Abstract
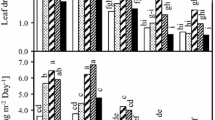
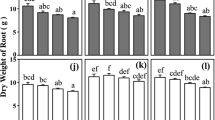
Excess salts in soil severely inhibit plant growth and yield. Various nutrients can relieve the inhibitory effect of salt on plants. Elaeagnus angustifolia is a tree species that is utilized in landscaping and ecological restoration in China and shows tolerance to saline soils. In this experiment, we first determined the optimal concentration of single-nutrient inputs for promoting growth of E. angustifolia seedlings and alleviating salt stress. The optimal nitrogen (NO3−), phosphorus (PO43−), potassium (K+), and calcium (Ca2+) concentrations under salt stress were 2, 0.6, 2, and 2 mM, respectively. Based on this result, we carried out an optimum nutrient ratio experiment by a four-factor and three-level orthogonal experiment. The results showed that under normal growth conditions, the optimal nutrient combinations for NO3−, PO43−, K+, and Ca2+ were 2, 0.6, 5, and 1 mM; 5, 0.2, 5, and 2 mM; and 5, 0.6, 1, and 5 mM, respectively, which increased plant height, biomass, and the chlorophyll content of E. angustifolia seedlings. Under salt stress, the optimal nutrient combinations were 5, 0.2, 5, and 2 mM; and 5, 0.6, 1, and 5 mM, respectively. This study provides a theoretical basis for optimal fertilization of E. angustifolia seedlings in saline-alkali soils.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant physiol 24(1):1–7
Chen M, Song J, Wang B-S (2010) NaCl increases the activity of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase in C3 halophyte Suaeda salsa callus. Acta Physiol Plant 32:27–36
Cho-Ruk K (2003) Phosphorus influence on the response of pasture plants to salinity, PhD thesis, Environmental Science, University of Wollongong. http://ro.uow.edu.au/theses/451. Accessed 2 Sept 2017
Cramer GR, Läuchli A, Polito VS (1985) Displacement of Ca2+ by Na+ from the plasmalemma of root cells a primary response to salt stress? Plant Physiol 79(1):207–211
Djumaeva D, Lamers JPA, Martius C, Khamzina A, Ibragimov N, Vlek PLG (2010) Quantification of symbiotic nitrogen fixation by Elaeagnus angustifolia L. on salt-affected irrigated croplands using two 15N isotopic methods. Nutr Cycl A 88:329–339
Feng Z-T, Deng Y-Q, Zhang S-C, Liang X, Yuan F, Hao J-L, Zhang J-C, Sun S-F, Wang B-S (2015) K+ accumulation in the cytoplasm and nucleus of the salt gland cells of Limonium bicolor accompanies increased rates of salt secretion under NaCl treatment using NanoSIMS. Plant Sci 238:286–296
Han G, Wang M, Yuan F, Na Sui, Song J, Wang B (2014) The CCCH zinc finger protein gene AtZFP1 improves salt resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 86:237–253
Hoagland D (1938) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil (California Agricultural Experiment Station), 347th edn. University of California, College of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station, Berkeley
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. University of California, College of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station, Berkeley
Hu Y, Schmidhalter U (2005) Drought and salinity: a comparison of their effects on mineral nutrition of plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 168(4):541–549
Khamzina A, Lamers JPA, Martius C, Worbes M, Vlek PLG (2006) Potential of nine multipurpose tree species to reduce saline groundwater tables in the lower Amu Darya River region of Uzbekistan. Agroforest Syst 68:151–165
Khavari-Nejad RA, Mostofi Y (1998) Effects of NaCl on photosynthetic pigments, saccharides, and chloroplast ultrastructure in leaves of tomato cultivars. Photosynthetica 35(1):151–154
Kong Q, He X, Shu L, Miao M (2017) Ofloxacin adsorption by activated carbon derived from luffa sponge: Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic analyses. Process Saf Environ Prot 112:254–264
Li J, Pu L, Han M, Zhu M, Zhang R, Xiang Y (2014) Soil salinization research in China: advances and prospects. J Geogr Sci 24(5):943–960
Lin J, Li JP, Yuan F, Yang Z, Wang BS, Chen M (2018) Transcriptome profiling of genes involved in photosynthesis in Elaeagnus angustifolia L. under salt stress. Photosynthetica 56(4):998–1009
