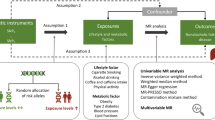
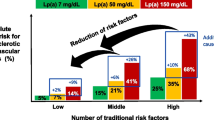
Abstract
Sixteen nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy lipoprotein measurements of more than 1,000 subjects of GOLDN study, at fasting and at 3.5 and 6 h after a postprandial fat (PPL) challenge at visits 2 and 4, before and after a 3 weeks Fenofibrate (FF) treatment, were included in 6 time-independent multivariate factor analyses. Their top 1,541 unique SNPs were assessed for association with GOLDN NMR-particles and classical lipids. Several SNPs with −log10 p > 7.3 and MAF ≥ 0.10, mostly intergenic associated with NMR-single traits near genes FAM84B (8q24.21), CRIPT (2p21), ACOXL (2q13), BCL2L11 (2q13), PCDH10 (4q28.3), NXPH1 (7p22), and SLC24A4 (14q32.12) in association with NMR-LDLs; HOMER1 (5q14.2), KIT (4q11–q12), VSNL1 (2p24.3), QPRT (16p11.2), SYNPR (3p14.2), NXPH1 (7p22), NELL1 (11p15.1), and RUNX3 (1p36) with NMR-HDLs; and DOK5-CBLN4-MC3R (20q13), NELL1 (11p15.1), STXBP6 (14q12), APOB (2p24-p23), GPR133 (12q24.33), FAM84B (8q24.21) and NR5A2 (1q32.1) in association with NMR-VLDLs particles. NMR single traits associations produced 75 % of 114 significant candidates, 7 % belonged to classical lipids and 18 % overlapped, and 16 % matched for time of discovery between NMR- and classical traits. Five proxy genes, (ACOXL, FAM84B, NXPH1, STK40 and VAPA) showed pleiotropic effects. While tagged for significant associations in our study and with some extra evidence from the literature, candidates as CBNL4, FAM84B, NXPH1, SLC24A4 remain unclear for their functional relation to lipid metabolism. Although GOLDN study is one of the largest in studying PPL and FF treatment effects, the relatively small samples (over 700–1,000 subjects) in association tests appeals for a replication of such a study. Thus, further investigation is needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CHYL:
-
Chylomicrons
- dbGaP:
-
The database of Genotypes and Phenotypes
- FF:
-
Fenofibrate
- GOLDN:
-
Genetics of Lipid Lowering Drugs and Diet Network study
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
- IDL:
-
Intermediate density lipoproteins
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- MAF:
-
Minor allele frequency
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy lipoprotein measurements
- NCBI:
-
The National Center for Biotechnology Information
- PPL:
-
Oral fat challenge
- SNPs:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TAG:
-
Triglycerides
- VLDL:
-
Very low density lipoprotein
References
Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report (2002) Circulation 106(25):3143–3421
Carmena R, Duriez P, Fruchart JC: Atherogenic lipoprotein particles in atherosclerosis (2004) Circulation 109(23 Suppl 1):III2–III7
Otvos JD, Jeyarajah EJ, Bennett DW, Krauss RM (1992) Development of a proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic method for determining plasma lipoprotein concentrations and subspecies distributions from a single, rapid measurement. Clin Chem 38(9):1632–1638
Garvey WT, Kwon S, Zheng D, Shaughnessy S, Wallace P, Hutto A, Pugh K, Jenkins AJ, Klein RL, Liao Y (2003) Effects of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes on lipoprotein subclass particle size and concentration determined by nuclear magnetic resonance. Diabetes 52(2):453–462
Blake GJ, Albert MA, Rifai N, Ridker PM (2003) Effect of pravastatin on LDL particle concentration as determined by NMR spectroscopy: a substudy of a randomized placebo controlled trial. Eur Heart J 24(20):1843–1847
Nofer JR (2011) Hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular disease: triglycerides—a revival of cardiovascular risk factor? Curr Opin Lipidol 22(4):319–321
Lada AT, Rudel LL (2004) Associations of low density lipoprotein particle composition with atherogenicity. Curr Opin Lipidol 15(1):19–24
