Abstract
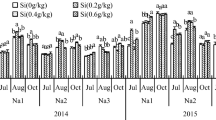
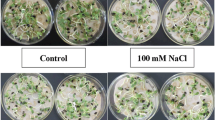
Soil salinity reduces growth of Glycyrrhiza uralensis in arid and semi-arid areas of north-west in China. Silicon (Si) nutrition may alleviate salt stress in many crops including grain crop, fruit crop, and vegetable crop. In this study, the alleviating effects of Si on growth characteristics, antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD and POD) and MDA concentration, and K+ and Na+ concentrations in G. uralensis seedlings subjected to 50 mM NaCl stress were investigated. The results showed that NaCl stress imposed significant reduction in root length, secondary root number, leaf number, and stem and total dry weight of G. uralensis. NaCl stress also significantly reduced the activities of SOD and POD, and ration of K+/Na+, but significantly increased MDA concentration in leaves of G. uralensis seedling. The addition of Si increased SOD and POD activities, and reduced MDA concentration, which resulting in greater reactive oxygen species detoxification and lower lipid peroxidation. Si also significantly increased the ratio of K+/Na+ in stem and leaves of G. uralensis. In conclusion, Si could alleviate adverse effects of salt stress probably by decreasing Na+ concentration and improving antioxidant enzyme activity of G. uralensis, and these alleviating effects were dependent on Si concentration and on Si processing time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abogadallah GM (2010) Antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:369–374
Acosta-Motos JR, Diaz-Vivancos P, Álvarez S, Fernández-García N, Sanchez-Blanco MJ, Hernández JA (2015) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of the ornamental Eugenia myrtifolia L. plants for coping with NaCl stress and recovery. Planta 242:829–846
Ahmad R, Zaheer SH, Ismail S (1992) Role of silicon in salt tolerance of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Sci 85:43–50
Al-aghabary K, Zhu Z, Shi Q (2005) Influence of silicon supply on chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence, and antioxidative enzyme activities in tomato plants under salt stress. J Plant Nutr 27:2101–2115
Ashraf M, Afzal M, Ahmed R, Mujeeb F, Sarwar A, Ali L (2010a) Alleviation of detrimental effects of NaCl by silicon nutrition in salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant genotypes of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). Plant Soil 326:381–391
Ashraf M, Ahmad R, Bhatti AS, Afzal M, Sarwar A, Maqsood MA, Kanwal S (2010b) Amelioration of salt stress in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) by supplying potassium and silicon in hydroponics. Pedosphere 20:153–162
Barba-Espín G, Clemente-Moreno MJ, Alvarez S, García-Legaz MF, Hernandez JA, Díaz-Vivancos P (2011) Salicylic acid negatively affects the response to salt stress in pea plants. Plant Biol 13:909–917
Bradbury M, Ahmad R (1990) The effect of silicon on the growth of Prosopis juliflora growing in saline soil. Plant Soil 125:71–74
Chen GD, Li YX, Zhang H, Chen J, Cai LY (2008) Effects of salt stress on growth and flavonoids content in different organs of two species of Epimedium. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin 28:2047–2054
Choudhury S, Panda P, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2013) Reactive oxygen species signaling in plants under abiotic stress. Plant Signal Behav 8:e23681
Davies KJ (1995) Oxidative stress: the paradox of aerobic life. Biochem Soc Symp 61:1–31
de Azevedo Neto AD, Prisco JT, Eneas J, de Abreu CEB, Gomes-Filho E (2006) Effect of salt stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of salt-tolerant and salt sensitive maize varieties. Environ Exp Bot 56:87–94
Deeba F, Pandey AK, Ranjan S, Mishra A, Singh R, Sharma YK, Shirke PA, Pandey V (2012) Physiological and proteomic responses of cotton (Gossypium herbaceum L.) to drought stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:6–18
