Abstract
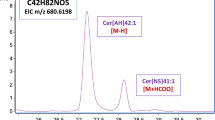
The stratum corneum (SC) requires ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids to provide the cutaneous permeability barrier. SC lipids can be analyzed by normal-phase high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC). However, without further analysis, some uncertainty remains about the molecular composition of lipids represented by every TLC band of an unknown sample. We therefore analyzed each ceramide band further by subjecting the isolated lipids to a direct coupling of reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (HPLC/ESI-MS, or IC/MS). IC/MS analysis and ESI-MS/MS negative ion and collision-induced dissociation experiments revealed that ceramide band 4 contained not only N-(ω-OH-acyl)acyl-6-OH-sphingosine, Cer(EOH), but also N-(α-OH-acyl)-sphingosine. Band 5 exclusively contained N-acyl-6-OH-sphingosine. Our results demonstrate the benefit of LC/MS analysis for selective identification of human SC ceramides. Moreover, the combination of HPTLC for pre-separation and LC/MS for identification of lipids is an even more powerful tool for detailed ceramide analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cer(AP):
-
N-(α-OH-acyl)-4-OH-sphinganine
- Cer(AS):
-
N-(α-OH-acyl)-sphingosine
- Cer(EOH):
-
N-(ω-OH-acyl)acyl-6-OH-sphingosine
- Cer(EOP):
-
an ω-esterified ceramide containing phytosphingosine as a sphingosine backbone and an ω-esterified linoleic acid
- Cer(EOS):
-
N-(ω-OH-acyl)acyl-sphinganine
- Cer(NH):
-
N-acyl-6-OH-sphingosine
- Cer(NP):
-
N-acyl-4-OH-sphinganine
- Cer(NS):
-
N-acyl-sphingosine
- CID:
-
collision-induced dissociation
- ELSD:
-
evaporative light-scattering detection
- ESI-MS:
-
electrospray ionization—mass spectrometry
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- HPTLC:
-
high-performance thin-layer chromatography
- LC-MS:
-
liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
- MS:
-
mass spectrometry
- MS/MS:
-
mass spectrometric fragmentation of specific ions
- NMR:
-
nuclear magnetic resonance
- RP:
-
reversed-phase
- SC:
-
stratum corneum
- TLC:
-
thin-layer chromatography
- UV:
-
ultraviolet
References
Proksch, E. (1992) Regulation der epidermalen Permeabilitäts-barriere durch Lipide und durch Hyperprofilation, Hautarzt 43, 331–338.
Schurer, N.Y., and Elias, P.M. (1991) The Biochemistry and Function of Stratum Corneum Lipids, Adv. Lipid Res. 24, 27–56.
Elias, P.M., Goerke, J., and Friend, D.S. (1977) Mammalian Epidermal Barrier Layer Lipids: Composition and Influence of Structure, J. Invest. Dermatol. 69, 535–546.
Elias, P.M. (1981) Epidermal Lipids, Membranes, and Keratinization, Int. J. Dermatol. 20, 1–19.
Downing, D.T., Stewart, M.E., Wertz, P.W., Colton, S.W., Abraham, W., and Strauss, J.S. (1987) Skin Lipids: An Update, J. Invest. Dermatol. 88, 2s-6s.
Brooks, G., and Idson, B. (1991) Skin Lipids., Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 13, 103–113.
Forslind, B. (1994) A Domain Mosaic Model of the Skin Barrier, Acta Derm. Venereol. 74, 1–6.
Downing, D.T., Wertz, P.W., and Stewart, M.E. (1986) The Role of Sebum and Epidermal Lipids in the Cosmetic Properties of Skin, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 8, 115–123.
Imokawa, G., Akasaki, S., Kawamata, A., Yano, S., and Takaishi, N. (1989) Water-retaining Function in the Stratum Corneum and Its Recovery Properties by Synthetic Pseudoceramides, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 40, 273–285
Motta, S., Monti, M., Sesana, S., Caputo, R., Carelli, S., and Ghidoni, R. (1993) Ceramide Composition of the Psoriatic Scale, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1182, 147–151.
Yamamoto, A., Serizawa, S., Ito, M., and Sato, Y. (1991) Stratum Corneum Abnormalities in Atopic Dermatitis, Arch. Dermatol. Res. 283, 219–223.
Imokawa, G., Abe, A., Jin, K., Higaki, Y., Kawashima, M., and Hidano, A. (1991) Decreased Level of Ceramides in Stratum Corneum of Atopic Dermatitis: An Etiologic Factor in Atopic Dry Skin?, J. Invest. Dermatol. 96, 523–526.
