Abstract
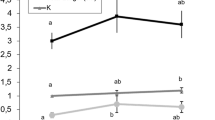
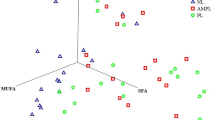
Thirty-five species of marine mollusk bivalves were analyzed for their fatty acid (FA) composition of cardiolipin (Ptd2Gro). All species showed a Ptd2Gro with strong selectivity for only a few polyunsaturated fatty acids, but three characteristic FA profiles emerged, with clear parallels to bivalve phylogeny. A first group of 12 species belonging to the Eupteriomorphia subgroup (Filibranchia) was characterized by a Ptd2Gro almost exclusively composed of 22:6n-3, whereas in the four Filibranchia Pteriomorph species analyzed, this FA was combined with substantial proportions of 18:2n-6 and 18:3n-3. Finally, a third group of 20 species, all belonging to the Heterodonta subclass, possessed Ptd2Gro containing predominantly both 22:6n-3 and 20:5n-3. Polyunsaturated FA moieties and arrangements in the Ptd2Gro of some marine species investigated in other classes of the mollusk phylum (Gastropoda, Polyplacophora) were found to be different. The present results suggest that the specific Ptd2Gro FA compositions in bivalves are likely to be controlled and conserved in species of the same phylogenetic group. Functional significances of the evolution of this mitochondrial lipid structure in bivalves are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daum G (1985) Lipids of mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 822:1–42
Robinson NC, Zborowski J, Talbert LH (1990) Cardiolipin-depleted bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase: binding stoichiometry and affinity for cardiolipin derivatives. Biochemistry 29:8962–8969
Hoch FL (1992) Cardiolipins and biomembrane function. Biochem Biophys Acta 1113:71–133
Berger A, German JB, Gershwin ME (1993) Biochemistry of CL: sensitivity to dietary fatty acids. In: Kissela JE (ed) Advances in food and nutrition research, vol 37. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 259–338
McAuley KE, Fyfe PK, Ridge JP, Isaacs NW, Cogdell RJ, Jones MR (1999) Structural details of an interaction between cardiolipin and an integral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:14706–14711
Schlame M, Rua D, Greenberg ML (2000) The biosynthesis and functional role of cardiolipin. Prog Lipid Res 39:257–288
Zhang M, Mileykovskaya E, Dowhan W (2002) Gluing the respiratory chain together: cardiolipin is required for supercomplex formation in the inner mitochondrial membrane. J Biol Chem 277:43553–43556
Pfeiffer K, Gohil VM, Stuart JA, Hunte C, Brandt U, Greenberg ML, Schägger H (2003) Cardiolipin stabilizes respiratory chain supercomplexes. J Biol Chem 278:52873–52880
Boekema EJ, Braun H-P (2006) Supramolecular structure of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system. J Biol Chem 282:1–4
Koshkin V, Greenberg ML (2000) Oxidative phosphorylation in cardiolipin-lacking yeast mitochondria. Biochem J 347:687–691
Tuominen EKJ, Carmichael CJA, Kinnunen PKJ (2002) Phospholipid–cytochrome c interaction. J Biol Chem 277:8822–8826
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2005) Cardiolipin oxidation sets cytochrome c free. Nat Chem Biol 1:188–189
Robinson NC (1982) Specificity and binding affinity of phospholipids to the high-affinity cardiolipin sites of beef heart cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry 21:184–188
Schlame M, Ren M, Xu Y, Greenberg ML, Haller I (2005) Molecular symmetry in mitochondrial cardiolipins. Chem Phys Lipids 138:38–49
Schlame M, Brody S, Hostetler K (1993) Mitochondrial CL in diverse eukaryotes. Comparison of biosynthetic reactions and molecular acyl species. Eur J Biochem 212:727–735
Schlame M, Ren M (2006) Barth syndrome, a human disorder of cardiolipin metabolism. FEBS Lett 580:5450–5455
Yamaoka S, Urade R, Kito M (1988) Mitochondrial function in rats is affected by modification of membrane phospholipids with dietary sardine oil. J Nutr 118:290–296
Yamaoka S, Urade R, Kito M (1990) Cardiolipin molecular species in rat heart mitochondria are sensitive to essential fatty acid-deficient dietary lipids. J Nutr 120:415–421
