Abstract
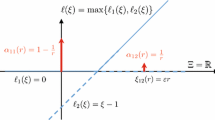
This paper deals with the problem of scenario tree reduction for stochastic programming problems. In particular, a reduction method based on cluster analysis is proposed and tested on a portfolio optimization problem. Extensive computational experiments were carried out to evaluate the performance of the proposed approach, both in terms of computational efficiency and efficacy. The analysis of the results shows that the clustering approach exhibits good performance also when compared with other reduction approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artzner P, Delbaen F, Eber JM, Heath D (1999) Coherent measures of risk. Math Financ 9:203–228
Beraldi P, De Simone F, Violi A (2010) Generating scenario trees: a parallel integrated simulation-optimization approach. J Comput Appl Math 23(9):2322–2331
Beraldi P, Bruni P, De Simone F (2010) Clustering algorithms for scenario reduction, Technical Report Lab. of Financial Engineering, DEIS, University of Calabria
Beraldi P, De Simone F, Violi A (2011) A decision support system for asset liability management. Decis Support Systems 51(3):549–561
Bertocchi M, Dupacová J, Moriggia V (2006) Horizon and stages in applications of stochastic programming in finance. Ann Oper Res 142:63–78
Consigli G, Dempster M (1998) Dynamic stochastic programming for asset liability management. Ann Oper Res 81:131–161
de Oliveira WL, Sagastiz C, Pennay DDJ, Maceiray MEP, Damazio JM (2010) Optimal scenario tree reduction for stochastic streamflows in power generation planning problems. Optim Methods Softw 25:917–936
Dupacová J, Consigli G, Wallace SW (2000) Scenarios for multistage stochastic programs. Ann Oper Res 100:25–53
Dupacová J, Gröwe-Kuska N, Römisch W (2003) Scenario reduction in stochastic programming: an approach using probability metrics. Math Program 95:493–511
Geyer A, Hanke M, Wiessensteiner A (2010) No-arbitrage conditions scenario trees and multi-asset financial optimization. Eur J Op Res 2006(3):609–613
Gülpinar N, Rustem B, Settergren R (2004) Simulation and optimization approaches to scenario tree generation. J Econ Dyn Control 28:1291–1315
Heitsch H, Römisch W (2003) Scenario reduction algorithms in stochastic programming. Comp Optim Appl 24:187–206
Heitsch H, Römisch W (2006) Stability and scenario trees for multistage stochastic programs. In: Infanger G (ed) Stochastic programming-the state of the art
Heitsch H, Römisch W (2007) A note on scenario reduction for two-stage stochastic programs. Oper Res Let 35:731–736
Heitsch H, Römisch W (2009a) Scenario tree modeling for multistage stochastic programs. Math Program 118:371–406
Heitsch H, Römisch W (2009b) Scenario tree reduction for multistage stochastic programs. Comput Manag Sci 6:117–133
Heitsch H, Römisch W, Strungarek C (2006) Stability in multistage stochastic programming. SIAM J Optimi 17:501–525
Henrion R, Küchler C, Römisch W (2008) Discrepancy distances and scenario reduction in two-stage stochastic integer programming. J Ind Manage Optim 4:363–384
Henrion R, Küchler C, Römisch W (2009) Scenario reduction in stochastic programming with respect to discrepancy distances. Comp Optim Appl 43:67–93
Kaut M, Wallace SW (2007) Evaluation of scenario generation methods for stochastic programming. Pac J Optim 3:257–271
Kaufman L, Rousseeuw PJ (1990) Finding groups in data: an introduction to cluster analysis. Wiley, New york
Latorre JM, Cerisola S, Ramos A (2007) Clustering algorithms for scenario tree generation: application to natural hydro inflows. Europ J Oper Res 181:1339–1353
Römisch W (2003) Stability of stochastic programming problems. In: Ruszczynski A, Shapiro A (eds) Stochastic programming, handbooks in operations research and management science, vol 10. Amsterdam, Elsevier, pp 483–554
Ruszczynski A, Shapiro A (2008) Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science: Stochastic Programming. Elsevier
Sutiene K, Makackas D, Pranevicius H (2010) K-Means clustering for scenario tree construction. Inform 21:123–138
Szego G (2004) Risk measures for 21st century. Wiley, New York
Zenios SA, Ziemba WT (2006) Handbook of Asset and Liability Management, Volume 1: Theory and Methodology. Elsevier
Zenios SA, Ziemba WT (2007) Handbook of Asset and Liability Management, Volume 2: Applications and Case Studies. Elsevier
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beraldi, P., Bruni, M.E. A clustering approach for scenario tree reduction: an application to a stochastic programming portfolio optimization problem. TOP 22, 934–949 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-013-0305-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-013-0305-9