Di Nardo, A., Wertz, P.W., Giannetti, A., and Seidenari, S. (1998). Ceramide and Cholesterol Composition of the Skin of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis, Acta Derm. Venereol. 78, 27–30.
Wertz, P.W., Miethke, M.C., Long, S.A., Strauss, J.S., and Downing, D.T. (1985) The Composition of the Ceramides from Human Stratum Corneum and from Comedones, J. Invest. Dermatol. 84, 410–412.
Robson, K.J., Stewart, M.E., Michelsen, S., Lazo, N.D., and Downing, D.T. (1994) 6-Hydroxy-4-sphingenine in Human Epidermal Ceramides, J. Lipid Res. 35, 2060–2068.
Stewart, M.E., and Downing, D.T. (1999) A New 6-Hydroxy-4-sphingenine-Containing Ceramide in Human Skin, J. Lipid Res. 40, 1434–1439.
Gildenast, T., and Lasch, J. (1997) Isolation of Ceramide Fractions from Human Stratum Corneum Lipid Extracts by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1346, 69–74.
Norlén L., Nicander, I., Lundsjo, A., Cronholm, T., and Forslind, B., (1998) A New HPLC-Based Method for Quantitative Analysis of Inner Stratum Corneum Lipids with Special Reference to the Free Fatty Acid Fraction, Arch. Dermatol. Res. 290, 508–516.
Gaudin, K., Chaminade, P., Ferrier, D., Baillet, A., and Tchapla, A. (1999) Analysis of Commercial Ceramides by Non-aqueous Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography with Evaporative Light-Scattering Detection, Chromatographia 49, 241–248.
Gaudin, K., Chaminade, P., Baillet, A., Ferrier, D., Bleton, J., Goursaud, S., and Tchapla, A. (1999) Contribution to Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Cutaneous Ceramides. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Rel. Technol. 22, 379–400.
Hoi Do, U., Pei, P.T., and Minard, R.D. (1981) Separation of Molecular Species of Ceramides as Benzoyl and P-Nitrobenzoyl Derivatives by High Performance Liquid Chromatography, Lipids 16, 855–862.
Guey, C., Arbey, E., and Gaetani, Q. (1998) Nonhydroxylated Long-Chain Fatty Acid/6-Hydroxy-4-sphingenine Ceramides or CER [NLH]: A Novel Class of Ceramides in Human Stratum Corneum Between Classes 5 and 6 of Downing Classification. Presented as a poster, at Stratum Corneum II, An International Symposium, Cardiff, 10–12 September 1998.
Liebisch, G., Drobnik, W., Reil, M., Truembach, B., Arnecke, R., Olgemoeller, B., Roscher, A., and Schmitz, G. (1999) Quantitative Measurement of Different Ceramide Species from Crude Cellular Extracts by Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS), J. Lipid Res. 40, 1539–1546.
Melnik, B.C., Hollmann, J., Erler, E., Verhoeven, B., and Plewig, G. (1989) Microanalytical Screening of All Major Stratum Corneum Lipids by Sequential High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography, J. Invest. Dermatol. 92, 231–234.
Lampe, M.A., Burlingame, A.L., Whitney, J., Williams, M.L., Brown, B.E., Roitman, E., and Elias, P.M. (1983) Human Stratum Corneum Lipids: Characterization and Regional Variations, J. Lipid Res. 24, 120–130.
Vietzke, J.-P., Strassner, M., and Hintze, U. (1999) Separation and Identification of Ceramides in the Human Stratum Corneum by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry and Electrospray Multiple-Stage Mass Spectrometry Profiling, Chromatographia 50, 15–20.
Raith, K., and Neubert, R. (1998) Structural Studies on Ceramides by Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry, Rapid Comm. Mass Spectrom. 12, 935–938.
Wertz, P.W., and van den Bergh, B. (1998) The Physical, Chemical and Functional Properties of Lipids in the Skin and Other Biological Barriers, Chem. Phys. Lipids 91, 85–96.
Bleck, O., Abeck, D., Ring, J., Hoppe, U., Vietzke, J.-P., Wolber, R., Brandt, O., and Schreiner, V. (1999) Two Ceramide Subfractions Detectable in Cer(AS) Position by HPTLC in Skin Surface Lipids of Non-lesional Skin of Atopic Eczema, J. Invest. Dermatol. 113, 894–900.
Hamanaka, S., Asagami, C., Suzuki, M., Inagaki, F., and Suzuki, A. (1989) Structure Determination of Glucosylβ1-N-(ω-O-linoleoyl)-acylsphingosines of Human Epidermis, J. Biochem. 105, 684–690.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Vietzke, JP., Brandt, O., Abeck, D. et al. Comparative investigation of human stratum corneum ceramides. Lipids 36, 299–304 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0721-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0721-9