Kettunen J, Tukiainen T, Sarin AP, Ortega-Alonso A, Tikkanen E, Lyytikainen LP, Kangas AJ, Soininen P, Wurtz P, Silander K et al (2012) Genome-wide association study identifies multiple loci influencing human serum metabolite levels. Nat Genet 44(3):269–276
Mora S, Otvos JD, Rosenson RS, Pradhan A, Buring JE, Ridker PM (2010) Lipoprotein particle size and concentration by nuclear magnetic resonance and incident type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes 59(5):1153–1160
Chasman DI, Pare G, Mora S, Hopewell JC, Peloso G, Clarke R, Cupples LA, Hamsten A, Kathiresan S, Malarstig A et al (2009) Forty-three loci associated with plasma lipoprotein size, concentration, and cholesterol content in genome-wide analysis. PLoS Genet 5(11):e1000730
Jenkins AJ, Lyons TJ, Zheng D, Otvos JD, Lackland DT, McGee D, Garvey WT, Klein RL (2003) Lipoproteins in the DCCT/EDIC cohort: associations with diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 64(3):817–828
Otvos JD, Collins D, Freedman DS, Shalaurova I, Schaefer EJ, McNamara JR, Bloomfield HE, Robins SJ (2006) Low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein particle subclasses predict coronary events and are favorably changed by gemfibrozil therapy in the Veterans Affairs High-Density Lipoprotein Intervention Trial. Circulation 113(12):1556–1563
Freedman DS, Otvos JD, Jeyarajah EJ, Shalaurova I, Cupples LA, Parise H, D’Agostino RB, Wilson PW, Schaefer EJ (2004) Sex and age differences in lipoprotein subclasses measured by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: the Framingham Study. Clin Chem 50(7):1189–1200
Kaess BM, Tomaszewski M, Braund PS, Stark K, Rafelt S, Fischer M, Hardwick R, Nelson CP, Debiec R, Huber F et al (2011) Large-scale candidate gene analysis of HDL particle features. PLoS ONE 6(1):e14529
Lai CQ, Arnett DK, Corella D, Straka RJ, Tsai MY, Peacock JM, Adiconis X, Parnell LD, Hixson JE, Province MA et al (2007) Fenofibrate effect on triglyceride and postprandial response of apolipoprotein A5 variants: the GOLDN study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(6):1417–1425
Kraja AT, Province MA, Straka RJ, Ordovas JM, Borecki IB, Arnett DK (2010) Fenofibrate and metabolic syndrome. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 10(2):138–148
Patsch JR, Miesenbock G, Hopferwieser T, Muhlberger V, Knapp E, Dunn JK, Gotto AM Jr, Patsch W (1992) Relation of triglyceride metabolism and coronary artery disease. Studies in the postprandial state. Arterioscler Thromb 12(11):1336–1345
Tsai MY, Georgopoulos A, Otvos JD, Ordovas JM, Hanson NQ, Peacock JM, Arnett DK (2004) Comparison of ultracentrifugation and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the quantification of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins after an oral fat load. Clin Chem 50(7):1201–1204
Otvos JD (2002) Measurement of lipoprotein subclass profiles by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Lab 48(3–4):171–180
Kenward MG, Roger JH (1997) Small sample inference for fixed effects from restricted maximum likelihood. Biometrics 53(3):983–997
Kraja AT, Rao DC, Weder AB, Mosley TH, Turner ST, Hsiung CA, Quertermous T, Cooper R, Curb JD, Province MA (2005) An evaluation of the metabolic syndrome in a large multi-ethnic study: the Family Blood Pressure Program. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2:17
Kim YJ, Go MJ, Hu C, Hong CB, Kim YK, Lee JY, Hwang JY, Oh JH, Kim DJ, Kim NH et al (2011) Large-scale genome-wide association studies in East Asians identify new genetic loci influencing metabolic traits. Nat Genet 43(10):990–995
Waterworth DM, Ricketts SL, Song K, Chen L, Zhao JH, Ripatti S, Aulchenko YS, Zhang W, Yuan X, Lim N et al (2010) Genetic variants influencing circulating lipid levels and risk of coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30(11):2264–2276
Kraja AT, Vaidya D, Pankow JS, Goodarzi MO, Assimes TL, Kullo IJ, Sovio U, Mathias RA, Sun YV, Franceschini N et al (2011) A bivariate genome-wide approach to metabolic syndrome: STAMPEED consortium. Diabetes 60(4):1329–1339
