Abstract
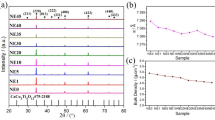
The origin of a high mechanical quality in CuO-doped (K, Na)NbO3-based ceramics is addressed by considering the correlations between the lattice positions of Cu ions and the hardening effect in K0.48Na0.52 + xNbO3-0.01CuO ceramics. The Cu ions simultaneously occupy K/Na and Nb sites of these ceramics with x = 0 and 0.02, only occupy the K/Na site of the ceramics with x = −0.02, and mostly form a secondary phase of the ceramics with x = −0.05. The Cu ions lead to the hardening of ceramics with an increase of E C and Q m by only occupying the K/Na site, together with the formation of double hysteresis loops in un-poled compositions. A defect model is proposed to illuminate the origin of a high Q m value, that is, the domain stabilization is dominated by the content of relatively mobile O2− ions in the ceramics, which has a weak bonding with CuK/Na defects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerthsen P, Härdtl K H, Schmidt N A. Correlation of mechanical and electrical losses in ferroelectric ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51(2): 1131
Uchino K, Zheng J H, Chen Y H, et al. Loss mechanisms and high power piezoelectrics. Journal of Materials Science, 2006, 41(1): 217–228
Zhang S, Xia R, Shrout T R. Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics vs PZT? Journal of Electroceramics, 2007, 19(4): 251–257
Rödel J, Jo W, Seifert K T P, et al. Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2009, 92(6): 1153–1177
Xiao D Q, Wu J G, Wu L, et al. Investigation on the composition design and properties study of perovskite lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(19): 5408–5419
Shrout T R, Zhang S J. Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: Alternatives for PZT? Journal of Electroceramics, 2007, 19(1): 113–126
Härdtl K H. Electrical and mechanical losses in ferroelectric ceramics. Ceramics International, 1982, 8(4): 121–127
Lin D, Kwok K W, Chan H L W. Double hysteresis loop in Cudoped K0.5Na0.5NbO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(23): 232903 (3 pages)
Gao Y, Uchino K, Viehland D. Effects of thermal and electrical histories on hard piezoelectrics: A comparison of internal dipolar fields and external dc bias. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101 (5): 054109 (6 pages)
Lin D, Kwok KW, Chan H LW. Double hysteresis loop and aging effect in K0.5Na0.5NbO3-K5.4Cu1.3Ta10O9 lead-free ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2009, 92(6): 1362–1365
Carl K, Hardtl K H. Electrical after-effects in Pb(Ti, Zr)O3 ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 1977, 17(1): 473–486
Ren X. Large electric-field-induced strain in ferroelectric crystals by point-defect-mediated reversible domain switching. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(2): 91–94
Zhang L, Ren X. Aging behavior in single-domain Mn-doped BaTiO3 crystals: Implication for a unified microscopic explanation of ferroelectric aging. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2006, 73: 094121
Tan Q, Li J, Viehland D. Role of lower valent substituent-oxygen vacancy complexes in polarization pinning in potassium-modified lead zirconate titanate. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 75(3): 418–420
Zhang Y, Li J, Fang D. Oxygen-vacancy-induced memory effect and large recoverable strain in a barium titanate single crystal. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2010, 82: 064103
Takao H, Saito Y, Aoki Y, et al. Microstructural evolution of crystalline-oriented (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 piezoelectric ceramics with a sintering aid of CuO. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(6): 1951–1956
Wang H-Q, Dai Y-J, Zhang X-W. Microstructure and hardening mechanism of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 lead-free ceramics with CuO doping sintered in different atmospheres. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(4): 1182–1184
Park H-Y, Seo I-T, Choi M-K, et al. Microstructure and piezoelectric properties of the CuO-added (Na0.5K0.5)-(Nb0.97Sb0.03)O3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(3): 034103 (7 pages)
Su S, Zuo R, Wang X, et al. Sintering, microstructure and piezoelectric properties of CuO and SnO2 co-modified sodium potassium niobate ceramics. Materials Research Bulletin, 2010, 45 (2): 124–128
Park B C, Hong I K, Jang H D, et al. Highly enhanced mechanical quality factor in lead-free (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 piezoelectric ceramics by co-doping with K5.4Cu1.3Ta10O29 and CuO. Materials Letters, 2010, 64(14): 1577–1579
Li E, Kakemoto H, Wada S, et al. Enhancement of Q m by codoping of Li and Cu to potassium sodium niobate lead-free ceramics. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2008, 55(5): 980–987
Park H Y, Seo I T, Choi J H, et al. Low-temperature sintering and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(1): 36–39
Alkoy E M, Papila M. Microstructural features and electrical properties of copper oxide added potassium sodium niobate ceramics. Ceramics International, 2010, 36(6): 1921–1927
Lin D, Kwok K W, Chan H L W. Piezoelectric properties and hardening behavior of K5.4Cu1.3Ta10O29-doped K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103(6): 064105 (5 pages)
Lim J B, Zhang S, Lee H J, et al. Shear-mode piezoelectric properties of modified-(K,Na)NbO3 ceramics for “hard” lead-free materials. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(9): 2519–2521
Lv Y G, Wang C L, Zhang J L, et al. Modified (K0.5Na0.5)-(Nb0.9Ta0.1)O3 ceramics with high Q m. Materials Letters, 2008, 62 (19): 3425–3427
Matsubara M, Yamaguchi T, Sakamoto W, et al. Processing and piezoelectric properties of lead-free (K,Na)(Nb,Ta)O3 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 88(5): 1190–1196
Yang M-R, Tsai C-C, Hong C-S, et al. Piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of CN-doped K0.5Na0.5NbO3 lead-free ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(9): 094103 (5 pages)
Körbel S, Marton P, Elsässer C. Formation of vacancies and copper substitutionals in potassium sodium niobate under various processing conditions. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2010, 81: 174115
Shigemi A, Wada T. Evaluations of phases and vacancy formation energies in KNbO3 by first-principles calculation. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 44(11): 8048–8054
Zhen Y, Li J F. Abnormal grain growth and new core-shell structure in (K,Na)NbO3-based lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(11): 3496–3502
Zuo R, Ye C, Fang X, et al. Processing and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.5K0.5)0.96Li0.04(Ta0.1Nb0.9)1 − x CuxO3 − 3x/2 lead-free ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(3): 914–917
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, WF., Xiao, DQ., Wu, JG. et al. Origin of high mechanical quality factor in CuO-doped (K, Na)NbO3-based ceramics. Front. Mater. Sci. 8, 165–175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-014-0245-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-014-0245-9