165 (2022)
Yang, S., Li, Q., Li, W., Li, X., Liu, A.-A.: Dual-level representation enhancement on characteristic and context for image-text retrieval. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(11), 8037–8050 (2022)
He, H., Xu, G., Pang, S., Zhao, Z.: AMTS: Adaptive multi-objective task scheduling strategy in cloud computing. China Commun. 13(4), 162–171 (2016)
Yadav, A.M., Tripathi, K.N., Sharma, S.C.: An enhanced multi-objective fireworks algorithm for task scheduling in fog computing environment,". Cluster Comput. 25(2), 983–998 (2022)
Abualigah, L., Yousri, D., Abd Elaziz, M., Ewees, A.A., Al-qaness, M.A.A., Gandomi, A.H.: Aquila optimizer: a novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm,". Comput. Ind. Eng. 157(2), 107250 (2021)
Jaganathan, A., Mathesan, K.: Risk prediction model and classification of various hazards in automobile industry using HAO based deep CNN,". Sādhanā 47(3), 165 (2022)
Sun, H., Yu, H., Fan, G., Chen, L.: Energy and time efficient task offloading and resource allocation on the generic IoT-fog-cloud architecture,". Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 13(2), 548–563 (2020)
Kishor, A., Chakarbarty, C.: Task offloading in fog computing for using smart ant colony optimization,". Wireless Personal Commun. 127(2), 1683–1704 (2022)
Khaledian, N., Khamforoosh, K., Azizi, S., Maihami, V.: IKH-EFT: An improved method of workflow scheduling using the krill herd algorithm in the fog-cloud environment. Sustain. Comput.: Inform. Syst. 37(1), 100834 (2023)
Azizi, S., Shojafar, M., Abawajy, J., Buyya, R.: Deadline-aware and energy-efficient IoT task scheduling in fog computing systems: a semi-greedy approach,". J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 201(1), 103333 (2022)
Shahryari, O.-K., Pedram, H., Khajehvand, V., TakhtFooladi, M.D.: Energy and task completion time trade-off for task offloading in fog-enabled IoT networks,". Pervasive and Mobile Comput. 74, 101395 (2021)
Hussain, S.M., Begh, G.R.: Hybrid heuristic algorithm for cost-efficient QoS aware task scheduling in fog–cloud environment,". J. Comput. Sci. 64(5), 101828 (2022)
Aburukba, R.O., Landolsi, T., Omer, D.: A heuristic scheduling approach for fog-cloud computing environment with stationary IoT devices,". J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 180, 102994 (2021)
Dai, X., Xiao, Z., Jiang, H., Lui, J.C.S.: UAV-assisted task offloading in vehicular edge computing networks,". IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2023.3259394
Qiu, S., et al.: Digital-twin-assisted edge-computing resource allocation based on the whale optimization algorithm," (in eng). Sens. (Basel, Switzerland) 22(23), 1–17 (2022)
Du, X., Du, C., Chen, J., Liu, Y.: An energy-aware resource allocation method for avionics systems based on improved ant colony optimization algorithm,". Comput. Electric. Eng. 105(1), 108515 (2023)
Jiang, H., Dai, X., Xiao, Z., Iyengar, A.K.: Joint task offloading and resource allocation for energy-constrained mobile edge computing,". IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2022.3190276
Dubey, K., Sharma, S.C.: A novel multi-objective CR-PSO task scheduling algorithm with deadline constraint in cloud computing,". Sustain. Comput.: Inform. Syst. 32, 100605 (2021)
Jafari, V., Rezvani, M.H.: Joint optimization of energy consumption and time delay in IoT-fog-cloud computing environments using NSGA-II metaheuristic algorithm,". J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03388-2
Jia, M., Yin, Z., Li, D., Guo, Q., Gu, X.: Toward improved offloading efficiency of data transmission in the IoT-cloud by leveraging secure truncating OFDM. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4252–4261 (2019)
Kandan, M., Krishnamurthy, A., Selvi, S.A.M., Sikkandar, M.Y., Aboamer, M.A., Tamilvizhi, T.: Quasi oppositional Aquila optimizer-based task scheduling approach in an IoT enabled cloud environment,". J. Supercomput. 78(7), 10176–10190 (2022)
Lu, S., Liu, M., Yin, L., Yin, Z., Liu, X., Zheng, W.: The multi-modal fusion in visual question answering: a review of attention mechanisms. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 9, e1400 (2023)
Duan, Y., Zhao, Y., Hu, J.: An initialization-free distributed algorithm for dynamic economic dispatch problems in microgrid: Modeling, optimization and analysis. Sustain. Energy, Grids and Netw. 34, 101004 (2023)
Shen, Y., Ding, N., Zheng, H.-T., Li, Y., Yang, M.: Modeling relation paths for knowledge graph completion. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 33(11), 3607–3617 (2020)
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyarivan, T.: A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(2), 182–197 (2002)
Lv, Z., Kumar, N.: Software defined solutions for sensors in 6G/IoE. Comput. Commun. 153, 42–47 (2020)
Li, R., Wu, X., Tian, H., Yu, N., Wang, C.: Hybrid memetic pretrained factor analysis-based deep belief networks for transient electromagnetic inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–20 (2022)
Li, B., Li, Q., Zeng, Y., Rong, Y., Zhang, R.: 3D trajectory optimization for energy-efficient UAV communication: a control design perspective. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 21(6), 4579–4593 (2021)
Zhu, H., Xue, M., Wang, Y., Yuan, G., Li, X.: Fast visual tracking with siamese oriented region proposal network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 29, 1437–1441 (2022)
Zhao, Z., Xu, G., Zhang, N., Zhang, Q.: Performance analysis of the hybrid satellite-terrestrial relay network with opportunistic scheduling over generalized fading channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 71(3), 2914–2924 (2022)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization," In: Proceedings of ICNN'95 - International Conference on Neural Networks, 1995, vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948 vol.4.
Yang, X.-S.: Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization," In: Stochastic Algorithms: Foundations and Applications, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009, pp. 169–178: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Babar, M., Din, A., Alzamzami, O., Karamti, H., Khan, A., Nawaz, M.: A bacterial foraging based smart offloading for Iot sensors in edge computing,". Comput. Electrical Engineering 102(1), 108123 (2022)
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.N. wrote the manuscript and carried out the experiment. A.G. and A.M. reviewed and supervised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This work did not require ethical approval under the research governance guidelines operating at the time of the research.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nematollahi, M., Ghaffari, A. & Mirzaei, A. Task offloading in Internet of Things based on the improved multi-objective aquila optimizer. SIViP 18, 545–552 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02761-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02761-2