Abstract
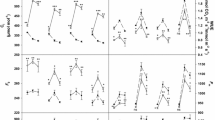
The planting of RR2 Intacta soybeans by farmers has been expanding strongly. However, some visual injuries have been noted after glyphosate application. The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of glyphosate application on chlorophyll, photosynthesis and water use of four Intacta RR2 soybean cultivars. The experiment was conducted in a greenhouse, in a randomized block design with a 3 × 4 factorial scheme, consisting of three glyphosate rates and four soybean cultivars. The glyphosate formula used was isopropylamine salt + potassium salt. The parameters analyzed were phytotoxicity at 7, 14, 21 and 28 days after application, and total chlorophyll index at 0, 3, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42 and 49 days after application. Furthermore, 40 days after application, the net CO2 assimilation rate (A), transpiration rate (E), stomatal conductance (G), and internal CO2 concentration (Ci) were evaluated as well. The water-use efficiency (WUE) and carboxylation efficiency were calculated. The data were submitted to analysis of variance and compared by the Tukey’s test (p ≤ 0.05), followed by regression analysis. The phytotoxicity influence could be seen until 21 days after application, in which Monsoy 6210 IPRO cultivar was the most injured. The increasing doses promoted a reduction of the chlorophyll level up to 35 days after application in Monsoy 6410 IPRO. The cultivars tested here showed similar chlorophyll index values. On the 3rd, 7th and 14th DAA (Fig. 5a–c), there was a significant linear decline in the chlorophyll index with rising glyphosate dose for all four cultivars. The chlorophyll index cultivars were not influenced by the doses on the 42nd and 49th DAA. There was no difference in water use and carboxylation efficiency. The parameters A, E and A/Ci showed a positive correlation as the doses increased, while Ci declined, in both cultivars. The application of glyphosate on these soybean cultivars causes different injuries according to the sensitivity. In general, RR2 soybeans have the ability to recover from visual intoxication injuries and reestablish the normal chlorophyll production and photosynthetic parameters after glyphosate application.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAA:
-
Days after application
- A:
-
Net CO2 assimilation rate
- E:
-
Transpiration rate
- G:
-
Stomatal conductance
- Ci:
-
Internal CO2 concentration
- WUE:
-
Water-use efficiency
- A/Ci:
-
Carboxylation efficiency
- AMPA:
-
Aminomethylphosphonic acid
- ALA:
-
Aminolaevulinic acid
References
Albrecht LP, Barbosa AP, Silva AFM, Mendes MA, Maraschi-Silva LM, Albrecht AJP (2011) Desempenho da soja roundup ready sob aplicação de glyphosate em diferentes estádios. Planta Daninha 29:585–590. doi:10.1590/S0100-83582011000300012
Albrecht AJP, Albrecht LP, Krenchinski FH, Placido HF, Lorenzetti JB, Victoria Filho R, Barroso AAM (2014) Behavior of rr soybeans subjected to different formulations and rates of glyphosate in the reproductive period. Planta Daninha 32:851–859
Bosco MRO, Oliveira AB, Hernandez FFF, Lacerda CF (2009) Efeito do NaCl sobre o crescimento, fotossíntese e relações hídricas de plantas de berinjela. Rev Ceres 56:296–302
Bott S, Tesfamariam T, Candan H, Cakmak I, Römheld V, Neumann G (2008) Glyphosate-induced impairment of plant growth and micronutrient status in glyphosate-resistant soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Soil 312:185–194. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9760-8
Cakmak I, Yazici A, Tutus Y, Ozturk L (2009) Glyphosate reduced seed and leaf concentrations of calcium, manganese, magnesium, and iron in non-glyphosate resistant soybean. Eur J Agron 31:114–119. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2009.07.001
Cataneo AC, Chamma KL, Ferreira LC, Déstro FG, Carvalho JC, Barbosa EL (2002) S-glutathione S-transferase activity in acetochlor, atrazine and (Zea oxyfluorfen metabolization in maize (Zea mays L.), sorghum (Triticum (Sorghum bicolor L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) (Poaceae). Acta Sci 24:619–623. doi:10.4025/actascibiolsci.v24i0.2366
Clive J (2014) Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2014. ISAAA Brief n. 49. ISAAA: Ithaca, NY
COMISSÃO TÉCNICA NACIONAL DE BIOSSEGURANÇA (CTNBio) (2015) Aprovações comerciais de soja. http://www.ctnbio.gov.br/index.php/content/view/14782.html. Accessed 27 Mar 2015
CONAB (2015) Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento. Acompanhamento da safra brasileira de grãos. V.2—Safra 2014/15, n. 6—Sexto Levantamento
Couée I, Sulmon C, Gouesbet G, Amrani E (2006) Involvement of soluble sugars in reactive oxygen species balance and responses to oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot 57:449–459
Coutinho CFB, Mazo LH (2005) Complexos metálicos com o herbicida glifosato: revisão. Quim Nova 28:1038–1045. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422005000600019
Da Matta FM, Loos RA, Rodrigues R, Barros RS (2001) Actual and potential photosynthetic rates of tropical crop species. Rev Bras Fisiol Veg 13:24–32
Ding W, Reddy KN, Zablotowicz RM, Bellaloui N, Bruns HA (2011) Physiological responses of glyphosate-resistant and glyphosate-sensitive soybean to aminomethylphosphonic acid, a metabolite of glyphosate. Chemosphere 83:593–598. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.008