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Gong HJ, Randall DP, Flowers TJ (2006) Silicon deposition in root reduces sodium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by reducing bypass flow. Plant Cell Environ 29:1970–1979
Guerrier G (1996) Fluxes of Na+, K+ and Cl−, and osmotic adjustment in Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium and L. esculentum during short- and long-term exposures to NaCl. Physiol Plant 97:583–591
Guntzer F, Keller C, Meunier JD (2012) Benefits of plant silicon for crops: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 32:201–213
Hashemi A, Abdolzadeh A, Sadeghipour HR (2010) Beneficial effects of silicon nutrition in alleviating salinity stress in hydroponically grown canola, Brassica napus L. plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56:244–253
Henriet C, Draye X, Oppitz I, Swenen R, Delvaux B (2006) Effects, distribution and uptake of silicon in banana (Musa spp.) under controlled conditions. Plant Soil 287:359–374
Khan MA, Ungar IA, Showalter AM (2000) Effects of sodium chloride treatments on growth and ion accumulation of the halophyte Haloxylon recurvum. Commun Soil Sci Plan 31:2763–2774
Kim SY, Lim JH, Park MR, Kim YJ, Park TI, Seo YW, Choi KG, Yun SJ (2005) Enhanced antioxidant enzymes are associated with reduced hydrogen peroxide in barley roots under saline stress. J Biochem Mol Biol 38:218–224
Lee SK, Sohn EY, Hamayun M, Yoon JY, Lee JJ (2010) Effect of silicon on growth and salinity stress of soybean plant grown under hydroponic system. Agrofor Syst 80:333–340
Liang YC (1999) Effects of silicon on enzyme activity, and sodium, potassium and calcium concentration in barley under salt stress. Plant Soil 209:217–224
Liang YC, Ding RX (2002) Influence of silicon on microdistribution of mineral ions in roots of salt-stressed barley as associated with salt tolerance in plants. Sci China Ser C 45:298–308
Liang YC, Chen Q, Liu Q, Zhang WH, Ding RX (2003) Exogenous silicon (Si) increases antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces lipid peroxidation in roots of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Plant Physiol 160:1157–1164
Mahajan S, Tuteja N (2005) Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 444:139–158
Modarresi M, Moranlan F, Nematzadeh GL (2014) Antioxidant responses of halophyte plant Aeluropus littoralis under long-term salinity stress. Biologia 69:478–483
Moussa HR (2006) Influence of exogenous application of silicon on physiological response of salt-stressed maize (Zea mays L.). Int J Agric Biol 8:293–297
Ozaki K, Shibano M (2014) Aim for production of Glycyrrhizae Radix in Japan (3): development of a new licorice cultivar. J Nat Med 68:358–362
Parihar P, Singh S, Singh R, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2015) Effect of salinity stress on plants and its tolerance strategies: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4056–4075
Rasool S, Hameed A, Azooz MM, Muneebu-rehman Siddiqi TO, Ahmad P (2013) Salt stress: causes, types and responses of plants. In: Ahmad P, Azooz MM, Prasad MNV (eds) Ecophysiology and responses of plants under salt stress. Springer, New York, pp 1–24
Rios-Gonzalez K, Erdei L, Lips SH (2002) The activity of antioxidant enzymes in maize and sunflower seedlings as affected by salinity and different nitrogen sources. Plant Sci 162:923–930
Romero-Aranda MR, Jurado O, Cuartero J (2006) Silicon alleviates the deleterious salt effect on tomato plant growth by improving plant water status. J Plant Physiol 163:847–855
Rouhier N, Jacquot JP (2008) Getting sick may help plants overcome abiotic stress. New Phytol 180:738–741
Seckin B, Turkan I, Sekmen AH, Ozfidan C (2010) The role of antioxidant defense systems at differential salt tolerance of Hordeum marinum Huds. (sea barleygrass) and Hordeum vulgare L. (cultivated barley). Environ Exp Bot 69:76–85
Shu LZ, Liu YH (2001) Effects of silicon on growth of maize seedlings under salt stress. Agro-Environ Prot 20:38–40
Soundararajan P, Manivannan A, Park YG, Muneer S, Jeong BR (2015) Silicon alleviates salt stress by modulating antioxidant enzyme activities in Dianthus caryophyllus ‘Tula’. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 56:233–239