Liu XJ, Yang YM, Li WQ, Li CZ, Duan DY, Tadano T (2004) Interactive effects of sodium chloride and nitrogen on growth and ion accumulation of a halophyte. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 35:2111–2123
Masutha TH, Muofhe ML, Dakora FD (1997) Evaluation of N2 fixation and agroforestry potential in selected tree legumes for sustainable use in South Africa. Soil Biol Biochem 29(5/6):993–998
Munns R (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol 167:645–663
Qi Y, Li J, Chen C, Li L, Zheng X, Liu J, Zhu T, Pang C, Wang B, Chen M (2018) Adaptive growth response of exotic Elaeagnus angustifolia L. to indigenous saline soil and its beneficial effects on the soil system in the Yellow River Delta. China. Trees 32(6):1723–1735 (Published online 31 July 2018)
Reddy KR, Debusk WF (1984) Growth characteristics of aquatic macrophytes cultured in nutrient-enriched water: I. water hyacinth, water lettuce, and pennywort. Econ Bot 38(2):229–239
Ródenas R, García-Legaz MF, López-Gómez E, Martínez V, Rubio F, Botella MÁ (2017) NO3 −, PO4 3− and SO4 2− deprivation reduced LKT1-mediated low-affinity K+ uptake and SKOR-mediated K+ translocation in tomato and Arabidopsis plants. Physiol Plant 160:410–424
Rubio JS, García-Sínchez F, Rubio F, Martínez V (2009) Yield, blossom-end rot incidence, and fruit quality in pepper plants under moderate salinity are affected by K+ and Ca2+ fertilization. Sci Hortic 119:79–87
Savci S (2012) Investigation of effect of chemical fertilizers on environment. APCBEE Proc 1:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.03.047
Shabala S, Demidchik SL, Cuin TA, Smith SJ, Miller AJ, Davies JM, Newman IA (2006) Extracellular Ca2+ ameliorates NaCl-induced K+ loss from Arabidopsis root and leaf cells by controlling plasma membrane K+-permeable channels. Plant Physiol 141:1653–1665
Shao Q, Han N, Ding T, Zhou F, Wang B (2014) SsHKT1;1 is a potassium transporter of the C3 halophyte Suaeda salsa that is involved in salt tolerance. Funct Plant Biol 41:790–802
Song J, Wang B (2015) Using euhalophytes to understand salt tolerance and to develop saline agriculture: Suaeda salsa as a promising model. Ann Bot 115:541–553
Song J, Shi G, Xing S, Yin C, Fan H, Wang B (2009) Ecophysiological responses of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa to the interactive effects of salinity and nitrate availability. Aquat Bot 91:311–317
Sui N, Han G (2014) Salt-induced photoinhibition of PSII is alleviated in halophyte Thellungiella halophila by increases of unsaturated fatty acids in membrane lipids. Acta Physiol Plant 36:983–992
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91(5):503–527
Yang Z, Wang Y, Wei X, Zhao X, Wang B, Sui N (2017) Transcription profiles of genes related to hormonal regulations under salt stress in Sweet Sorghum. Plant Mol Biol Rep 35(6):586–599
Yuan F, Leng B, Wang B (2016) Progress in studying salt secretion from the salt glands in Recretohalophytes: how do plants secrete salt? Front Plant Sci 7:977
Zhou L, Shi W, Wu S (2013) Performance optimization in a centrifugal pump impeller by orthogonal experiment and numerical simulation. Adv Mech Eng 3:1–7
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Zhu JK, Liu J, Xiong L (1998) Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in Arabidopsis: evidence for a critical role of potassium nutrition. Plant Cell 10(7):1181–1191
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the major projects of science and technology in Shandong province (2017CXGC0311, 2017CXGC0313) and the Program for Scientific Research Innovation Team in Colleges and Universities of Shandong Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Renault.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zhu, T., Liu, J. et al. An orthogonal test of the effect of NO3−, PO43−, K+, and Ca2+ on the growth and ion absorption of Elaeagnus angustifolia L. seedlings under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 41, 179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2969-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2969-8