Yamaoka-Koseki S, Urade R, Kito M (1991) Cardiolipins from rats fed different dietary lipids affect bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase activity. J Nutr 121:956–958
Watkins SM, Lin TY, Davis RM, Ching JR, DePeters EJ, Halpern GM, Walzem RL, German JB (2001) Unique phospholipid metabolism in mouse heart in response to dietary docosahexaenoic or alpha-linoleic acids. Lipids 36:247–254
Xu Y, Sutachan JJ, Plesken H, Kelley RI, Schlame M (2005) Characterization of lymphoblast mitochondria from patients with Barth syndrome. Lab Invest 85:823–830
Kraffe E, Soudant P, Marty Y, Kervarec N, Jehan P (2002) Evidence of a tetradocosahexaenoic cardiolipin in some marine bivalves. Lipids 37:507–514
Kraffe E, Soudant P, Marty Y, Kervarec N (2005) Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic enriched cardiolipin in the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Lipids 40(6):619–625
Giribet G, Wheeler WC (2002) On bivalve phylogeny: a high-level analysis of the Bivalvia (Mollusca) based on combined morphology and DNA sequence data. Invertebr Biol 121:271–324
Waller TR (1998) Origin of the molluscan class bivalvia and a phylogeny of major groups. In: Johnston PA, Haggart JW (eds) Bivalves: an eon of evolution—paleobiological studies honoring Norman D. Newell. University of Calgary Press, Calgary, pp 1–45
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Nelson GJ (1993) Isolation and purification of lipids from biological matrices. In: Perkins EG (ed) Analyse of fats, oils and derivatives. AOCS Press, Champaign, pp 20–89
Marty Y, Delaunay F, Moal J, Samain JF (1992) Changes in the fatty acid composition of the scallop Pecten maximus (L.) during larval development. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 163:221–234
Soudant P, Marty Y, Moal J, Masski H, Samain JF (1998) Fatty acid composition of polar lipid classes during larval development of scallop Pecten maximus (L.). Comp Biochem Phys A 121:279–288
Napolitano GE, Ackman RG (1993) Fatty acid dynamics in sea scallops Placopecten magallanicus (Gmelin, 1791) from Georges Bank, Nova Scotia. J Shell Res 12:267–277
Delaunay F, Marty Y, Moal J, Samain JF (1993) The effect of monospecific algal diets on growth and fatty acid composition of Pecten maximus (L.) larvae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 173:163–179
Soudant P, Marty Y, Moal J, Robert R, Quéré C, Le Coz JR, Samain JF (1996) Effect of food fatty acids and sterol quality on Pecten maximus gonad composition and reproduction process. Aquaculture 143:361–378
Soudant P, Moal J, Marty Y, Samain JF (1996) Impact of the quality of dietary fatty acids on metabolism and the composition of polar lipid classes in female gonads of Pecten maximus (L.). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 205:149–163
Soudant P, Moal J, Marty Y, Samain JF (1997) Composition of polar lipid classes in male gonads of Pecten maximus (L.). Effect of nutrition. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 215:103–114
Pernet F, Tremblay R, Bourget E (2003) Biochemical indicator of sea scallop (Placopecten magellanicus) quality based on lipid class composition. Part I: Broodstock conditionning and young larvae performance. J Shell Res 22:365–376
De Moreno JEA, Moreno VJ, Brenner RR (1976) Lipid metabolism of the yellow clam, Mesodesma mactroïdes: 2—polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism. Lipids 11:561–566
Chu FLE, Webb KL (1984) Polyunsaturated fatty acids and neutral lipids in developing larvae of the oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Lipids 19:815–820
Waldock MJ, Holland DL (1984) Fatty acid metabolism in young oysters, Crassostrea gigas: polyunsaturated fatty acids. Lipids 19:332–336
Ackman RG (1983) Fatty acid metabolism of bivalves. In: Proceedings of the second international conference on aquaculture nutrition. Special Publication 2, pp 358–375
Clandinin MT, Field CJ, Hargraves K, Morson L, Zsigmond E (1985) Role of diet fat in subcellular structure and function. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 63:546–556
