Abstract
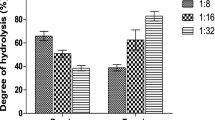
The antioxidant and antithrombotic activities of crude rapeseed peptides (CRPs) and peptide fractions (RP25 and RP55) prepared from aqueous enzymatic extraction (AEE) of rapeseed were determined. The reducing power of RP55 and CRPs was higher than that of RP25 at the same concentrations. Rapeseed peptides exhibited marked antioxidant activities. The median effective dose (ED50) values of CRPs, RP25 and RP55 for α,α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging were 72, 499 and 41 μg/mL, respectively. The ED50 values for RP25 and RP55 for hydroxyl radicals scavenging were 2.53 and 6.79 mg/mL, respectively while the ED50 values of RP55 and CRPs for inhibition of lipid peroxidation in a liposome model system were 4.06 and 4.69 mg/mL, respectively. The inhibitory effect on lipid oxidation of RP55 was similar to that of ascorbic acid at a concentration of 5.0 mg/mL. A good positive correlation existed between the peptide concentration and antioxidant activity. RP55 generally showed more potent antioxidant activities except for hydroxyl radicals scavenging ability than RP25 and CRPs at the same concentrations, which was thought to relate to the significantly higher contents of hydrophobic amino acid, tannin, and the brown color substances in RP55. Rapeseed peptides possessed marked inhibitory activities on the thrombin-catalyzed coagulation of fibrinogen, however, their inhibitory effects were not comparable to that of heparin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang SB, Wang Z, Xu SY (2007) Optimization of aqueous enzymatic extraction of rapeseed oil and protein hydrolysates. J Am Oil Chem Soc 84:97–105
Zhang SB, Wang Z, Xu SY (2007) Downstream processes for aqueous enzymatic extraction of rapeseed oil and protein hydrolysates. J Am Oil Chem Soc 84:693–700
Korhonen H, Pihlanto A (2006) Bioactive peptides: production and functionality. Int Dairy J 16:945–960
Hartmann R, Meisel H (2007) Food-derived peptides with biological activity: from research to food application. Curr Opin Biotechnol. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2007.01.013
Marczak ED, Usui H, Fujita H, Yang Y, Yokoo M, Lipkowski AW, Yoshikawa M (2003) New antihypertensive peptides isolated from rapeseed. Peptides 24:791–798
Yust MM, Pedroche J, Megias C, Calle JG, Alaiz M, Millan F, Vioque J (2004) Rapeseed protein hydrolysates: a source of HIV protease peptide inhibitors. Food Chem 87:387–392
Halliwell B (1994) Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: curiosity, cause, or consequence. Lancet 344:721–724
Scheraga HA (2004) The thrombin–fibrinogen interaction. Biophys Chem 112:117–130
Laudano AP, Doolittle RF (1978) Synthetic peptides derivatives that bind to fibrinogen and prevent the polymerization of fibrin monomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3085–3089
Silva SV, Malcata FX (2005) Caseins as source of bioactive peptides. Int Dairy J 15:1–15
Yang WG, Wang Z, Xu SY (2007) A new method for determination of antithrombotic activity of egg white protein hydrolysate by microplate reader. Chinese Chem Lett. doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2007.02.014
Wu HC, Chen HM, Shiau CY (2003) Free amino acids and peptides as related to antioxidant properties in protein hydrolysates of mackerel (Scomber austriasicus). Food Res Int 36:949–957
Sakanaka S, Tachibana Y, Ishihara N, Juneja LR (2004) Antioxidant activity of egg-yolk protein hydrolysates in a linoleic acid oxidation system. Food Chem 86:99–103
Zhu K, Zhou H, Qian H (2006) Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase. Process Biochem 41:1296–1302
Pihlanto A (2006) Antioxidative peptides derived from milk proteins. Int Dairy J 16:1306–1314
Chang CY, Wu KC, Chiang SH (2007) Antioxidant properties and protein compositions of porcine haemoglobin hydrolysates. Food Chem 100:1537–1543
Oyaizu M (1986) Studies on products of browning reactions: antioxidative activities of products of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. Jpn J Nutr 44:307–315
Shimada K, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T (1992) Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the antioxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J Agric Food Chem 40:945–948
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC, Aruoma OI (1987) The deoxyribose method: a simple ‘test tube’ assay for determination of rate constants for reactions of hydroxyl radicals. Anal Biochem 165:215–219
Peňa-Ramos EA, Xiong YL (2001) Antioxidative activity of whey protein hydrolysates in a liposomal system. J Dairy Sci 84:2577–2583
Sakanaka S, Tachibana Y (2006) Active oxygen scavenging activity of egg-yolk protein hydrolysates and their effects on lipid oxidation in beef and tuna homogenates. Food Chem 95:243–249
Rajapakse N, Mendis E, Jung WK, Je JY, Kim SK (2005) Purification of a radical scavenging peptide from fermented mussel sauce and its antioxidant properties. Food Res Int 38:175–182
Erickson MC, Hultin HO (1992) Influence of histidine on lipid peroxidation in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Arch Biochem Biophys 292:427–432
Kim SY, Je JY, Kim SK (2007) Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptide from hoki (Johnius belengerii) frame protein by gastrointestinal digestion. J Nutr Biochem 18:31–38
Je J, Qian Z, Byun H, Kim S (2007) Purification and characterization of an antioxidant peptide obtained from tuna backbone protein by enzymatic hydrolysis. Process Biochem 42:840–846
Chen HM, Muramoto K, Yamauchi F, Nokihara K (1996) Antioxidant activity of designed peptides based on the antioxidative peptide isolated from digests of a soybean protein. J Agric Food Chem 44:2619–2623
Dávalos A, Miguel M, Bartolomé B, López-Fandiño R (2004) Antioxidant activity of peptides derived from egg white proteins by enzymatic hydrolysis. J Food Prot 67:1939–1944
Cheng Z, Ren J, Li Y, Chang W, Chen Z (2003) Establishment of a quantitative structure-activity relationship model for evaluating and predicting the protective potentials of phenolic antioxidants on lipid peroxidation. J Pharm Sci 92:475–484
Yoshie-Stark Y, Wada Y, Schott M, Wäsche A (2006) Functional and bioactive properties of rapeseed protein concentrates and sensory analysis of food application with rapeseed protein concentrates. LWT 39:503–512
Yoshimura Y, Iijina T, Watanabe T, Nakazawa H (1997) Antioxidative effect of Maillard reaction products using glucose-glycine model system. J Agric Food Chem 45:4106–4109
Laudano AP, Doolittle RF (1980) Studies on synthetic peptides that bind to fibrinogen and prevent fibrin polymerization. Structural requirements, number of binding sites, and species differences. Biochemistry 19:1013–1019
Jones JD (1979) Rapeseed protein concentrate preparation, evaluation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 56:716–721
Lacroix M, Amiot J, Brisson GJ (1983) Hydrolysis and ultrafiltration treatment to improve the nutritive value of rapeseed proteins. J Food Sci 48:1644–1645
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S.B., Wang, Z. & Xu, S.Y. Antioxidant and Antithrombotic Activities of Rapeseed Peptides. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85, 521–527 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-008-1217-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-008-1217-y