Abstract
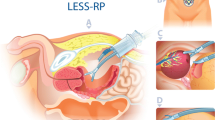
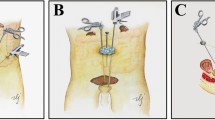
To describe the evolution of robotic laparoendoscopic single-site radical prostatectomy (R-LESS-RP) performed with the daVinci Single-Site Platform® and a home-made multiport aimed to overcome classical drawbacks of LESS, still present with this platform. Between 09/2015 and 06/2017 12 patients underwent R-LESS RP for clinical localized prostate cancer. Following a “phase 1 (development-stage)” innovation, development, exploration, assessment, long-term study (IDEAL) framework, different solutions were drawn to overcome drawbacks of daVinci Single-Site Platform®, included 3 (A, B, and C) multi-ports developed and evaluated in term of advantages/drawbacks concerning ergonomy. The end points of this study were: feasibility, safety, efficacy, by reporting rational description of multiports configuration, demographics, perioperative variables, functional and oncological results. Semi-flexible robotic 5-mm needle-holder instead of Maryland forceps, 30° lenses up and barbed-suture allowed overcoming limits of robotic-platform. Multiport-C (GelPOINT Advanced-Access® and an extra 8-mm robotic trocar outside the multiport) showed the best compromise to ensure both surgeon and bed-side assistant to reproduce a standard robotic procedure. No conversion to either standard robotic or open technique or intraoperative complications occur in any case. Two patients experienced “high-grade” Clavien-Dindo complications. After 12.4 months follow-up, all patients were continent without any sign of biochemical relapse and among 5 preoperative potent patients submitted to nerve-sparing dissection, 4 reported good erectile-function. R-LESS-RP is feasible and safe in the hands of experienced minimally-invasive surgeons. Do date, we recommend a hybrid solution with a home-made multiport and use of an additional standard robotic trocar which allows the use endowrist® technology instruments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pini G, Rassweiler J (2012) Minilaparoscopy and laparoendoscopic single-site surgery: mini- and single-scar in urology. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 21:8
Gaboardi F, Gregori A, Santoro L et al (2011) ‘LESS’ radical prostatectomy: a pilot feasibility study with a personal original technique. BJU Int 107:460
Kaouk JH, Autorino R, Kim FJ et al (2011) Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery in urology: worldwide multi-institutional analysis of 1076 cases. Eur Urol 60:998
Sorokin I, Canvasser NE, Irwin B et al (2017) The decline of laparoendoscopic single-site surgery: a survey of the endourological society to identify shortcomings and guidance for future directions. J Endourol 31:1049
Haber GP, White MA, Autorino R et al (2010) Novel robotic da Vinci instruments for laparoendoscopic single-site surgery. Urology 76:1279
Gaboardi F, Pini G, Suardi N et al (2016) V12 Robotic laparoendoscopic single-site (r-LESS) radical prostatectomy: IDEAL phase 1. Eur Urol Suppl 15(3):eV12
McCulloch P, Altman DG, Campbell WB et al (2009) No surgical innovation without evaluation: the IDEAL recommendations. Lancet 374:1105
Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (2002) International Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects. http://www.cioms.ch/images/stories/CIOMS/guidelines/guidelines_nov_2002_blurb.htm. Accessed 13 October 2013
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205
Stolzenburg JU, Schwaibold H, Bhanot SM et al (2005) Modular surgical training for endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 96:1022
Wren SM, Curet MJ (2011) Single-port robotic cholecystectomy: results from a first human use clinical study of the new da Vinci single-site surgical platform. Arch Surg 146:1122
Kroh M, El-Hayek K, Rosenblatt S et al (2011) First human surgery with a novel single-port robotic system: cholecystectomy using the da Vinci Single-Site platform. Surg Endosc 25:3566
Tewari AK, Srivastava A, Huang MW et al (2011) Anatomical grades of nerve sparing: a risk-stratified approach to neural-hammock sparing during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP). BJU Int 108:984
Steineck G, Bjartell A, Hugosson J et al (2015) Degree of preservation of the neurovascular bundles during radical prostatectomy and urinary continence 1 year after surgery. Eur Urol 67:559
Cornford P, Bellmunt J, Bolla M et al (2017) EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate Cancer. Part II: treatment of relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol 71:630
Mattevi D, Luciani LG, Vattovani V, et al. (2017) First case of robotic laparoendoscopic single-site radical prostatectomy with single-site VesPa platform. J Robot Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-017-0724-y
Cestari A, Buffi NM, Lista G, et al (2012) Feasibility and preliminary clinical outcomes of robotic laparoendoscopic single-site (R-LESS) pyeloplasty using a new single-port platform. Eur Urol 62:175
Kaouk JH, Palmer JS (2008) Single-port laparoscopic surgery: initial experience in children for varicocelectomy. BJU Int 102:97
Martin OD, Azhar RA, Clavijo R, et al (2016) Single port radical prostatectomy: current status. J Robot Surg 10:87
Leewansangtong S, Vorrakitkatorn P, Amornvesukit T et al (2010) Laparo-endoscopic single site (LESS) robotic radical prostatectomy in an Asian man with prostate cancer: an initial case report. J Med Assoc Thai 93(3):383–387
Desai MM, Aron M, Berger A et al (2008) Transvesical robotic radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 102:1666
White MA, Haber GP, Autorino R et al. (2010) Robotic laparoendoscopic single-site radical prostatectomy: technique and early outcomes. Eur Urol 58(4):544–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.06.040 (epub 2010 Jul 14)
Barret E, Sanchez-Salas R, Cathelineau X et al (2009) Re: Initial complete laparoendoscopic single-site surgery robotic assisted radical prostatectomy(LESS-RARP). Int Braz J Urol 35:92
Akca O, Zargar H, Kaouk JH (2015) Robotic surgery revives radical perineal prostatectomy. Eur Urol 68:340
Silberstein JL, Power NE, Touijer KA (2011) Laparoendoscopic single site (LESS) radical prostatectomy: a review of the initial experience. Minerva Urol Nefrol 63:123
Kaouk JH, Haber GP, Autorino R et al (2014) A novel robotic system for single-port urologic surgery: first clinical investigation. Eur Urol 66:1033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors involved in the article had nothing to disclose about commercial associations that might create a conflict of interest in connection with submitted manuscripts. Franco Gaboardi, Giovannalberto Pini, Nazareno Suardi, Francesco Montorsi, Giovanni Passaretti, Salvatore Smelzo declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaboardi, F., Pini, G., Suardi, N. et al. Robotic laparoendoscopic single-site radical prostatectomy (R-LESS-RP) with daVinci Single-Site® platform. Concept and evolution of the technique following an IDEAL phase 1. J Robotic Surg 13, 215–226 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-018-0839-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-018-0839-9