Kathiresan S, Melander O, Guiducci C, Surti A, Burtt NP, Rieder MJ, Cooper GM, Roos C, Voight BF, Havulinna AS et al (2008) Six new loci associated with blood low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides in humans. Nat Genet 40(2):189–197
Burkhardt R, Toh SA, Lagor WR, Birkeland A, Levin M, Li X, Robblee M, Fedorov VD, Yamamoto M, Satoh T et al (2010) Trib1 is a lipid- and myocardial infarction-associated gene that regulates hepatic lipogenesis and VLDL production in mice. J Clin Invest 120(12):4410–4414
Kathiresan S, Manning AK, Demissie S, D’Agostino RB, Surti A, Guiducci C, Gianniny L, Burtt NP, Melander O, Orho-Melander M et al (2007) A genome-wide association study for blood lipid phenotypes in the Framingham Heart Study. BMC Med Genet 8(Suppl 1):S17
Melzer D, Perry JR, Hernandez D, Corsi AM, Stevens K, Rafferty I, Lauretani F, Murray A, Gibbs JR, Paolisso G et al (2008) A genome-wide association study identifies protein quantitative trait loci (pQTLs). PLoS Genet 4(5):e1000072
Meigs JB, Manning AK, Fox CS, Florez JC, Liu C, Cupples LA, Dupuis J (2007) Genome-wide association with diabetes-related traits in the Framingham Heart Study. BMC Med Genet 8(Suppl 1):S16
Benjamin EJ, Dupuis J, Larson MG, Lunetta KL, Booth SL, Govindaraju DR, Kathiresan S, Keaney JF Jr, Keyes MJ, Lin JP et al (2007) Genome-wide association with select biomarker traits in the Framingham Heart Study. BMC Med Genet 8(Suppl 1):S11
Marroni F, Pfeufer A, Aulchenko YS, Franklin CS, Isaacs A, Pichler I, Wild SH, Oostra BA, Wright AF, Campbell H et al (2009) A genome-wide association scan of RR and QT interval duration in 3 European genetically isolated populations: the EUROSPAN project. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2(4):322–328
Teslovich TM, Musunuru K, Smith AV, Edmondson AC, Stylianou IM, Koseki M, Pirruccello JP, Ripatti S, Chasman DI, Willer CJ et al (2010) Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature 466(7307):707–713
Kathiresan S, Willer CJ, Peloso GM, Demissie S, Musunuru K, Schadt EE, Kaplan L, Bennett D, Li Y, Tanaka T et al (2009) Common variants at 30 loci contribute to polygenic dyslipidemia. Nat Genet 41(1):56–65
Murea M, Lu L, Ma L, Hicks PJ, Divers J, McDonough CW, Langefeld CD, Bowden DW, Freedman BI (2011) Genome-wide association scan for survival on dialysis in African-Americans with type 2 diabetes. Am J Nephrol 33(6):502–509
Tabassum R, Mahajan A, Chauhan G, Dwivedi OP, Ghosh S, Tandon N, Bharadwaj D (2010) Evaluation of DOK5 as a susceptibility gene for type 2 diabetes and obesity in North Indian population. BMC Med Genet 11:35
Santos JL, De la Cruz R, Holst C, Grau K, Naranjo C, Maiz A, Astrup A, Saris WH, MacDonald I, Oppert JM et al (2011) Allelic variants of melanocortin 3 receptor gene (MC3R) and weight loss in obesity: a randomised trial of hypo-energetic high- versus low-fat diets. PLoS ONE 6(6):e19934
Mencarelli M, Dubern B, Alili R, Maestrini S, Benajiba L, Tagliaferri M, Galan P, Rinaldi M, Simon C, Tounian P et al (2011) Rare melanocortin-3 receptor mutations with in vitro functional consequences are associated with human obesity. Hum Mol Genet 20(2):392–399
Soininen P, Kangas AJ, Wurtz P, Tukiainen T, Tynkkynen T, Laatikainen R, Jarvelin MR, Kahonen M, Lehtimaki T, Viikari J et al (2009) High-throughput serum NMR metabonomics for cost-effective holistic studies on systemic metabolism. Analyst 134(9):1781–1785
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Jim Otvos of Liposciences Inc. for providing comments on a preliminary draft of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by the GOLDN NIH grant R01 HL09135701.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Kraja, A.T., Borecki, I.B., Tsai, M.Y. et al. Genetic Analysis of 16 NMR-Lipoprotein Fractions in Humans, the GOLDN Study. Lipids 48, 155–165 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-012-3740-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-012-3740-8