Soylemezoglu G, Demr K, Inal A, Gunes A (2009) Effect of silicon on antioxidant and stomatal response of two grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) rootstocks grown in boron toxic, saline and boron toxic-saline soil. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 123:240–246
Tang XM, Wang WQ, Yang Q, Liu CL (2008) Effect of NaCl treatment on growth, physiological index and content of effective composition of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. J Jilin Agric Univ 30:172–175 (in Chinese)
Tiryakioglu M, Eker S, Ozkutlu F, Husted S, Cakmak I (2006) Antioxidant defense system and cadmium uptake in barley genotypes differing in cadmium tolerance. J Trace Elem Med Biol 20:181–189
Tuna AL, Kaya C, Higgs D, Murillo-amador B, Demir Girgin AR (2008) Silicon improves salinity tolerance in wheat plants. Environ Exp Bot 62:10–16
Wan CY, Wang D, Hou JL, Wang WQ, Peng F (2011) Effects of NaCl stress on growth and antioxidant enzyme activities of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Prog in Mod Biomed 11:1805–1809 (in Chinese)
Wang XS, Han JG (2007) Effects of NaCl and silicon on ion distribution in the roots, shoots and leaves of two alfalfa cultivars with different salt tolerance. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53:278–285
Wang HM, Xiao XR, Yang MY, Gao ZL, Zang J, Fu XM, Chen YH (2014) Effects of salt stress on antioxidant defense system in the root of Kandelia candel. Bot Stud 55:57–63
Yang XU, Li JM, Dong XU, Duan LS, Li ZH (2006) Effects of salt stress on growth and some physiological indexes in Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch seedlings. Acta Agric Boreali-Occident Sin 21:39–42 (in Chinese)
Yeo AR, Flowers SA, Rao G, Welfare K, Senanayke N, Flowers JF (1999) Silicon reduces sodium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in saline conditions and this is accounted for by a reduction in the transpirational bypass flow. Plant Cell Environ 22:559–565
Yin SS, Zhang Y, Gao WY, Wang J, Man SL, Liu H (2014) Effects of nitrogen source and phosphate concentration on biomass and metabolites in adventitious root culture of Glycyrrhiza uralesis Fisch. Acta Physiol Plant 36:915–921
Yu BJ, Luo QY, Liu YL (2010) Effects of salt stress on growth and ionic distribution of salt-born Glycine soja. Acta Agro Sin 27:776–780 (in Chinese)
Zhang PY, Peng ZX (1960) Liquorice in Northwest of China. J Lanzhou Univ 1:57–87
Zhang XH, Lang DY, Zhang EH, Bai CC, Wang HZ (2013) Diurnal changes in photosynthesis and antioxidants of Angelica sinensis as influenced by cropping systems. Photosynthetica 51:252–258
Zhang XH, Zhou D, Cui JJ, Ma HL, Lang DY, Wu XL, Wang ZS, Qiu HY, Li M (2015) Effect of silicon on seed germination and the physiological characteristics of Glycyrrhiza uralensis under different levels of salinity. J Hortic Sci Biotech 90:439–443
Zhu YX, Gong HJ (2014) Beneficial effects of silicon on salt and drought tolerance in plants. Agron Sustain Dev 4:455–472
Zhu JK, Wei GQ, Li J, Qian QQ, Yu JQ (2004) Silicon alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzymes activity in leaves of salt-stressed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Sci 167:527–533
Zushi K, Matsuzoe N, Kitano M (2009) Developmental and tissuespecific changes in oxidative parameters and antioxidant systems in tomato fruits grown under salt stress. Sci Hortic 122:362–368
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 31260304 and 31460330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by LA Kleczkowski.
Y.-T. Li and W.-J. Zhang contributed to the manuscript equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YT., Zhang, WJ., Cui, JJ. et al. Silicon nutrition alleviates the lipid peroxidation and ion imbalance of Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 38, 96 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2108-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2108-8