Duke SO (2010) Glyphosate degradation in glyphosate-resistant and-susceptible crops and weeds. J Agric Food Chem 59:5835–5841. doi:10.1021/jf102704x
Eker S, Ozturk L, Yazici A, Erenoglu B, Romheld V, Cakmak I (2006) Foliar-applied glyphosate substantially reduced uptake and transport of iron and manganese in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) plants. J Agric Food Chem 54:10019–10025. doi:10.1021/jf0625196
Ferreira DF (2011) Sisvar: a computer statistical analysis system. Ciênc Agrotecnol 35:1039–1042
Gomes MP, Smedbol E, Chalifour A, Hénault-Ethier L, Labrecque M, Lepage L, Lucotte M, Juneau P (2014) Alteration of plant physiology by glyphosate and its by-product aminomethylphosphonic acid: an overview. J Exp Bot 65:4691–4703. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru269
Jadoski SO, Klar AE, Salvador ED (2005) Relações hídricas e fisiológicas em plantas de pimentão ao longo de um dia. Ambiência 1:11–19
Kremer RJ, Means NE, Kim S (2005) Glyphosate affects soybean and root exudation and rhizosphere micro-organims. Int J Environ Anal Chem 85:1165–1174
Procópio SO, Santos JB, Silva AA, Martinez CA, Werlang RC (2004) Características fisiológicas das culturas de soja e feijão e de três espécies de plantas daninhas. Planta Daninha 22:211–216
Radetski CM, Cotelle S, Férard JF (2000) Classical and biochemical endpoints in the evaluation of phytotoxic effects caused by the herbicide trichloroacetate. Environ Exp Bot 44:221–229
Reddy KN, Zablotowicz RM (2003) Glyphosate-resistant soybean response to various salts of glyphosate and glyphosate accumulation in soybean nodules. Weed Sci 51:496–502. doi:10.1614/0043-1745(2003)051[0496:GSRTVS]2.0.CO;2
Reddy KN, Rimando AM, Duke SO (2004) Aminomethylphosphonic acid, a metabolite of glyphosate, causes injury in glyphosate-treated, glyphosate-resistant soybean. J Agric Food Chem 52:5139–5143. doi:10.1021/jf049605v
Remaeh LMR (2004) Estresse oxidativo induzido pelo herbicida lactofen em plantas de soja (Glycine max L. Merril): resposta de enzymes antioxidantes. Botucatu, Dissertação (Mestrado)—Instituto de Biociências, Universidade Estadual Paulista, p 87
Sunohara Y, Matsumoto H (2004) Oxidative injury induced by the herbicide quinclorac on Echinochloa oryzicola Vasing and the involvement of antioxidative ability in its highly selective action in grass species. Plant Sci 167:597–606. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.05.005
Taiz L, Zeiger E (2013) Mineral nutrition. Plant physiology. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, pp 111–144
Trezzi MM, Vidal RA (2001) Herbicidas inibidores de ALS. In: Vidal RA, Merotto Júnior A (eds) Herbicidologia. Porto Alegre, Artmed, pp 25–36
USDA (2015) United States Department of Agriculture. PSD: production, supply and distribution online. Soybeans: World Supply and Distribution. Washington, D.C. http://www.fas.usda.gov/psdonline. Accessed 27 Mar 2015
Venisse JS, Malnoy M, Faize M, Paulin JP, Brisset MN (2002) Modulation of defense responses of Malus spp. during compatible and incompatible interactions with Erwinia amylovora. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:1204–1212
Vidal RA (1997) Herbicidas: mecanismos de ação e resistência de plantas. Palote, Porto Alegre, pp 39–44
Zablotowicz RM, Reddy KN (2004) Impact of Glyphosate on the Symbiosis with Glyphosate-Resistant Transgenic Soybean. J Environ Quality 33:825–831
Zaidi A, Khan MDS, Rizvi PQ (2005) Effect of herbicides on growth, nodulation and nitrogen content of greengram. Agron Sustain Dev 25:497–504
Zobiole LHS, Kremer RJ, Oliveira RS, Constantin J (2010a) Effect of glyphosate on symbiotic N2 fixation and nickel concentration in glyphosate-resistant soybeans. Appl Soil Ecol 44:319–330. doi:10.1002/jpln.201000434
Zobiole LHS, Bonini EA, de Oliveira RS, Kremer RJ, Ferrarese-Filho O (2010b) Glyphosate affects lignin content and amino acid production in glyphosateresistant soybean. Acta Physiol Plant 32:831–837. doi:10.1007/s11738-010-04670
Zobiole LHS, Kremer RJ, Oliveira RS, Constantin J (2010c) Glyphosate affects chlorophyll, nodulation and nutrient accumulation of “second generation” glyphosate-resistant soybean (Glycine max L.). Pestic Biochem Physiol 99:53–60. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2010.10.005
Zobiole LHS, Oliveira RS, Kremer RJ, Muniz AS, Oliveira Junior AD (2010d) Nutrient accumulation and photosynthesis in glyphosate-resistant soybeans is reduced under glyphosate use. J Plant Nutr 33:1860–1873. doi:10.1080/01904167.2010.491890
Zobiole LHS, Oliveira RS Jr, Kremer RJ, Constantin J, Yamada T, Castro C, Oliveira FA (2010e) Effect of glyphosate on symbiotic N2 fixation and nickel concentration in glyphosate-resistant soybeans. Appl Soil Ecol 44:319–330. doi:10.1002/jpln.201000434
Zobiole LHS, Kremer RJ, de Oliveira RS, Constantin J (2010f) Glyphosate affects photosynthesis in first and second generation of glyphosate-resistant soybeans. Plant Soil 336:251–265. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0474-3
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by Universidade Federal do Parana.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F Araniti.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krenchinski, F.H., Albrecht, L.P., Albrecht, A.J.P. et al. Glyphosate affects chlorophyll, photosynthesis and water use of four Intacta RR2 soybean cultivars. Acta Physiol Plant 39, 63 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2358-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2358-0