Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) on the expression of erythropoie-tin-producing hepatocyte receptor B2 (EphB2) in the cortex around the infracted area of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) rats at different timing, and to reveal the possible mechanism of acupuncture in the treatment of cerebral ischemia.
Methods
A total of 180 male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into a sham operation group, a model group, an acupoint group and a non-acupoint group, with 45 rats in each group. Rats in each group were further divided into three subgroups: postoperative 3 d, postoperative 14 d and postoperative 21 d groups, with 15 rats in each subgroup. The MCAO model was made by the modified occlusion method. The neurological function score, 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, immunohistochemistry assay, immunofluorescence double labeling method and Western blot were used to detect the corresponding indicators.
Results
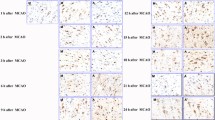
The neurological impairment of rats was most obvious at postoperative 3 d, and then gradually improved with time, which was more significant in the acupoint group (P<0.05). The change of infarcted volume was consistent with the neurological function impairment. The number of EphB2 positive cells (EphB2+) around the infarcted area was decreased significantly at postoperative 3 d, and then gradually improved with time, which returned to the same level as that in the sham operation group at postoperative 21 d. The increase was most significant in the acupoint group (P<0.05), and the positive cell number was higher than that in the sham operation group (P<0.01). Western blot and immunohistochemistry results were basically consistent. Immunofluorescence displayed that EphB2+ and postsynaptic density-95 positive (PSD-95+) were co-expressed, after the MCAO operation, in the cortical neuron around the infracted area, and the number of co-expressing cells was increased gradually with time, which was most significant in the acupoint group (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Electroacupuncture at Ganshu (BL 18) and Shenshu (BL 23) can significantly improve the neurological function and cerebral infarcted volume ratio of MCAO rats, which may be related to the activation of EphB2 expression in cortex around the infracted area and the promotion of synaptic remodeling.
摘要
目的
观察电针对大脑中动脉梗塞(MCAO) 模型大鼠不同时间点梗死灶周围皮层促红细胞生成素产生肝 细胞受体B2 (EphB2)表达的影响, 以期揭示针刺治疗脑缺血病的可能作用机制。
方法
将180 只雄性Sprague-Dawley (SD)大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、穴位组和非穴位组, 每组45 只; 各组又分为术后3 d, 14 d 及21 d 三个亚组, 每组15 只。采用改良线栓法复制MCAO 大鼠模型, 采用神经功能评分、2,3,5-氯化三苯基四氮唑(TTC) 染色、免疫组化法、免疫荧光双标法及Western blot 法进行相应指标检测。
结果
大鼠术后神经功能缺损在3 d 时最明显, 之后随着时间延长逐渐改善, 其中以穴位组更显著(P<0.05); 且梗死灶体积变化与神经功能缺损基本 一致。术后3 d 梗死灶周围EphB2 阳性(EphB2+)细胞数明显减少, 随着时间推移表达逐渐增加,至21 d 恢复至假手 术组水平, 其中以穴位组增加最明显(P<0.05), 且阳性细胞数高于假手术组(P<0.01)。Western blot 与免疫组化 检测结果基本一致。免疫荧光显示大鼠术后EphB2+与突触后致密物-95 阳性(PSD-95+)在梗死灶周围皮层神经细胞 上共表达, 且随时间延长共表达细胞数逐渐增加, 以穴位组增加最明显(P<0.05)。
结论
电针肝俞、肾俞能明显 改善MCAO 大鼠神经功能及脑梗死体积比, 可能与激活梗死灶周围皮层EphB2 表达, 促进突触重塑有关。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klein R. Bidirectional modulation of synaptic functions by Eph/ephrin signaling. Nat Neurosci, 2009, 12(1): 15–20.
Mcallister AK. Dynamic aspects of CNS synapse formation. Annu Rev Neurosci, 2007, 30: 425–450.
Himanen JP, Chumley MJ, Lackmann M, Li C, Barton WA, Jeffrey PD, Vearing C, Geleick D, Feldheim DA, Boyd AW, Henkemeyer M, Nikolov DB. Repelling class discrimination: ephrin-A5 binds to and activates EphB2 receptor signaling. Nat Neurosci, 2004, 7(5): 501–509.
Shen DK, Hou SW, Xu NG. Histopathological study on the protective effect of electroacupuncture on neuronal injury in rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Keji, 1998, 5(5): 269–270.
Zhang XC, Zhao H, Ma JH, Liu N. Experimental study on the model of focal cerebral ischemia in rats with suture-occluded method. Yixue Yanjiu Zazhi, 2013, 42(6): 55–58.
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke, 1989, 20(1): 84–91.
Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2003: 327–329.
Sun JF. Animal Experimental Methodology. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2001: 11.
Liu ZB, Niu XM. Neuroanatomical basis of the location of new Beishu points. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi, 2013, 19(1): 83–85.
Zhong YH, Tang XJ, Li GQ, Huang HR. Effects of electroacupuncture at different acuponts on neuroethology and expression of neurocan after focal cerebral infarction in rats. Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun Yu Shijian, 2013, 19(5): 444–447.
Li TL. Comparison on Therapeutic Effects by Electroacupuncturing Different Points on Rats with Acute Cerebral Ischemia and Study of the Related Mechanism. Changsha: Doctor Thesis of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2005.
Liu F, Schafer DP, McCullough LD. TTC, fluoro-Jade B and NeuN staining confirm evolving phases of infarction induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurosci Methods, 2009, 179(1): 1–8.
Biederer T, Stagi M. Signaling by synaptogenic molecules. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2008, 18(3): 261–269.
Parrinello S, Napoli I, Ribeiro S, Wingfield Digby P, Fedorova M, Parkinson DB, Doddrell RD, Nakayama M, Adams RH, Lloyd AC. EphB signaling directs peripheral nerve regeneration through Sox2-dependent Schwann cell sorting. Cell, 2010, 143(1): 145–155.
Murphy TH, Corbett D. Plasticity during stroke recovery: from synapse to behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2009, 10(12): 861–872.
Leon S, Yin Y, Nguyen J, Irwin N, Benowitz LI. Lens injury stimulates axon regeneration in the mature rat optic nerve. J Neurosci, 2000, 20(12): 4615–4626.
Shen AG, Gao SF, Cheng C, Zhao J, Chen ML, Li X, Niu SQ. The expression of postsynaptic density protein-95 in the developing spinal cord of rat. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepouxue Zazhi, 2007, 25(4): 419–423.
Zhang XJ, Wu Q. Effects of elcetroacupuncture at different acupoints on learning and memory ability and PSD-95 protein expression on hippocampus CA1 in rats with autism. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2013, 33(7): 627–631.
Kayser MS, Nolt MJ, Dalva MB. EphB receptors couple dendritic filopodia motility to synapse formation. Neuron, 2008, 59(1): 56–69.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Open Fund for Colleges and Universities Innovation Platform of Hunan Province (湖南省高校创新平台开放基金, No. 14K070); Key Project of Hunan Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (湖南省中医药管理局重点项目, No. 201310); Innovation Fund Project for Graduate Student of Hunan Province ( 湖南省研究生创新基金, No. CX2014B360).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Hl., Xiang, J., Ouyang, Lz. et al. Effect of electroacupuncture at Ganshu (BL 18) and Shenshu (BL 23) on the expression of EphB2 protein in cortex around cerebral infracted area of rat. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 15, 14–21 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-0968-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-0968-0
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Point, Ganshu (BL 18)
- Point, Shenshu (BL 23)
- Brain Ischemia
- Infarction
- Middle Cerebral Artery
- Rats