Abstract
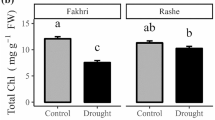
Effects of cinnamic acid on the physiological characteristics of cucumber (Shandong Mici) seedlings under salt stress were studied, and the best concentration and treatment time were ascertained. The results showed that cinnamic acid relatively increased the leaf relative water content and the chlorophyll content, decreased plasma membrane permeability, mitigated membrane damage, inhibited the accumulation of malondialdehyde (product of membrane lipid peroxidation), and promoted the activity of membrane protective enzymes such as super oxide dismutase and peroxidase, therefore improving the adaptabilities of cucumber to salt stress. It is concluded that the best treatment time of cinnamic acid is in the two euphylla period, and the best treatment concentration of cinnamic acid is 50 μmol/L.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen R D, Yu L X, Greer A F, Cheriti H, Tabaeizadeh Z (1994). Isolation of an osmotic stress and abscisic acid-induced gene encoding an acidic endochitinase from lycopersicon chilense. Molecular General Genetics, 245: 195–202
Flowers T J, Yeo A R (1995). Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: where next? Aust J Plant Physiol, 22: 875–884
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernnoi J B (1993). Requirement of the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science, 261: 754–756
Greenway H (1980). Mechanism of tolerance in non-halophytes. Ann Rev Plant Physiol, 31: 149–190
Hao Z B, Cang J, Xu Z (2002). Plant-physiology Experimental Technique. Harbin: Harbin Press, 46–48, 110–113, 106–108, 115–116 (in Chinese)
Holappa L D, Walker-Simmons M K (1995). The wheat abscisic acid-responsive protein kinase mRNA, PKAB1, is up-regulated by dehydration, cold temperature, and osmotic stress. Plant Physiology, 108: 1203–1210
Pean C (1993). Aspirin prevents wounding-induced gene expression in tobacco levels by blocking jasmonic acid biosynthesis. Planta, 191: 123–128
Peng Y, Zhang C L, Shen Q R, Zhou H J, Yang G C (2003). Effects of two phenolic acids on seed germination and activities of some enzymes in cucumber seedlings under salt stress. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 26(1): 33–36 (in Chinese)
She X P, He J M, Zhang J, Zou Q C (2002). Mitigative effect of salicylic acid on salt stress-induced growth inhibition in cucumber seedling. Acta Botanica Boreali-occidentalia Sinica, 22(2): 401–405 (in Chinese)
Skriver, K, Mundy J (1990). Gene expression in response to abscisic acid and osmotic stress. Plant Cell, 2: 503–512
Wang Q, Li X L (2003). Effects of benzoic and cinnamic acids on watermelon seedling growth and fusarium wilt occurrence. Journal of China Agricultural University, 8(1): 85–88 (in Chinese)
Wang X J (1998). Analysis of secondary salination in protected soils. Northern Horticulture, 3(4): 12–13 (in Chinese)
Werner J E, Finkelstein R R (1995). Arabidopsis mutants with reduced response to NaCl and osmotic stress. Physiologia Plantarum, 93: 659–666
Wu F Z (2002). Studies on physiological and biochemical mechanism of exogenous phenolic acids on cucumber’s auto-toxic effect. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 81–82 (in Chinese)
Zhang S G, Gao J Y (1999). Mitigative effects of salicylic acid and aspirin on salt stress induced injuries in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica, 25(2): 159–164 (in Chinese)
Zhang S G, Gao J Y, Song J Z, Weng Y J (1998). Mitigative effects of salicylic acid and aspirin on salt stress-induced injuries in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) during the stage of seedling growth. Acta Botanica Boreali-occidentalia, 18(4): 549–554 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2006, 37(3): 352–355 [译自: 沈阳农业大学学报]
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, H., Wu, F. et al. Effects of cinnamic acid on the physiological characteristics of cucumber seedlings under salt stress. Front. Agric. China 1, 58–61 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-007-0010-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-007-0010-2