Abstract
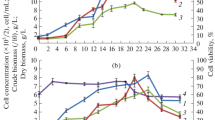
Biosynthesis of six saponins (ginsenosides) in suspension culture of P. quinquefolium Z5 was investigated. Ginsenoside content in biomass reached the highest level, nearly 30 mg g−1 d.w., between 25 and 30 days of the culture. Saponins were synthesized simultaneously with cell growth but their synthesis rate was not proportional to the growth rate. During the phase of rapid biomass multiplication, after which biomass reached 90% of its maximum yield, only half examined ginsenosides was produced. The second half of the final saponins yield was produced during the slow growth phase, in which only 10% of biomass was grown. During the intensive growth phase the productivity of six saponins examined per biomass (dry weight) unit was 3.4 μg mg−1 d.w. day−1, however, this parameter calculated for slow growth phase reached nearly 30 μg mg−1 d.w. day−1. There were differences in increase of the contents of six saponins determined in biomass, and it was the highest for saponins Re (20(S)-protopanaxatriol-6-[O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 2)-β-d-glucopyranoside]-20-O-β-d-glucopyranoside) and Rg1 (20(S)-protopanaxatriol-6,20-di-O-β-d-glucoside).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akalezi CO, Liu S, Li QS, Yu JT, Zhong JJ (1999) Combined effects of initial sucrose concentration and inoculum size on cell growth and ginseng saponin production by suspension cultures of Panax ginseng. Process Biochem 34:639–642
Belegortsera N, Yoon JY, Kim KH (2000) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori hemagglutination by polysaccharide fractions from roots of Panax ginseng. Planta Med 66:217–220
Keith I, Block MD (2003) Immune system effects of echinacea, ginseng and astralagus: a review. Integr Cancer Ther 2(3):247–267
Khodakovsaya MV, Bulgakov VP, Chernoded GK, Zhuravlev YN (1998) The approaches for the productivity improvement of the cultured ginseng cells. In: Ginseng in Europe. Proceedings of the 1st European ginseng congress. Magburg, pp 217–220
Kochan E, Kołodziej B, Gadomska G, Chmiel A (2008) Ginsenoside contents in Panax quinquefolium organs from field cultivation. Z Naturforsch 63c:91–95
Lee SH, Jung BH, Kim SY, Lee EH, Chung BCh (2006) The antistress effect of ginseng total saponin and ginsenoside Rg3 and Rb1 evaluated by brain polyamine level under immobilization stress. Pharmacol Res 54:46–49
Lian XY, Zhang Z, Stringer JL (2005) Protective effect of ginseng components in a rodent model of neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol 57(5):642–648
Liu S, Zhong JJ (1996) Effects of potassium ion on cell growth and production of ginseng saponin and polysaccharide in suspension cultures of Panax ginseng. J Biotechnol 52:121–126
Liu S, Zhong JJ (1997) Simultaneous production of ginseng saponin and polysaccharide by suspension cultures of Panax ginseng: nitrogen effects. Enzym Microb Technol 21:518–524
Mathur A, Shukla YN, Pal M, Ahuja PS, Uniyal GC (1994) Saponin production in callus and cell suspension cultures of Panax quinquiefolium. Phytochemistry 35(5):1221–1225
Naval MV, Gómez-Serranillos MP, Carretero ME, Villar AM (2007) Neuroprotective effect of a ginseng (Panax ginseng) root extract on astrocytes primary culture. J Ethnopharmacol 112:262–270
Predy Gn, Goel V, Lovlin R, Donner A, Stitt L, Basu TK (2005) Efficacy of an extract of North American ginseng containing poly-furanosyl-saccharides for preventing upper respiratory tract infections: a randomized controlled trial. Can Med Assoc J 173(9):1043–1048
Rai D, Bhatia G, Sen T, Palit G (2003) Anti-stress effect of Ginko biloba and Panax ginseng: a comparative study. J Pharmacol Sci 93:458–464
Zhang YH, Zhong JJ, Yu JT (1996) Enhancement of ginseng saponin production in suspension cultures of Panax notoginseng: manipulation of medium sucrose. J Biotechnol 51:49–56
Zhong JJ, Wang DJ (1996) Improvement of cell growth and production of ginseng saponin and polysaccharide in suspension cultures of Panax notoginseng Cu2+ effect. J Biotechnol 46:69–72
Zhong JJ, Wang SJ (1998) Effects of nitrogen source on the production of ginseng saponin and polysaccharide by cell cultures of Panax quinquefolium. Process Biochem 33:671–675
Zhong JJ, Chen F, Hu WW (1999) High density cultivation of Panax notoginseng cells in stirred bioreactors for the production of ginseng biomass and ginseng saponins. Process Biochem 35:491–496
Acknowledgments
The project was financed by Medical University in Łódź from its research grant no. 502-13-754 and by State Committee for Scientific Research grant no. 3PO5F01523.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Werbrouck.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kochan, E., Chmiel, A. Dynamics of ginsenoside biosynthesis in suspension culture of Panax quinquefolium . Acta Physiol Plant 33, 911–915 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0619-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0619-2