Abstract
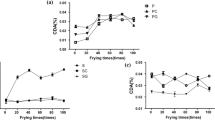
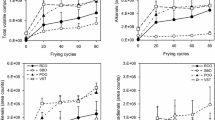
In this study, the effect of deep fat frying on oil degradation, total phenols (TP) and total antioxidant activity (TAA) of hazelnut, corn, soybean and olive oils were investigated. Oil degradation and oxidation were monitored by measuring the total polar compounds (TPC) and the peroxide value (PV). The amount of TPC in corn, soybean and olive oils increased significantly with the time increment (p < 0.05). The PV of the oils did not exceed the maximum acceptable limit of 10 mequiv O2/kg after 125 min frying except for hazelnut oil (10.64 mequiv O2/kg). Deep-fat frying did not cause any significant change in the TP of corn oil, soybean oil and olive oil (p < 0.05). A significant decrease in the antioxidant activity was observed after 50 min frying using hazelnut oil and corn oil (p < 0.05). However, the antioxidant activity of soybean oil and olive oil significantly decreased after 75 and 25 min frying, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saguy IS, Dana D (2003) Integrated approach to deep fat frying: engineering, nutrition, health and consumer aspects. J Food Eng 56:143–152
Yamsaengsung R, Moreira RG (2002) Modelling the transport phenomena and structural changes during deep fat frying. Part II: model solution and validation. J Food Eng 53:11–25
Xu X-Q (2000) A new spectrophotometric method for rapid assessment of deep frying oil quality. JAOCS 77:1083–1086
Pokorny J (2002) Frying. In: Henry CJK, Chapman C (eds) The nutrition handbook for food processors. CRC Press, New York
Sánchez-Gimeno AC, Negueruela AI, Benito M, Vercet A, Oria R (2008) Some physical changes in Bajo Aragón extra virgin olive oil during the frying process. Food Chem 110:654–658
Rossi M, Alamprese C, Ratti S (2007) Tocopherols and tocotrienols as free radical-scavengers in refined vegetable oils and their stability during deep-fat frying. Food Chem 102:812–817
Farhoosh R, Moosavi SMR (2008) Carbonyl value in monitoring of the quality of used frying oils. Anal Chim Acta 617:18–21
Gertz C (2000) Chemical and physical parameters as quality indicators of used frying fats. Eur J Food Sci Technol 102:566–572
Doborganes MC, Velasco J, Dieffenbacher A (2000) Determination of polar compounds, polymerized and oxidized triacylglycerols, and diacylglycerols in oils and fats. Pure Appl Chem 72:1563–1575
Hara K, Hasegana K, Endo Y, Fugimoto K (1994) Polymer and polar material content determination as basis for assessing thermally oxidative deterioration of soybean oil for potato heat cooking. J Jpn Oil Chem Soc 43:57–60
Andrikopoulos NK, Kalogeropoulos N, Falirea A, Barbagianni MN (2002) Performance of virgin olive oil and shortening during domestic deep-frying and pan frying of potatoes. Int J Food Sci Tech 37:177–180
Lopez-Varela S, Sanchez-Huniz FY, Garrido-Polonio C, Arroyo R, Cuesta C (1995) Relationship between chemical and physical indexes and column and HPSE chromatography methods for evaluating frying oil. Z Ernährungswıss 34:308–313
Carlson BL, Tabacchi MH (1986) Frying oil deterioration and vitamin loss during food service operation. J Food Sci 51:218–221
Katragadda HR, Fullana A, Sidhu S, Carbonell-Barrachina AA (2010) Emissions of volatile aldehydes from heated cooking oils. Food Chem 120:59–65
AOCS Official Method Cd 8b-90 (1989) Peroxide value acetic acid–isooctane method. In: Official methods and recommended practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society (4th edn). AOCS press, Campaign
Singleton VL, Lamuela-Raventos RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. Method Enzymol 299:152–178
Shadidi F, Naczk M (1995) Food phenolics: sources, chemistry, effects and applications. Technomic Publishing Company, USA, pp 292–293
Xu BJ, Chang SKC (2007) A comparative study on phenolic and antioxidant activities of legumes as affected by extraction solvents. J Food Sci 72:159–166
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset C (1995) Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und -Technologie/Food Sci Technol 28:25–30
Gil B, Cho YJ, Yoon SH (2004) Rapid determination of polar compounds in frying fats and oils using image analysis. Lebensm Wiss Technol 37:657–661
Benedito J, Mulet A, Velasco J, Dobarganes MC (2002) Ultrasonic assessment of oil quality during frying. J Agric Food Chem 50:4531–4536
TCS, Turkish Codex Standards (accessed Jan. 2010) Bitki Adı ile Anılan Yemeklik Yağlar Tebliği. http://www.kkgm.gov.tr/TGK/Tebliğ/2001-29.html
Bešter E, Butinar B, Bucar-Miklavcic M, Golob T (2008) Chemical changes in extra virgin olive oils from Slovenian Istra after thermal treatment. Food Chem 108:446–454
Naz S, Siddiqi R, Sheikh H, Sayeed SA (2005) Deterioration of olive, corn and soybean oils due to air, light, heat and deep-frying. Food Res Int 38:127–134
Kalogeropoulos N, Mylona A, Chiou A, Ioannou MS, Andrikopoulos NK (2007) Retention and distribution of natural antioxidants (α-tocopherol, polyphenols and terpenic acids) after shallow frying of vegetables in virgin olive oil. LWT-Food Sci Technol 40:1008–1017
Quiles JL, Ramírez-Tortosa MC, Gómez YA, Huertas JR, Mataix J (2002) Role of vitamin E and phenolic compounds in the antioxidant capacity, measured by ESR of virgin olive, olive and sunflower oils after frying. Food Chem 76:461–468
Gómez-Alanzo S, Fregapane G, Salvador MD, Gordon MH (2003) Changes in phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of virgin olive oil during frying. J Agric Food Chem 51:667–672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Karakaya, S., Şimşek, Ş. Changes in Total Polar Compounds, Peroxide Value, Total Phenols and Antioxidant Activity of Various Oils Used in Deep Fat Frying. J Am Oil Chem Soc 88, 1361–1366 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-011-1788-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-011-1788-x