Abstract
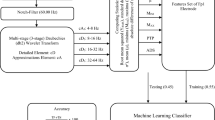
A novel steady state visual evoked potential (SSVEP)-based BCI system for driver’s sleepiness monitoring is proposed. Detecting the driver’s concentration is one of the most challenging assignments for researchers in these decades. A continuous attention and awareness is necessary to drive safely. Otherwise, one tragedy of drowsy driving would probably happen. Therefore, real-time sleepiness detection can restrain accidents effectively. In this study, SSVEPs are used for running the proposed system and two experimental setups consisting four single and paired light-emitting diodes (LEDs) using two different fast Fourier transform-based feature extraction methods, and three different classifiers of the linear discriminant analysis, the support vector machine (SVM) and the Max ones on the accuracy of the system are studied. For real-time application, related features are extracted from four different sweep lengths (temporal durations) of 0.5, 1, 2, and 3 s. The experimental results show that higher sweeps have higher accuracies and the SVM classifier, experimental setup of 4-paired LEDs in sweep length of 3 s has the highest accuracy of 98.2 %, while with the comparable information transfer rate (ITR) value of 24 bits/min within the sweep length of 1 s, this time is considered as the best response time. Therefore, this study demonstrates the feasibility of the proposed system in a practical driving application.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, P.L., Wu, C.H., Hsieh, J.C., Wu, Y.T.: Visual evoked potential actuated brain computer interface: a brain-actuated cursor system. Electron. Lett. 41(15), 832–834 (2005)
McFarland, D.J., Sarnacki, W.A., Vaughan, T.M., Wolpaw, J.R.: Brain–computer interface (BCI) operation: signal and noise during early training sessions. Clin. Neurophysiol. 116(1), 56–62 (2005)
Wadsworth, H.M., Kana, R.K.: Brain mechanisms of perceiving tools and imagining tool use acts: a functional MRI study. Neuropsychologia 49(7), 1863–1869 (2011)
Shyu, K.K., Lee, P.L., Liu, Y.J., Sie, J.J.: Dual-frequency steady-state visual evoked potential for brain computer interface. Neurosci. Lett. 483, 28–31 (2010)
Wu, Z., Lai, Y., Xia, Y., Wu, D., Yao, D.: Stimulator selection in SSVEP-based BCI. Med. Eng. Phys. 30(8), 1079–1088 (2008)
Mukesh, T.M.S., Jaganathan, V., Reddy, M.R.: A novel multiple frequency stimulation method for steady state VEP based brain computer interfaces. Physiol. Meas. 27(1), 61–71 (2006)
Shen, H., Zhao, L., Bian, Y., Xiao, L.: Research on SSVEP-based controlling system of multi-DoF manipulator. Adv. Neural Netw. 5553, 171–177 (2009)
Grace, R., Byrne, V.E., Bierman, D.M., Legrand, J.M.: A drowsy driver detection system for heavy vehicles. Digit. Avion. Syst. Conf. 2(136), 1–8 (1998)
McCartt, A.T., Ribner, S.A., Pack, A.I., Hammer, M.C.: The scope and nature of the drowsy driving problem in New York State. Accid. Anal. Prev. 28(4), 511–517 (1996)
Papadelis, C., Chen, Z., Kourtidou-Papadeli, C., Bamidis, P.D., Chouvarda, I., Bekiaris, E., Maglaveras, N.: Monitoring sleepiness with on-board electrophysiological recordings for preventing sleep-deprived traffic accidents. Clin. Neurophysiol. 118(9), 1906–1922 (2007)
Yeo, M.V.M., Li, X., Shen, K., Wilder, E.P.V.: Can SVM be used for automatic EEG detection of drowsiness during car driving? Saf. Sci. 47(1), 115–124 (2009)
Ji, Q., Yang, X.: Real-time eye, gaze, and face pose tracking for monitoring driver vigilance. Real-Time Imaging 8(5), 357–377 (2002)
Reddy, B.S., Basir, O.A., Leat, S.J.: Estimation of driver attention using visually evoked potentials. In: IEEE Conference on Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 588–593 (2007)
Resalat, S.N., Saba, V., Afdideh, F., Heidarnejad, A.: High-speed SSVEP-based BCI: study of various frequency pairs and inter-sources distances. In: IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics, Hong Kong, Shenzhen, pp. 220–223 (2012)
Wu, Z.: The difference of SSVEP resulted by different pulse duty-cycle. In: International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems, pp. 605–607 (2009)
Resalat, S.N., Saba, V., Afdideh, F.: A novel system for driver’s sleepiness detection using SSVEP. In: IEEE International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Signal Processing, Iran, Shiraz, pp. 343–347 (2012)
Huang, M., Wu, P., Liu, Y., Bi, L., Chen, H.: Application and contrast in brain–computer interface between Hilbert–Huang transform and wavelet transform. In: IEEE International Conference for Young Computer Scientists, pp. 1706–1710 (2008)
Resalat, S.N., Setarehdan, S.K.: A study on the effect of the inter-sources distance on the performance of the SSVEP-based BCI systems. Am. J. Biomed. Eng. 2(1), 24–31 (2012)
Wu, C., Chang, H., Lee, P., Li, K., Sie, J., Sun, C., Yang, C., Li, P., Deng, H., Shyu, K.: Frequency recognition in an SSVEP-based brain computer interface using empirical mode decomposition and refined generalized zero-crossing. J. Neurosci. Methods 196(1), 170–181 (2011)
Krajewski, J., Schnieder, S., Sommer, D., Batliner, A., Schuller, B.: Applying multiple classifiers and non-linear dynamics features for detecting sleepiness from speech. Neurocomputing 84, 65–75 (2012)
Daza, I.G., Hernandez, N., Bergasa, L.M., Parra, I., Yebes, J.J., Gavilan, M., Quintero, R., Llorca, D.F., Sotelo, M.A.: Drowsiness monitoring based on driver and driving data fusion. In: IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp. 1199–1204 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resalat, S.N., Saba, V. A practical method for driver sleepiness detection by processing the EEG signals stimulated with external flickering light. SIViP 9, 1751–1757 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-015-0760-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-015-0760-x