Napolitano GE, Ratnayake WMN, Ackman RG (1988) Fatty acid components of larval Ostrea edulis (L.): importance of triacylglycerols as a fatty acid reserve. Comp Biochem Phys 90B:875–883
Leray C, Chapelle S, Duportail G, Florentz A (1984) Changes in fluidity and 22:6(n-3) content in phospholipids of trout intestinal bruxh-border membrane as related to environmental salinity. Biochim Biophys Acta 7711:233–238
Hazel JR (1988) Homeoviscous adaptation in animal cell membranes. In: Aloia RC, Curtain CC, Gordon LM (eds) Physiological regulation of membrane fluidity. A.R. Liss, New York, pp 149–188
Hazel JR (1995) Thermal adaptation in biological membranes: is homeoviscous adaptation the explanation? Annu Rev Physiol 57:19–42
Glémet HC, Ballantyne JS (1995) Influences of environmental salinity on the structure and function of gill mitochondria membranes of an osmoconforming invertebrate, Crassostrea virginica. Mar Biol 121:673–683
Green J (1957) The growth of Scrobicularia plana (da Costa) in the gwendraeth estuary. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 36:41–47
Xu Y, Kelley RI, Blanck TJJ, Schlame M (2003) Remodeling of cardiolipin by phospholipid transacylation. J Biol Chem 278:51380–51385
Xu Y, Malhotra A, Ren M, Schlame M (2006) The enzymatic function of tafazzin. J Biol Chem 281:39217–39224
Cao J, Liu Y, Lockwood J, Burn P, Shi Y (2004) A novel cardiolipin-remodeling pathway revealed by a gene encoding an endoplasmic reticulum-associated acyl-CoA:lysocardiolipin acyltransferase (ALCAT1) in mouse. J Biol Chem 279:31727–31734
Van Q, Liu J, Lu B, Feingold KR, Shi Y, Lee RM, Hatch GM (2007) Phospholipid scramblase-3 regulates cardiolipin de novo biosynthesis and its resynthesis in growing HeLa cells. Biochem J 401:103–109
Gohil VM, Hayes P, Matsuyama S, Schägger H, Schlame M, Greenberg ML (2004) Cardiolipin biosynthesis and mitochondrial respiratory chain function are interdependent. J Biol Chem 279:42612–42618
Hoch FL (1998) Minireview: cardiolipins and mitochondrial proton-selective leakage. J Bioenerg Biomembr 30:511–532
Gonzalvez F, Gottlieb E (2007) Cardiolipin: setting the beat of apoptosis. Apoptosis 12:877–885
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Pistolese M, Ruggiero FM (2002) Reactive oxygen species affect mitochondrial electron transport complex I activity through oxidative cardiolipin damage. Gene 286:135–141
Wodtke E (1981) Temperature adaptation of biological membranes. Compensation of the molar activity of cytochrome c oxidase in the mitochondrial energy-transducing membrane during thermal acclimation of the carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Biochim Biophys Acta 640:710–720
Kraffe E, Marty Y, Guderley H (2007) Changes in mitochondrial oxidative capacities during thermal acclimation of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: roles of membrane proteins, phospholipids and their fatty acid compositions. J Exp Biol 210:149–165
Valianpour F, Wanders RJA, Overmars H, Vreken P, van Gennip AH, Baas F, Plecko B, Santer R, Becker K, Barth PG (2002) Cardiolipin deficiency in X-linked cardioskeletal myopathy and neutropenia (Barth syndrome, MIM 302060): a study in cultured skin fibroblast. J Pediatr 141:729–733
Schlame M, Towbin JA, Heerdt PM, Jehle R, DiMauro S, Blank TJJ (2002) Deficiency of tetralinoleyl-cardiolipin in Barth syndrome. Ann Neurol 51:634–637
Ma L, Vaz FM, Gu Z, Wanders RJA, Greenberg ML (2004) The human TAZ gene complements mitochondrial dysfunction in the yeast taz1D mutant. Implications for Barth syndrome. J Biol Chem 279:44394–44399
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank A. Wacker, E. Palacios, and A. Druinker for supply of some bivalve species. This work was supported by a grant from “Ministère de l’Education Nationale de la Recherche et de la Technologie” (M.E.N.R.T., France).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kraffe, E., Grall, J., Le Duff, M. et al. A Striking Parallel Between Cardiolipin Fatty Acid Composition and Phylogenetic Belonging in Marine Bivalves: A Possible Adaptative Evolution?. Lipids 43, 961–970 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-008-3219-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-008-3219-9